|
Thornhill, Dumfries And Galloway
Thornhill ( gd, Bàrr na Driseig Archived frothe original on 5 March 2014) is a village in the Mid Nithsdale area of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, south of Sanquhar and north of Dumfries on the main A76 road. Thornhill sits in the Nithsdale valley with the Carsphairn and Scaur range to the west and the Lowther hills to the east. It was initially a small village, planned and built in 1717 on the Queensberry Estate on the road linking Dumfries to Glasgow. The Earl of Queensberry initially named the village ' New Dalgarnock' however the name did not achieve popular approval. The village is primarily comprised a grid pattern with the main street of Drumlanrig Street (the A76), East and West Morton Streets, New Street, Townhead Street and Gill Road (the A702). The village is near Drumlanrig Castle, a 17th-century turreted mansion once the ancient Douglas stronghold, now home to the Duke of Buccleuch and Queensberry. The grounds contain Tibbers Castle which was founded in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries And Galloway
Dumfries and Galloway ( sco, Dumfries an Gallowa; gd, Dùn Phrìs is Gall-Ghaidhealaibh) is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It covers the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel coast, some to the west of Dumfries. Following the 1975 reorganisation of local government in Scotland, the three counties were joined to form a single regions and districts of Scotland, region of Dumfries and Galloway, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a unitary local authority. For lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy purposes, the area is divided into three lieutenancy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
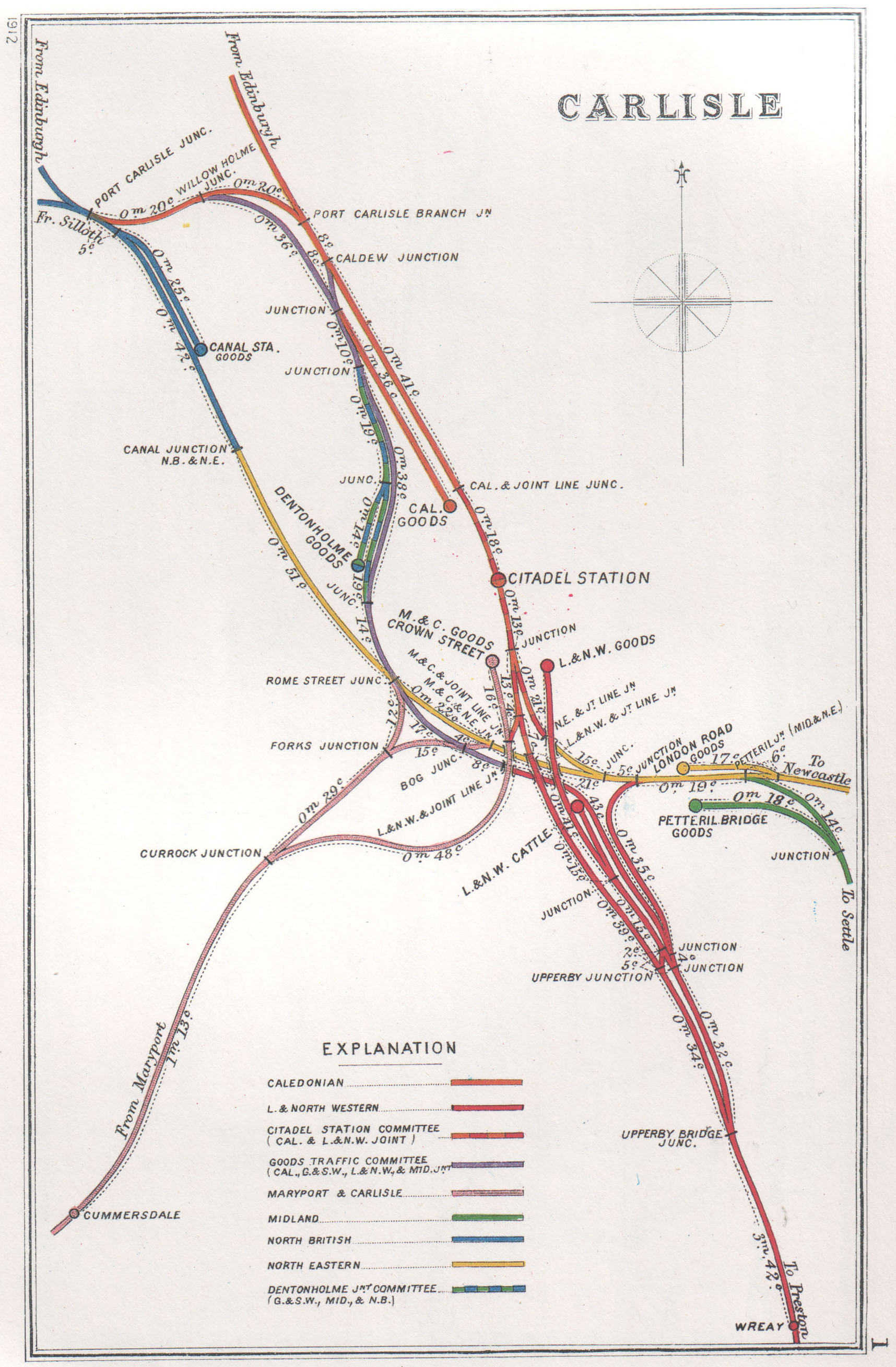
Carlisle Railway Station
Carlisle railway station, or Carlisle Citadel, is a Grade II* listed railway station serving the city of Carlisle, Cumbria, England. It is on the West Coast Main Line, south-east of and north north-west of . It is the northern terminus of the Settle and Carlisle Line, a continuation of the Midland Main Line from , and . It was formerly the southern terminus of the partially-closed Waverley Route from Edinburgh. It is so named because it is adjacent to Carlisle Citadel, a former medieval fortress. The station is owned by Network Rail. In September 1847, the first services departed the station, even though construction was not completed until the following year. It was built in a neo- Tudor style to the designs of English architect William Tite. Carlisle station was one of a number in the city; the others were Crown Street and London Road, but it became the dominant station by 1851. The other stations had their passenger services redirected to it and were closed. Between 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gatelawbridge
Gatelawbridge is a hamlet in the region of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. It is situated two and a half miles east of Thornhill and near the gorge Crichope Linn. The origin of the name is unknown though in the past the locals called it Gateley Bridge, so perhaps it takes its name from a type of bridge over the Cample River in the centre of the settlement. The river divides the parishes, with all those east of the river being in Closeburn Parish, and those west of the river being in Morton Parish. The African explorer Joseph Thomson lived in Gatelawbridge from the age of 10 until leaving for Edinburgh. He attended the secondary school Morton Academy in Thornhill (now Wallace Hall), making the journey each day on his pony called Donald. His father was the quarry master and presumably that is where his interest in rocks began. He studied geology at the University of Edinburgh. After graduating he was engaged on several explorations in East and North Africa. He discovered the Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penpont
Penpont is a village about west of Thornhill in Dumfriesshire, in the Dumfries and Galloway region of Scotland. It is near the confluence of the Shinnel Water and Scaur Water rivers in the foothills of the Southern Uplands. It has a population of about 400 people. Archaeology There are several archaeological sites nearby, including Late Bronze Age hill forts on Tynron Doon and Grennan Hill and a long cairn at Capenoch Loch dating from the 2nd or 3rd century. History The toponym ''Penpont'' means "bridge-head" in the Cumbric language once spoken in the region. The A702 road passes through Penpont. West of Thornhill it crosses the River Nith on a two-arched stone bridge in Penpont parish. It was built in the 1760s after the presbytery of Penpont raised £680 toward the cost. Work started about 1774, but in 1776 the bridge collapsed. The bridge was completed in 1778 and strengthened in 1930–31. It is a Category A listed building. Penpont's Church of Scotland parish chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson's Gazelle
Thomson's gazelle (''Eudorcas thomsonii'') is one of the best known species of gazelles. It is named after explorer Joseph Thomson and is sometimes referred to as a "tommie". It is considered by some to be a subspecies of the red-fronted gazelle and was formerly considered a member of the genus ''Gazella'' within the subgenus ''Eudorcas'', before ''Eudorcas'' was elevated to genus status. Thomson's gazelles can be found in numbers exceeding 200,000 in Africa and are recognized as the most common type of gazelle in East Africa. A small fast antelope, the Thomson's gazelle is claimed to have top speeds up to . It is the fourth-fastest land animal, after the cheetah (its main predator), pronghorn, and springbok. Taxonomy and etymology The current scientific name of Thomson's gazelle is ''Eudorcas thomsonii''. It is a member of the genus ''Eudorcas'' and is classified under the family Bovidae. Thomson's gazelle was first described by British zoologist Albert Günther in 1884. The rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Thomson (explorer)
Joseph Thomson (14 February 1858 – 2 August 1895) was a British geologist and explorer who played an important part in the Scramble for Africa. Thomson's gazelle and Thomson's Falls, Nyahururu are named after him. Excelling as an explorer rather than an exact scientist, he avoided confrontations among his porters or with indigenous peoples, neither killing any native nor losing any of his men to violence. His motto is often quoted to be ''"He who goes gently, goes safely; he who goes safely, goes far."'' Early life Born in Penpont, Dumfriesshire, he was apprenticed into his father's stone-masonry and quarrying business. He developed a keen amateur interest in geology and botany, which eventually led to his formal education at the University of Edinburgh, studying under Archibald Geikie and Thomas Henry Huxley. Royal Geographical Society On graduating in 1878, he was appointed geologist and naturalist to Alexander Keith Johnston's Royal Geographical Society expedition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowls
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which the objective is to roll biased balls so that they stop close to a smaller ball called a "jack" or "kitty". It is played on a bowling green, which may be flat (for "flat-green bowls") or convex or uneven (for "crown green bowls"). It is normally played outdoors (although there are many indoor venues) and the outdoor surface is either natural grass, artificial turf or cotula (in New Zealand). History Bowls is a variant of the ''boules'' games (Italian ''Bocce''), which, in their general form, are of ancient or prehistoric origin. Ancient Greek variants are recorded that involved throwing light objects (such as flat stones, coins, or later also stone balls) as far as possible. The aspect of tossing the balls to approach a target as closely as possible is recorded in ancient Rome. This game was spread to Roman Gaul by soldiers or sailors. A Roman sepulchre in Florence shows people playing this game, stooping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is to score more goals than the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into a rectangular framed goal defended by the opposing side. Traditionally, the game has been played over two 45 minute halves, for a total match time of 90 minutes. With an estimated 250 million players active in over 200 countries, it is considered the world's most popular sport. The game of association football is played in accordance with the Laws of the Game, a set of rules that has been in effect since 1863 with the International Football Association Board (IFAB) maintaining them since 1886. The game is played with a football that is in circumference. The two teams compete to get the ball into the other team's goal (between the posts and under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish League Cup
The Scottish League Cup (also known as the Viaplay Cup for sponsorship reasons) is a football competition open to all Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL) clubs. First held in 1946–47, it is the oldest national League Cup in existence. The competition had a straight knockout format but became a group and knockout competition from 2016–17. Rangers are the record holders of the cup, winning 27 times. Celtic are the holders, winning their 20th title after beating Hibernian 2–1 at Hampden Park on 19 December 2021. The domestic television rights are held by Viaplay, whose predecessor company Premier Sports replaced BT Sport from the 2019–20 season. Format Historically, the Scottish League Cup has oscillated between being a straightforward single-elimination knockout tournament and having an initial group phase. Since the 2016–17 season, the League Cup has used a group phase format. The format has eight groups of five teams playing each other once in a ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bobby Black (Scottish Footballer)
Bobby Black (c.1927 – 4 June 2012) was a Scottish footballer from Thornhill, Dumfries and Galloway who played for East Fife and Queen of the South and was also capped by the Scottish League. Black later was an all England bowls champion. East Fife Having played at East Fife during undoubtedly the best period in the club's history Black won a League Cup medal with them in 1949–50. The Methil side made the Scottish Cup final that season and finished fourth in Scotland's top division. Two seasons later (Bobby Black's last at the club) they would surpass this league position and finish third – an achievement unsurpassed by the club and equalled only once. Other players at the club in this era included 1938 Scottish Cup winners with East Fife Tommy Adams and Willie Laird and players who played for Scotland while with the club, Allan Brown, Henry Morris, George Aitken, Davie Duncan, Charlie Fleming and Andy Matthew. Jimmy Philp was another like Black who enjoyed Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Coltart
Andrew John Coltart (born 12 May 1970) is a Scottish professional golfer and TV commentator. He had a successful amateur career and played in the 1991 Walker Cup. As a professional he won twice on the European Tour, the 1998 Qatar Masters and the 2001 Great North Open, and played in the 1999 Ryder Cup. Junior and amateur Coltart was born in Dumfries. As an amateur, he won the 1987 Scottish Boys Championship. In 1989 he won the Standard Life Amateur Champion Gold Medal with a 4 under total of 280. He won the 1991 Scottish Amateur Stroke Play Championship and participated in the 1991 Walker Cup. Professional Coltart turned professional in 1991 and has been a member of the European Tour since 1993. His first professional win came at the Scottish Professional Championship in 1994, which was a non sanctioned event. He has two wins on the main European Tour, the 1998 Qatar Masters and the 2001 Great North Open. In 1995 he was a member of the winning Scottish team in the Alfred Dunhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closeburn, Dumfries And Galloway
Closeburn (Scottish Gaelic: ''Cill Osbairn'') is a village and civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. The village is on the A76 road south of Thornhill. In the 2001 census, Closeburn had a population of 1,119. Closeburn is recorded as ''Killosbern'' in 1185. The first element of the name is Gaelic ''cill'' 'cell or church'. The second element is a saint's name, but none has definitely been identified. Between 1849 and 1961 the village had a railway station. Although Closeburn railway station is now closed, the Glasgow South Western Line still runs through the village. The nearest stations are at Sanquhar and Dumfries. The village is the former location of Wallace Hall Academy, founded in 1723 and now based in Thornhill. The former schoolhouse, built in 1795 and incorporating the original buildings from the 1720s, is a Category A listed building. Situated east of the village is Closeburn Castle, a Category B listed tower house that was until 1783 the family sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Gazella_isabella_(white_background).png)

