|
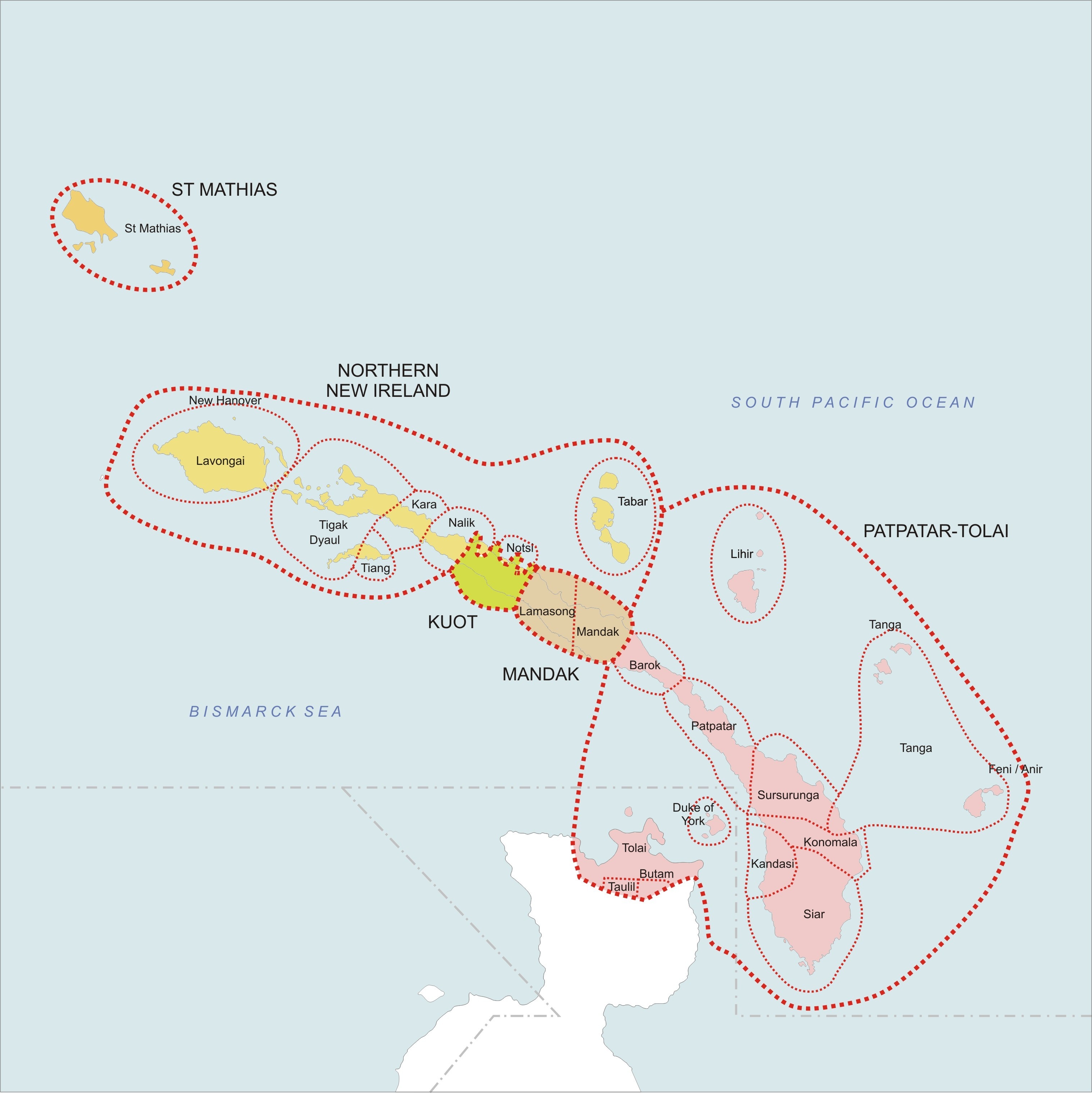
Tiang Language
The Tiang language also known as Djaul is a language spoken in Papua New Guinea.Tiang Ethnologue, 2012, access date 05-01-2012 Overview It is spoken on and in 1972 there were 790 speakers reported by Beaumont. On that island Tigak and are also spoken. Tigak is predominant on the northern half of the island and Tiang on the southern half. The former may be related closely to Tiang. It is also spoken on some other nearby areas in |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Oceanic Languages
The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by . Classification The West Oceanic linkage is made up of three sub-linkages:. * North New Guinea linkage * Meso-Melanesian linkage * Papuan Tip linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Willaumez Peninsula The Willaumez Peninsula is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province. It was named after Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez (7 August 1763 – 17 May 1845) was a French sailor, ... on the north coast of New Britain. Notes References * * {{Austronesian languages Oceanic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Melanesian Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a Linkage (linguistics), linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Uneapa language, Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: *Willaumez Peninsula, Willaumez linkage: Bola language (Austronesian), Bola, Bulu language (Oceanic), Bulu, Meramera language, Meramera, Nakanai language, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Uneapa language, Bali (Uneapa), Vitu language, Vitu (Muduapa) [may be a single language] *New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak language, Tigak, Tungag language, Tungag, Nalik language, Nalik, Laxudumau language, Laxudumau, Kara language (Papua New Guinea), Kara, Tiang language, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Mandara language, Madara (Tabar), Lihir language, Lihir, Notsi language, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok language, Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong language, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungag–Nalik Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: * Willaumez linkage: Bola, Bulu, Meramera, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Bali (Uneapa), Vitu (Muduapa) ay be a single language*New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak ** Tomoip **St George linkage *** Niwer Mil *** Warwar Feni *** Fanamaket *** Sursurunga *** Konomala ***Patpatar–Tolai: Patpatar, Lungalunga (Minigir), Tolai (Kuanua) ***Label–Bilur: Label, Bilur ***Kandas–Ramoaaina: Kandas, Ramoaaina *** Siar *** Northwest Solomonic linkage ''Ethnologue'' adds Guramalum to the St George linkage. The Willaumez Peninsula on the north coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyaul Island
Dyaul Island (also Djaul) is an island in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i .... Its area is 100 km2. The inhabitants live mainly in seven villages, and frequently visit Kavieng, the capital of the province, for supplies or to sell produce and fish. There are two languages, not counting Tok Pisin, spoken on Dyaul; Tigak and Tiang. Tigak is widely spoken on the western end of the island in two villages. Tiang is spoken across the remainder of the island. References Islands of Papua New Guinea New Ireland Province {{PapuaNewGuinea-island-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigak Language
Tigak (or Omo) is an Austronesian language spoken by about 6,000 people (in 1991) in the Kavieng District of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The Tigak language area includes the provincial capital, Kavieng. Phonology Phoneme inventory of the Tigak language: /r/ can also be realized as allophonically. Both /k, ɡ/ are back-released as ̠, ɡ̠ Two vowels /i u/ in word-initial form can also be released as consonantal allophones j External links * Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to ... includea number of collections with Tigak language materials References Meso-Melanesian languages Languages of New Ireland Province {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tok Pisin Language
Tok Pisin (,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student’s Handbook'', Edinburgh ; Tok Pisin ), often referred to by English speakers as "New Guinea Pidgin" or simply Pidgin, is a creole language spoken throughout Papua New Guinea. It is an official language of Papua New Guinea and the most widely used language in the country. However, in parts of the southern provinces of Western, Gulf, Central, Oro, and Milne Bay, the use of Tok Pisin has a shorter history and is less universal, especially among older people. Between five and six million people use Tok Pisin to some degree, although not all speak it fluently. Many now learn it as a first language, in particular the children of parents or grandparents who originally spoke different languages (for example, a mother from Madang and a father from Rabaul). Urban families in particular, and those of police and defence force members, often communicate among themselves in Tok Pisin, either never gaining fluency in a local l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland Province
New Ireland Province, formerly New Mecklenburg (german: Neu-Mecklenburg), and Nova Hibernia, is the northeasternmost province of Papua New Guinea. Physical geography The largest island of the province is New Ireland. Also part of the province are numerous smaller islands, including Saint Matthias Group (Mussau, Emirau), New Hanover, Djaul, Tabar Group ( Tabar, Tatau, Simberi), Lihir, Tanga Group (Malendok, Boang), Feni Islands (Ambitle, Babase) and Anir. The land area of the province is around 9 560 km². The sea area within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of New Ireland Province is around 230,000 km². Ecology In the early days of the French Revolution while searching for a lost scientific expedition the vessel La Recherche passed by New Ireland. On board was the prominent botanist Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière who noted in his journal fine stands of teak (tectona grandis) trees growing at the southern end of the island. This marks the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swidden
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed vegetation, or "slash", is then left to dry, usually right before the rainiest part of the year. Then, the biomass is burned, resulting in a nutrient-rich layer of ash which makes the soil fertile, as well as temporarily eliminating weed and pest species. After about three to five years, the plot's productivity decreases due to depletion of nutrients along with weed and pest invasion, causing the farmers to abandon the field and move to a new area. The time it takes for a swidden to recover depends on the location and can be as little as five years to more than twenty years, after which the plot can be slashed and burned again, repeating the cycle. In Bangladesh and India, the practice is known as jhum or jhoom. Slash-and-burn is a type of shif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |