|
Tianwen-4
''Tianwen-4'' is a planned interplanetary mission by China to study the Jovian system and its environs, sharing a launch with a spacecraft which will make a flyby of Uranus. Prior to its naming as ''Tianwen-4'', the mission was known as ''Gan De''. Overview The goals of the planned ''Tianwen-4'' Jupiter mission were detailed in an article published in a Chinese academic journal, they include the following: study of the interaction between magnetic fields and plasma present in the Jovian system, examination of the compositional variations in the Jovian atmosphere, exploration of the internal structures and surface characteristics of either Ganymede or Callisto, as well as investigation of the space environment surrounding the aforementioned Galilean satellites. According to reports in the Western media, there are two competing mission profiles as of January 2021: the 'Jupiter Callisto Orbiter' (JCO) and the 'Jupiter System Observer' (JSO). 'JCO' would involve a spacecraft con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-3
''Tianwen-3'' is a planned interplanetary mission by China to send two spacecrafts (an orbiter/Earth-returner and a lander/ascent-vehicle) via two separate launches to Mars. Together, the two spacecrafts will seek to obtain samples of Martian rocks and soil and then return the cached samples to Earth. Overview In summer 2022 during a deep space exploration technology forum held at Nanjing University, Sun Zezhou, chief designer of the Tianwen-1 mission, detailed plans for a Mars sample-return mission based on a two-launch architecture. The mission, which appears to have the backing of senior government and space-industry authorities, is known as "Tianwen-3" and constitutes part of the Tianwen series of space missions. The current mission architecture envisions two launches during 2028 by the Long March 5 carrier rocket. One launch occurring in November 2028 will send an orbiter/return-vehicle on a " Trans Mars Injection" trajectory; this spacecraft is anticipated to enter Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
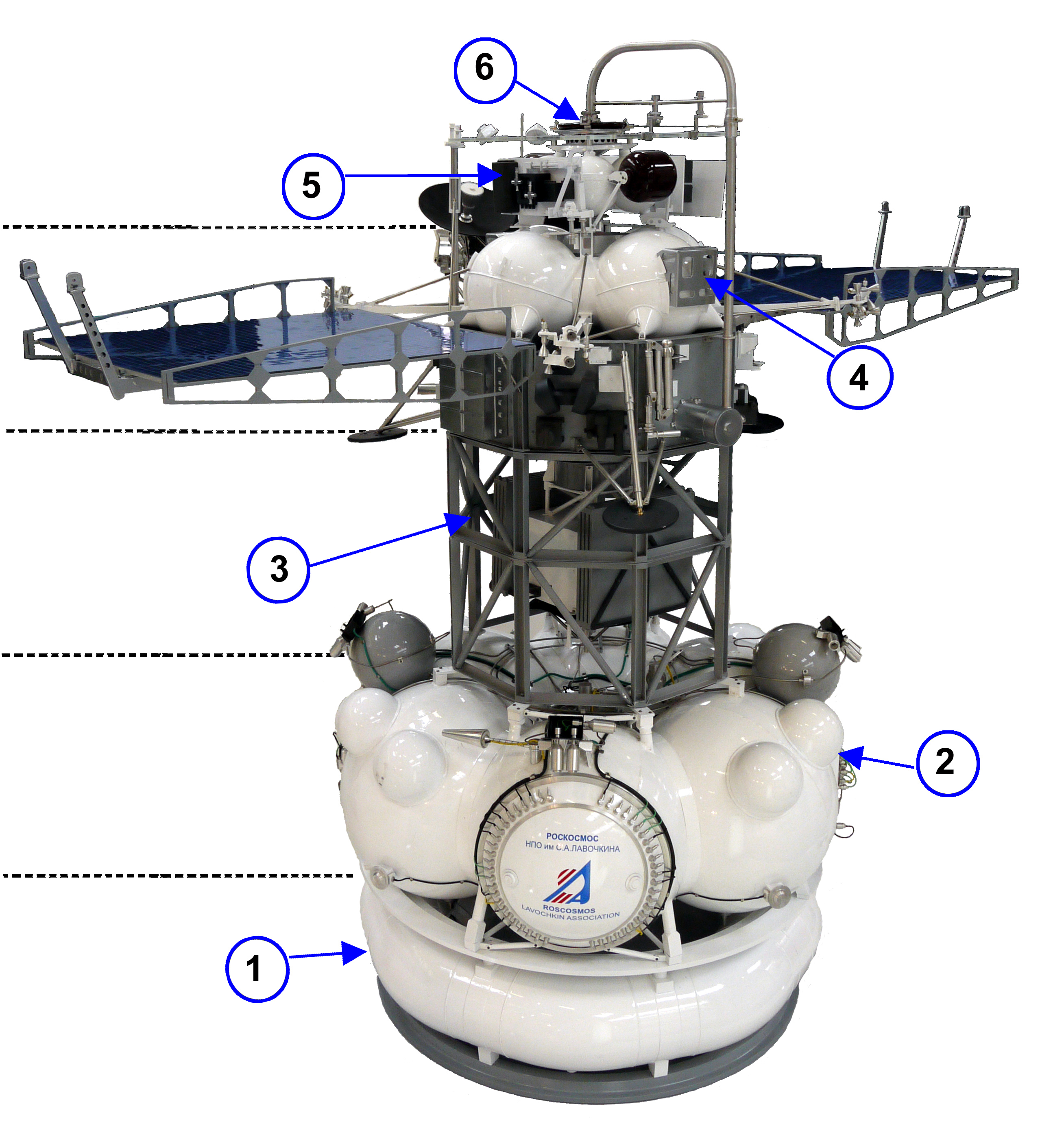
Gan De
Gan De (; fl. 4th century BC), also known as the Lord Gan (Gan Gong), was an ancient Chinese astronomer and astrologer born in the State of Qi. Along with Shi Shen, he is believed to be the first in history known by name to compile a star catalogue, preceded by the anonymous authors of the early Babylonian star catalogues and followed by the Greek Hipparchus who is the first known in the Western tradition of Hellenistic astronomy to have compiled a star catalogue. He also made observations of the planets, particularly Jupiter. His writings are lost, but some of his works' titles and fragments quoted from them are known from later texts. Gan De may have been the first to describe one of the Galilean moons of Jupiter, usually invisible without the aid of telescopes. In the 20th century, a fragment of Gan's work, in a later compilation of astronomical texts, was identified by Xi Zezong as describing a naked-eye observation of either of the two largest and brightest moons, Ganymede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Exploration Of China
The Planetary Exploration of China (PEC; ), also known as Tianwen (), is the robotic interplanetary spaceflight program conducted by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). The program aims to explore planets of the Solar System, starting from Mars, and will be expanded to Jupiter and more in the future. The program was initially known as the Mars mission of China at the early stage. It was later announced as Planetary Exploration of China in April 2020. The series of missions was named ''Tianwen''. The first mission of the program, Tianwen-1 Mars exploration mission, began on July 23, 2020. A spacecraft, which consisted of an orbiter, a lander, and a rover, was launched by a Long March 5 rocket from Wenchang. The Tianwen-1 was inserted into Mars orbit in February 2021 after a seven-month journey, followed by a successful soft landing of the lander and ''Zhurong'' rover on May 14, 2021, making China the second country in the world to successfully soft-land a fully opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Space Administration
China National Space Administration (CNSA; ) is the government agency of the People's Republic of China that is responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation, including organizing or leading foreign exchanges and cooperation in the aerospace field. An administrative agency under the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, its headquarters are located in Haidian, Beijing. Founded in 1993, CNSA has pioneered a number of achievements in space for China despite its relatively short history, including becoming the first space agency to land on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e 4, bringing material back from the Moon with Chang'e 5, and being the second agency who successfully landed a rover on Mars with Tianwen-1. As the governing body of civil space activities, China National Space Administration does not execute any space program. The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation executes China's state space programs instead. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 1
Chang'e 1 (; ) was an unmanned Chinese lunar-orbiting spacecraft, part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The spacecraft was named after the Chinese Moon goddess, Chang'e. Chang'e 1 was launched on 24 October 2007 at 10:05:04 UTC from Xichang Satellite Launch Center. It left lunar transfer orbit on 31 October and entered lunar orbit on 5 November. The first picture of the Moon was relayed on 26 November 2007. On 12 November 2008, a map of the entire lunar surface was released, produced from data collected by Chang'e 1 between November 2007 and July 2008. The mission was scheduled to continue for a year, but was later extended and the spacecraft operated until 1 March 2009, when it was taken out of orbit. It impacted the surface of the Moon at 08:13 UTC. Data gathered by Chang'e 1 was used to create an accurate and high resolution 3-D map of the lunar surface. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese unmanned lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and conducted research from a 100-km-high lunar orbit in preparation for the December 2013 soft landing by the Chang'e 3 lander and rover. Chang'e 2 was similar in design to Chang'e 1, although it featured some technical improvements, including a more advanced onboard camera. Like its predecessor, the probe was named after Chang'e, an ancient Chinese moon goddess. After completing its primary objective, the probe left lunar orbit for the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point, to test the Chinese tracking and control network, making the China National Space Administration the third space agency after NASA and ESA to have visited this point. It entered orbit around L2 on 25 August 2011, and began transmitting data from its new position in September 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 3
Chang'e 3 (; ) is a robotic lunar exploration mission operated by the China National Space Administration (CNSA), incorporating a robotic lander and China's first lunar rover. It was launched in December 2013 as part of the second phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The mission's chief commander was Ma Xingrui. The spacecraft was named after Chang'e, the goddess of the Moon in Chinese mythology, and is a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 and Chang'e 2 lunar orbiters. The rover was named ''Yutu'' () following an online poll, after the mythological rabbit that lives on the Moon as a pet of the Moon goddess. Chang'e 3 achieved lunar orbit on 6 December 2013 and landed on 14 December 2013, becoming the first spacecraft to soft-land on the Moon since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 in 1976 and the third country to successfully achieve the feat. On 28 December 2015, Chang'e 3 discovered a new type of basaltic rock, rich in ilmenite, a black mineral. Overview The Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-1
-1 (TW-1; zh, t=, s=, l='Heavenly Questions') is an interplanetary mission by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) which sent a robotic spacecraft to Mars, consisting of 6 spacecraft: an orbiter, two deployable cameras, lander, remote camera, and the ' rover. The spacecraft, with a total mass of nearly five tons, is one of the heaviest probes launched to Mars and carries 14 scientific instruments. It is the first in a series of planned missions undertaken by CNSA as part of its Planetary Exploration of China program. The mission's scientific objectives include: investigation of Martian surface geology and internal structure, search for indications of current and past presence of water, and characterization of the space environment and the atmosphere of Mars. The mission was launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on 23 July 2020 on a Long March 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. After seven months of transit through the inner Solar System, the spacecraft ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main-belt Comet
Active asteroids are small Solar System bodies that have asteroid-like orbits but show comet-like visual characteristics. That is, they show comae, tails, or other visual evidence of mass-loss (like a comet), but their orbit remains within Jupiter's orbit (like an asteroid). These bodies were originally designated main-belt comets (MBCs) in 2006 by astronomers David Jewitt and Henry Hsieh, but this name implies they are necessarily icy in composition like a comet and that they only exist within the main-belt, whereas the growing population of active asteroids shows that this is not always the case. The first active asteroid discovered is 7968 Elst–Pizarro. It was discovered (as an asteroid) in 1979 but then was found to have a tail by Eric Elst and Guido Pizarro in 1996 and given the cometary designation 133P/Elst-Pizarro. Orbits Unlike comets, which spend most of their orbit at Jupiter-like or greater distances from the Sun, active asteroids follow orbits within the orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-2
''Tianwen-2'', formerly known as ''ZhengHe'', is a planned Chinese asteroid sample-return and comet exploration mission that is currently under development. Overview ''Tianwen-2'' is planned to be launched by a Long March 3B rocket around 2025. It will use solar electric propulsion to explore the co-orbital near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS. The spacecraft will rendezvous with Kamoʻoalewa and conduct remote sensing observations in orbit, before landing on the asteroid to collect a sample of of regolith. A nano-orbiter and nano-lander will be deployed to conduct remote sensing and sampling observations, and explosives will be used to expose potential subsurface volatiles for detection. The spacecraft will use both anchor-and-attach and touch-and-go methods to attempt collection of a sample from the asteroid. It would be the first time an anchor-and-attach method has been used on an asteroid, as both OSIRIS-REx and ''Hayabusa2'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
