|
Tikitere Graben
The Tikitere Graben is a intra-rift graben in the North Island of New Zealand that contains the Ohau Channel which drains Lake Rotorua into Lake Rotoiti but with a minimal drop. Geography The Ohau Channel ultimately allows both lakes to drain into the Kaituna River through drainage that is also associated with the graben. The Tikitere Graben also is associated with the geothermal tourist attraction of Hell's Gate and the western aspects of Lake Rotoiti. Geology The tectonically subsiding Tikitere Graben at 2mm/year has destroyed the Rotorua Caldera rim at this point so providing the natural outlet for Lake Rotorua. The graben is an intra-rift graben in the Taupo Rift and is delimited by two unnamed active faults in the current active NZ fault database (#3590 and #2210). Historically some suspect that the graben did not exists after the caldera forming Mamaku eruption of approximately 240,000 years ago when the lake filled to a maximum elevation of above sea level. Drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
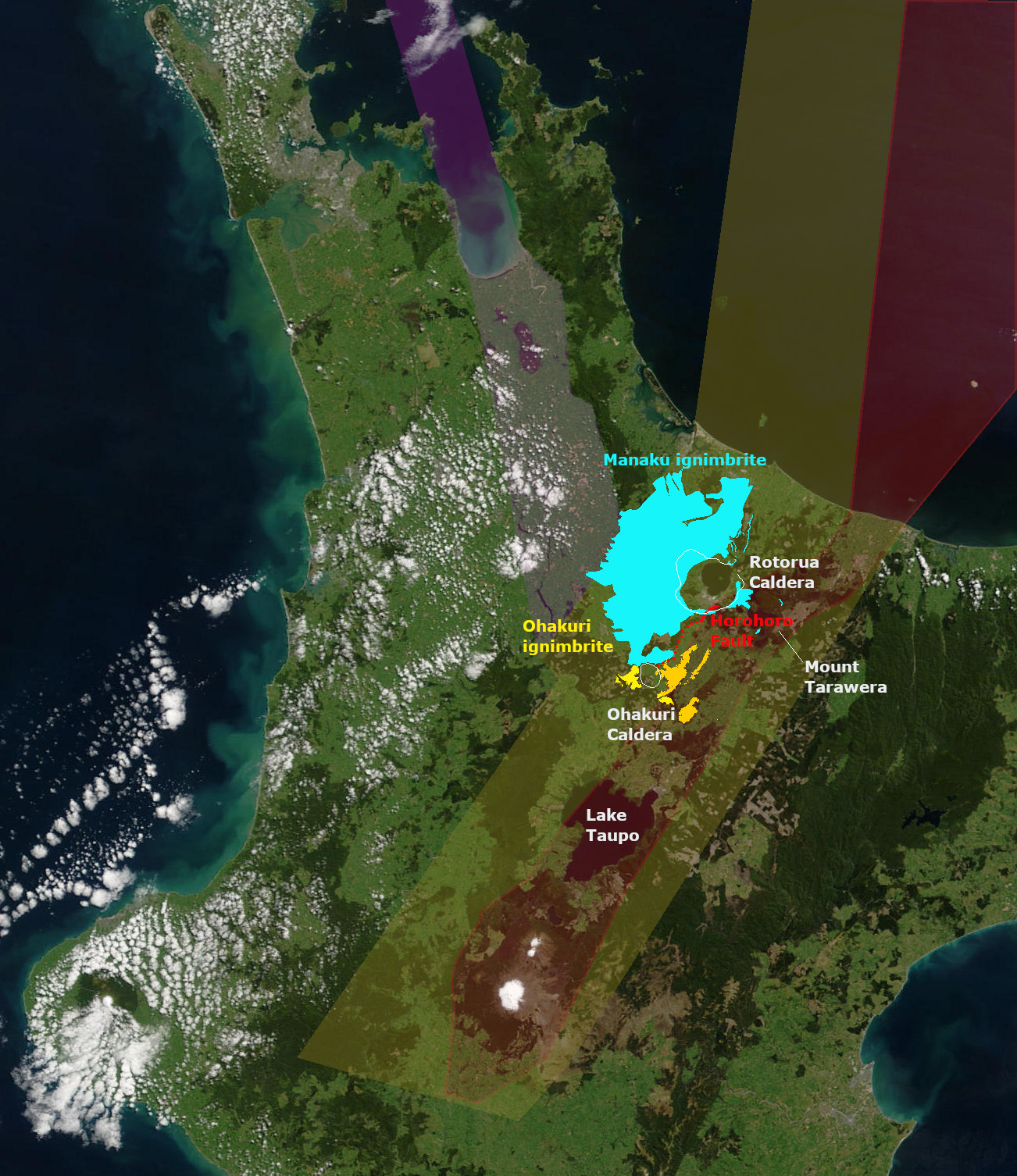
Rotorua Caldera
The Rotorua Caldera, now in filled with Lake Rotorua, is a large rhyolitic caldera. It is one of several large volcanoes located in the TaupŇć Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand. Geography The major regional settlement of Rotorua is located in the caldera. There is geothermal activity in the city of Rotorua and the geothermal areas of Tikitere and Whakarewarewa are associated with the caldera. These areas are still associated with small hydrothermal eruptions. Geology Eruption history The caldera was formed in a single event paired List of large volcanic eruptions, major eruption, that lasted only weeks, is now dated about 240,000 years ago, and which ejected more than of rhyolitic Mamaku ignimbrite giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7. The eruption has been reinterpreted as a paired eruption with a very slightly later, slightly smaller southerly eruption from the same mush body feeding the Ohakuri Caldera. Ignimbrite, up to thick covering about , was depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompassing Rotorua and several other nearby towns. Rotorua has an estimated resident population of , making it the country's 12th largest urban area, and the Bay of Plenty's second largest urban area behind Tauranga. Rotorua is a major destination for both domestic and international tourists; the tourism industry is by far the largest industry in the district. It is known for its geothermal activity, and features geysers ‚Äď notably the PŇćhutu Geyser at Whakarewarewa ‚Äď and hot mud pools. This thermal activity is sourced to the Rotorua Caldera, in which the town lies. Rotorua is home to the Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology. History The name Rotorua comes from the MńĀori language, where the full name for the city and lake is . ''Roto'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotoiti (Bay Of Plenty)
Lake Rotoiti is a lake in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand. It is the northwesternmost in a chain of lakes formed within the Okataina Caldera. The lake is close to the northern shore of its more famous neighbour, Lake Rotorua, and is connected to it via the Ohau Channel. It drains to the Kaituna River, which flows into the Bay of Plenty near Maketu. The full name of the lake is Te Rotoiti-kite-a-ń™henga, which in the MńĀori language means "The Small Lake Discovered By ń™henga", the MńĀori people, MńĀori explorer also credited with discovering Lake Rotorua. Legend says that the lake was named as such because when Ihenga first saw it, he was only able to see a small part of it and thought the lake was a lot smaller. Since the 1960s, the quality of lake water has been negatively affected by inflows of nitrogen rich water from Lake Rotorua, agricultural run-off from surrounding farms and seepage from domestic septic tanks. The effects of this included an almost permanent alga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-MńĀui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-largest island. The world's 28th-most-populous island, Te Ika-a-MńĀui has a population of accounting for approximately % of the total residents of New Zealand. Twelve main urban areas (half of them officially cities) are in the North Island. From north to south, they are WhangńĀrei, Auckland, Hamilton, Tauranga, Rotorua, Gisborne, New Plymouth, Napier, Hastings, Whanganui, Palmerston North, and New Zealand's capital city Wellington, which is located at the south-west tip of the island. Naming and usage Although the island has been known as the North Island for many years, in 2009 the New Zealand Geographic Board found that, along with the South Island, the North Island had no official name. After a public consultation, the board officially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses‚ÄĒthe North Island () and the South Island ()‚ÄĒand over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive MńĀori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and MńĀori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty ( mi, Te Moana-a-Toi) is a region of New Zealand, situated around a bight of the same name in the northern coast of the North Island. The bight stretches 260 km from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. The Bay of Plenty Region, governed by the Bay of Plenty Regional Council, incorporates several large islands in the bay, in addition to the mainland area. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toi'' (the Sea of Toi) in the MńĀori language after Toi, an early ancestor, the name 'Bay of Plenty' was bestowed by James Cook in 1769 when he noticed the abundant food supplies at several MńĀori villages there, in stark contrast to observations he had made earlier in Poverty Bay. History According to local MńĀori traditions, the Bay of Plenty was the landing point of several migration canoes that brought MńĀori settlers to New Zealand. These include the ''MńĀtaatua'', ''Nukutere'', ''TńĀkitimu'', '' Arawa'' and ''Tainui'' canoes. Many of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotorua
, image = Lake Rotorua.jpg , caption = Lake Rotorua , alt = Lake Rotorua , image_bathymetry = , pushpin_map=New Zealand#North Island , pushpin_map_alt = Location of Lake Rotorua , pushpin_relief=yes , caption_bathymetry = , location = Rotorua Lakes, Bay of Plenty Region, North Island , coords = , type = crater lake , inflow = Utuhina, Hamurana Spring, NgongotahńĀ , outflow = Ohau Channel , catchment = , basin_countries = New Zealand , length = , width = , area = , depth = , max-depth = , volume = , residence_time = , shore = , elevation = , islands = Mokoia Island , cities = Rotorua , reference = Lake Rotorua ( mi, Te Rotorua nui ńĀ Kahumatamomoe) is the second largest lake in the North Island of New Zealand by surface area, and covers 79.8 km2. With a mean depth of only 10 metres it is considerably smaller than nearby Lake Tarawera in terms of volume of water. It is located within the Rotorua Caldera in the Bay of Plenty region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaituna River
The Kaituna River is in the Bay of Plenty region of the North Island of New Zealand. It is the outflow from Lakes Lake Rotorua, Rotorua and Lake Rotoiti (Bay of Plenty), Rotoiti, and flows northwards for , emptying into the Bay of Plenty near Te Puke. It was the subject of a claim concerning the effluent flowing down the river from Lake Rotorua, which resulted in movement to a land treatment system. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "eat eels" for ''Kaituna''. The upper section of the Kaituna, also referred to as Okere River, offers some of the best whitewater kayaking and rafting in the world, with the Okere Falls area containing the highest commercially rafted waterfall, , in the world. It is also famous for its trout fishing. Cultural claim During the 1970s Lake Rotorua was becoming eutrophication, eutrophic under heavy nutrient loadings, leading the New Zealand Ministry of Works, Ministry of Works to propose diverting some sewage flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tikitere
Tikitere, also known as "Hell's Gate", is a suburb in Rotorua's most active geothermal area on State Highway 30, between Lake Rotorua and Lake Rotoiti in the Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. It includes many geothermal features such as steaming lakes, mudpools, fumaroles, a mud volcano and the Kakahi Falls, the largest hot waterfall in the southern hemisphere. The area is operated under the name "Hell‚Äôs Gate", and offers self-guided and guided tours of the geothermal park, information about its history and MńĀori culture, and a mud spa. It is part of the wider Tikitere-Ruahine geothermal field. History and culture The thermal area was formed approximately 10,000 years ago in a series of geothermal eruptions that drained an ancient lake and formed the Lake Rotoiti and Lake Rotorua. The absence of the pressure of the water on top of the rock caused it to create faults from which steam and gases can escape. At less than 2 km below ground, the heat source of this thermal ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆkataina Caldera
ŇĆkataina Caldera (ŇĆkataina Volcanic Centre, also spelled Okataina) is a massive, recently active volcanic caldera and its associated volcanoes located in TaupŇć Volcanic Zone of New Zealand's North Island. It is just east of the smaller Rotorua Caldera and southwest of the much smaller RotomńĀ Embayment which is usually regarded as an associated volcano. It is best known for its high rates of explosive rhyolitic volcanism although its last eruption was basaltic. Confusingly the postulated Haroharo Caldera contained within it, has sometimes been described in almost interchangeable terms with the ŇĆkataina Caldera or volcanic complex or centre and by other authors as a separate complex. Since 2010 other terms such as the Haroharo vent alignment, Utu Caldera, Matahina Caldera, Rotoiti Caldera and a postulated Kawerau Caldera have replaced this classification. Geography The caldera covers an area of about , stretching from Lake Rotoehu in the north to Lake Rotomahana in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |