|
Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin from the anterior pituitary. TRH has been used clinically for the treatment of spinocerebellar degeneration and disturbance of consciousness in humans. Its pharmaceutical form is called protirelin (INN) (). Synthesis and release TRH is synthesized within parvocellular neurons of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. It is translated as a 242-amino acid precursor polypeptide that contains 6 copies of the sequence -Gln-His-Pro-Gly-, flanked by Lys-Arg or Arg-Arg sequences. To produce the mature form, a series of enzymes are required. First, a protease cleaves to the C-terminal side of the flanking Lys-Arg or Arg-Arg. Second, a carboxypeptidase removes the Lys/Arg residues leaving Gly as the C-terminal residue. Then, this Gly is converted into an amide residue by a series of enzym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Formula
The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure (determined by structural chemistry methods), showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing o ...ing within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. Unlike other chemical formula types, which have a limited number of symbols and are capable of only limited descriptive power, structural formulas provide a more complete geometric representation of the molecular structure. For example, many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different enantiomeric structures but the same molecular formula. There are multiple types of ways to draw these stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactotropic Cell
A lactotropic cell (also known as prolactin cell, epsilon acidophil, lactotrope, lactotroph, mammatroph, mammotroph) is a cell in the anterior pituitary which produces prolactin in response to hormonal signals including dopamine which is inhibitory and thyrotropin-releasing hormone which is stimulatory. Other regulators include oxytocin, estrogen and progesterone. Prolactin is involved in the maturation of mammary glands and their secretion of milk in association with oxytocin, estrogen, progesterone, glucocorticoids, and others. Prolactin has numerous other effects in both sexes. Prolactin cells are acidophilic by hematoxylin & eosin stains and comprise about 20% of all cells in the anterior pituitary gland. If these cells undergo neoplastic transformation, they will give rise to a prolactinoma, a prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma. See also * Hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin axis The hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin axis (HPP axis), also known as the hypothalami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactagogues
A galactagogue, or galactogogue (from el, γάλα �αλακτ- milk, + ἀγωγός, leading), also known as a lactation inducer or milk booster, is a substance that promotes lactation in humans and other animals. It may be synthetic, plant-derived, or endogenous. They may be used to induce lactation and to treat low milk supply. Pharmaceutical Synthetic galactagogues such as domperidone and metoclopramide interact with the dopamine system in such a way to increase the production of prolactin; specifically, by blocking the D2 receptor. There is some evidence to suggest that mothers who are unable to meet their infants' breastfeeding needs may benefit from galactogogues. Galactagogues may be considered when non-pharmacologic interventions are found to be insufficient. For example, domperidone may be an option for mothers of preterm babies who at over 14 days from delivery and after full lactation support still have difficulty expressing breast milk in sufficient quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin Axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin axis (HPP axis), also known as the hypothalamic–pituitary–mammary axis or hypothalamic–pituitary–breast axis, is a hypothalamic–pituitary axis which includes the secretion of prolactin (PRL; luteotropin) from the lactotrophs of the pituitary gland into the circulation and the subsequent action of prolactin on tissues such as, particularly, the mammary glands or breasts. It is involved in lobuloalveolar maturation of the mammary glands during pregnancy and the induction and maintenance of lactation following parturition. Hormones that control the secretion of prolactin from the pituitary gland include dopamine ("prolactin-inhibiting factor", or "PIF"), estradiol, progesterone, thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), and vasoactive intestinal peptide Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid Axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis (HPT axis for short, a.k.a. thyroid homeostasis or thyrotropic feedback control) is part of the neuroendocrine system responsible for the regulation of metabolism and also responds to stress. As its name suggests, it depends upon the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the thyroid gland. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormone ( Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4)) and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The TRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid hormone until levels in the blood return to normal. Thyroid hormone exerts negative feedback control over the hypothalamus as well as anterior pituitary, thus controlling the release of both TRH from hypothalamus and TSH from anterior pituitary gland. The HPA, HPG, and HPT axes are three pathways in which the hypothalamus and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone Receptor
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds thyrotropin-releasing hormone. The TRHR is found on the cell membrane of thyrotropes of the anterior pituitary. When the TRHR binds TRH it activates phospholipase C, which causes the formation of inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). This leads to an increase in cytoplasmic calcium ion concentrations which stimulates the exocytosis of thyroid-stimulating hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of ... (TSH) into the blood. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is useful in spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pain management applications. This route is also used to introduce drugs that fight certain infections, particularly post-neurosurgical. The drug needs to be given this way to avoid being stopped by the blood–brain barrier. The same drug given orally must enter the blood stream and may not be able to pass out and into the brain. Drugs given by the intrathecal route often have to be compounded specially by a pharmacist or technician because they cannot contain any preservative or other potentially harmful inactive ingredients that are sometimes found in standard injectable drug preparations. The route of administration is sometimes simply referred to as "intrathecal"; however, the term is also an adjective that refers to something occurrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results from excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Acromegaly is usually caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone. In more than 95% of cases the excess production is due to a benign tumor, known as a pituitary adenoma. The condition is not inherited from a person's parents. Acromegaly is rarely due to a tumor in another part of the body. Diagnosis is by measuring growth hormone after a person has consumed a glucose solution, or by measuring insulin-like growth factor I in the blood. After diagnosis, medical imaging of the pituitary is carried out to determine i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
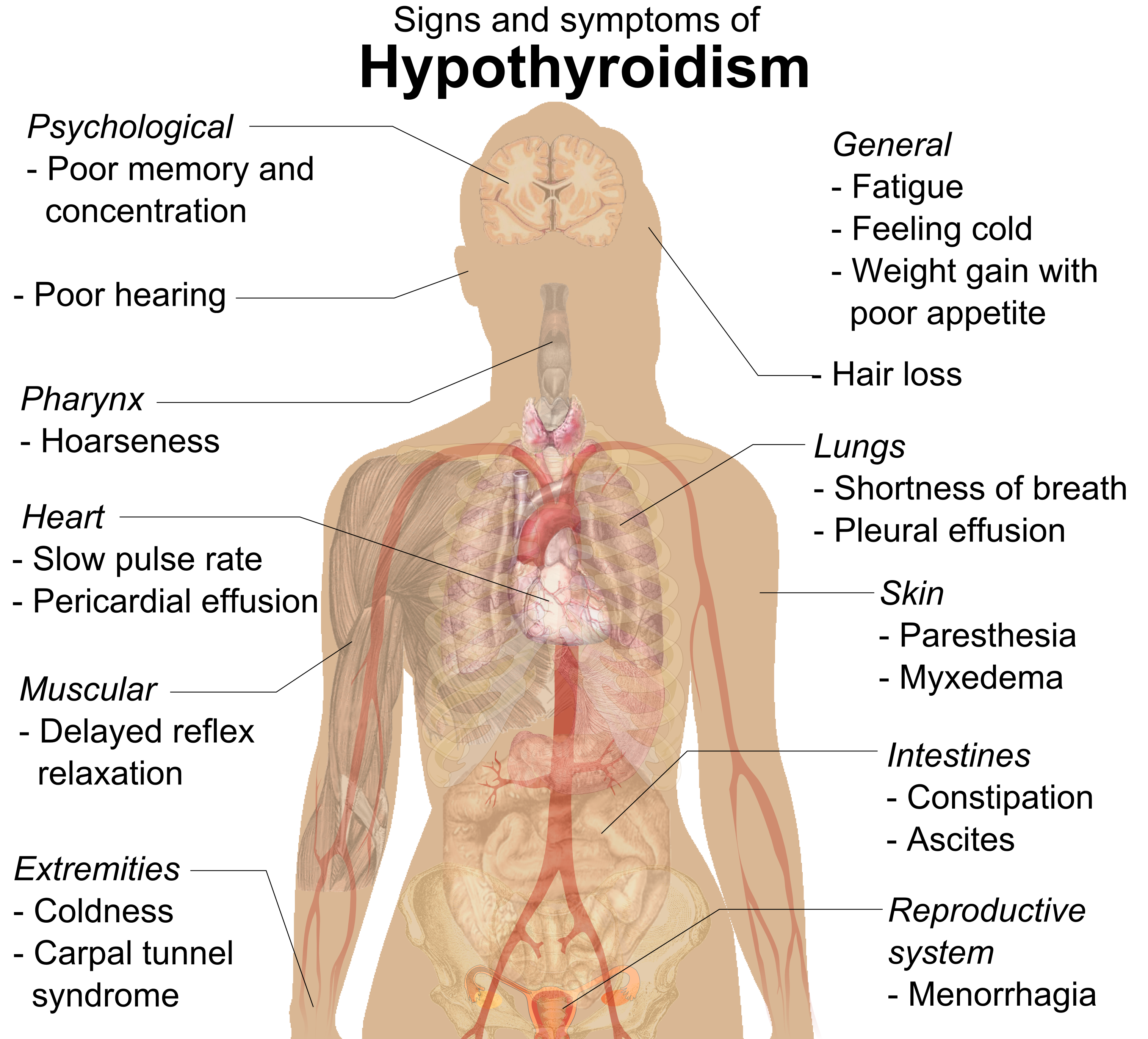
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRH Test
Prior to the availability of sensitive TSH assays, thyrotropin releasing hormone or TRH stimulation tests were relied upon for confirming and assessing the degree of suppression in suspected hyperthyroidism. Typically, this stimulation test involves determining basal TSH levels and levels 15 to 30 minutes after an intravenous bolus of TRH. Normally, TSH would rise into the concentration range measurable with less sensitive TSH assays. Third generation TSH assays do not have this limitation and thus TRH stimulation is generally not required when third generation TSH assays are used to assess degree of suppression. Differential diagnosis use TRH-stimulation testing however continues to be useful for the differential diagnosis of secondary (pituitary disorder) and tertiary (hypothalamic disorder) hypothyroidism. Patients with these conditions appear to have physiologically inactive TSH in their circulation that is recognized by TSH assays to a degree such that they may yield misle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pituitary Gland
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels. Structure The pituitary gland sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica (''Turkish chair/saddle''). It is composed of three lobes: the anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes. In many animals, these lobes are distinct. However, in humans, the intermediate lobe is but a few cell layers thick and indistinct; as a result, it is often considered part of the anterior pituitary. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |