|
Tideglusib
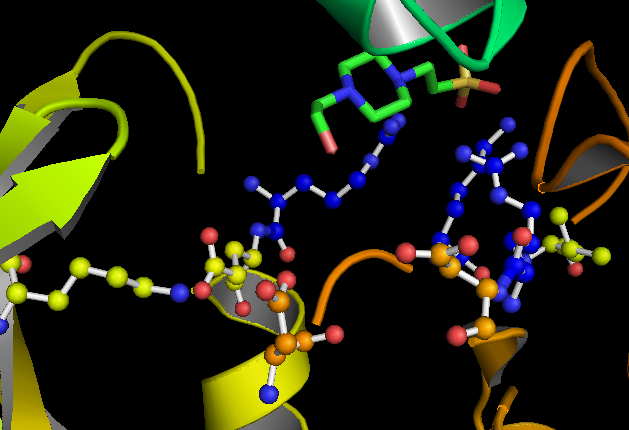
Tideglusib (NP-12, NP031112) is a potent and irreversible small molecule glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitor. Other GSK inhibitors There are few classes of GSK-inhibitors, including lithium (Martinez et al., 2011), the small peptide L803mts10, and members of the thiazolidinedione family, containing inhibitors of GSK-3, such as TDZD-8 (Shapira et al., 2007) or Tideglusib® (Noscira, Madrid, and Spain), the latter having an irreversible inhibitory effect on GSK-3 (Dominguez et al., 2012). The inhibition of the GSK-3 pathways through distinct mechanisms has been associated with a wide range of adverse reactions, ranging from mild, such as vertigo—or diarrhea (del Ser et al., 2013)—to very severe, such as hypoglycemia—or tumorigenesis (Martinez et al., 2011). The use of Tideglusib specifically was associated with mild-moderate adverse reactions, which included transient increases in serum creatine kinase, ALT—or gGT—diarrhea, nausea, cough, fatigue, and headache ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules onto serine and threonine amino acid residues. First discovered in 1980 as a regulatory kinase for its namesake, glycogen synthase (GS), GSK-3 has since been identified as a protein kinase for over 100 different proteins in a variety of different pathways. In mammals, including humans, GSK-3 exists in two isozymes encoded by two homologous genes GSK-3α (GSK3A) and GSK-3β (GSK3B). GSK-3 has been the subject of much research since it has been implicated in a number of diseases, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, inflammation, cancer, addiction and bipolar disorder. GSK-3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that phosphorylate either threonine or serine, and this phosphorylation controls a variety of biological activities, such as glycogen metabolism, cell signaling, cellular transport, and others. GS inhibition by GSK-3β leads to a decrease in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset degenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases. PSP affects about six people per 100,000. The first symptoms typically occur at 60–70 years of age. Males are slightly more likely to be affected than females. No association has been found between PSP and any particular race, location, or occupation. Signs and symptoms The initial symptoms in two-thirds of cases are loss of balance, lunging forward when mobilizing, fast walking, bumping into objects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
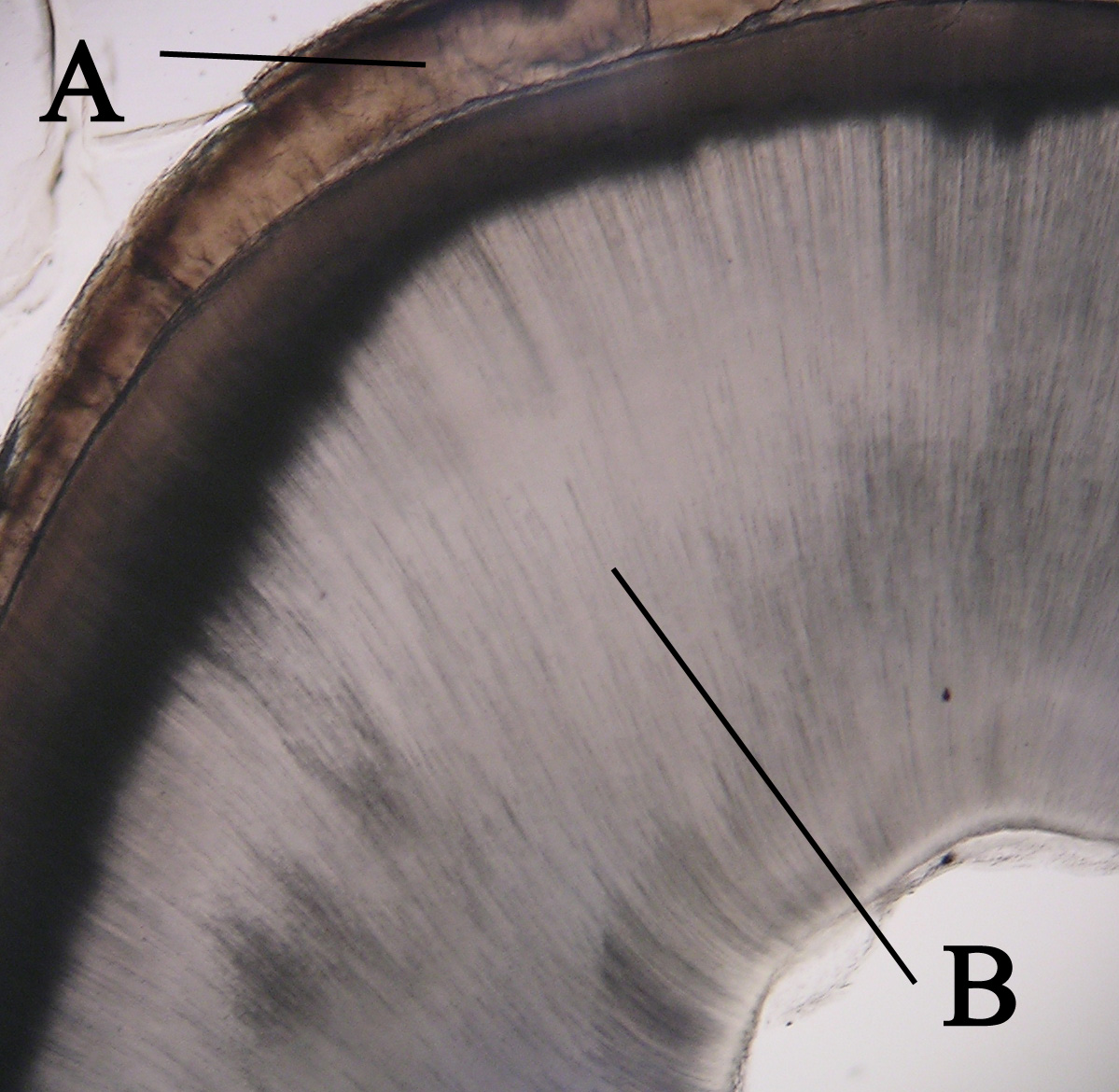
Dentine
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. In DM, muscles are often unable to relax after contraction. Other manifestations may include cataracts, intellectual disability and heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and an inability to have children. While myotonic dystrophy can occur at any age, onset is typically in the 20s and 30s. Myotonic dystrophy is caused by a genetic mutation in one of two genes. Mutation of the '' DMPK'' gene causes myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Mutation of ''CNBP'' gene causes type 2 (DM2). DM is typically inherited from a person's parents, following an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, and it generally worsens with each generation. A type of DM1 may be apparent at birth. DM2 is generally milder. Diagnosis is confirmed by genetic testing. There is no cure. Treatments may include braces or wheelchairs, pacemakers and non-invas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease Research
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of APOE. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |