|
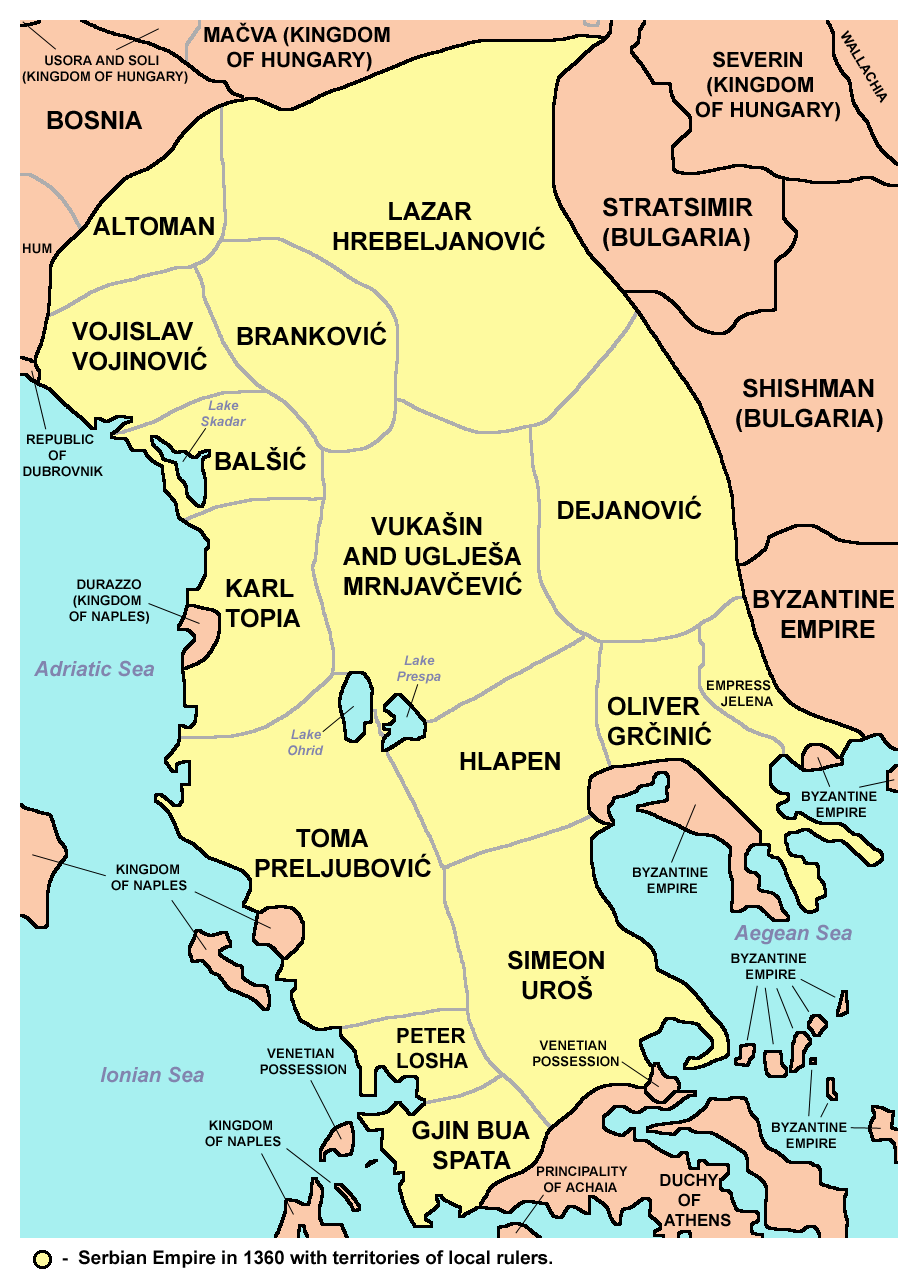
Thomas Preljubović
Thomas Preljubović ( sr, Тома Прељубовић / Toma Preljubović; el, Θωμάς Κομνηνός Παλαιολόγος, Thōmas Komnēnos Palaiologos) was ruler of the Despotate of Epirus in Ioannina from 1366 to his death on December 23, 1384. He also held the title of Albanian-slayer (Greek: Αλβανοκτόνος/Αλβανιτόκτονος) after torturing Albanian prisoners in order to terrify his enemies. Toma is remembered for presenting several outstanding icons to the monastery of the Transfiguration at Meteora and in Cuena, in Spain. He also made gifts to the Athonite monasteries of Great Lavra, Vatopedi and Hilandar. Toma Preljubović was particularly attached to his namesake the apostle Thomas. In one of the icons at Meteora, a composition of Doubting Thomas includes Toma's wife, Maria-Angelina, among the apostles. It is not unlikely that he was responsible for having the frescoes painted in the Hilandar parekklesion of the Holy Archangels, where in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Despot Of Epirus
The despot of Epirus was the ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, one of the successor states of the Byzantine Empire in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade. The name "Despotate of Epirus" and the title "despot of Epirus" are modern historiographical names, and were not in use by the despots themselves. In the Byzantine Empire, the title of despot ( el, δεσπότης, despótēs) was a prestigious court title and did not designate rule over some specific territory. Though several of the early Greek rulers of the Epirote realm did use the title of despot, it was never in reference to the lands they governed, but instead in reference to their position in the imperial hierarchy. It was only with Epirus falling into the hands of foreign dynasties that the title of despot became applied not to the imperial hierarchy, but to the territory, sometimes to the dismay of the local population. "Despot of Epirus" is not recorded in contemporary documents for the rulers of foreign origin, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Angelina Doukaina Palaiologina
Maria Angelina Doukaina Palaiologina or Marija Angelina Nemanjić or Anna Maria Angelina Doukaina Palaiologina ( el, Μαρία Αγγελίνα Δούκαινα Παλαιολογίνα, sr-cyr, Марија Ангелина Немањић; 1349 – 28 December 1394) was a Byzantine Greek- Serbian aristocrat and the self-proclaimed ''basilissa'' (Greek: βασίλισσα; Empress, queen) of Epirus from 1384–85, succeeding the rule of her murdered husband Thomas Preljubović. Maria and her husband were a famed couple as patrons of the arts during Tomo's rule of Ioannina from 1366 to 1384. She is portrayed in the icons. Life Maria was the daughter of the Serbian Emperor of Thessaly, Simeon Uroš, the half-brother of Emperor Stephen Uroš IV Dušan of Serbia (Nemanjić dynasty), and Thomais Orsini. Her maternal grandfather was John Orsini of Epirus. In 1361, Maria, then only 12 years old, married Thomas Preljubović, who was appointed the governor ( despot) of Epirus in Ioann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelokastro (Aetolia-Acarnania)
Angelokastro (Greek: Αγγελόκαστρο) is a village and a former municipality in Aetolia-Acarnania, West Greece, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Agrinio Agrinio (Greek: Αγρίνιο, , Latin: ''Agrinium'') is the largest city of the Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit of Greece and its largest municipality, with 106,053 inhabitants. It is the economical center of Aetolia-Acarnania, although its capi ..., of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 55.726 km2. References Sources * * Populated places in Aetolia-Acarnania {{WGreece-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arta, Greece
Arta ( el, Άρτα) is a city in northwestern Greece, capital of the regional unit of Arta, which is part of Epirus region. The city was known in ancient times as Ambracia ( grc, Ἀμβρακία). Arta is known for the medieval bridge over the Arachthos River. Arta is also known for its ancient sites from the era of Pyrrhus of Epirus and its well-preserved 13th-century castle. Arta's Byzantine history is reflected in its many Byzantine churches; perhaps the best known is the Panagia Paregoretissa (Mother of God the Consoling), built about 1290 by Despot Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas. Etymology The origin of the city's name is quite uncertain. It's either derived from a corruption of the river Arachthos, either from the Latin word "artus" (narrow) either from the Slavic word "balta" (swamp). History Antiquity The first settlement in the area of the modern city dates to the 9th century B.C. Ambracia was founded as a Corinthian colony in the 7th century B.C. In 294 BC, af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastoria
Kastoria ( el, Καστοριά, ''Kastoriá'' ) is a city in northern Greece in the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Macedonia. It is the capital of Kastoria (regional unit), Kastoria regional unit, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia. It is situated on a promontory on the western shore of Lake Orestiada, in a valley surrounded by limestone mountains. The town is known for its many Byzantine Empire, Byzantine churches, Byzantine architecture, Byzantine and Ottoman architecture, Ottoman-era domestic architecture, its lake and its fur clothing industry. Name The city is first mentioned in 550 AD, by Procopius as follows: "There was a certain city in Thessaly, Diocletianopolis by name, which had been prosperous in ancient times, but with the passage of time and the assaults of the barbarians it had been destroyed, and for a very long time it had been destitute of inhabitants; and a certain lake chances to be clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edessa, Greece
Edessa ( el, Έδεσσα, ; also known as the "''City of Waters and of the 5 Senses''"), until 1923 Vodena ( el, link=no, Βοδενά), is a city in northern Greece and the capital of the Pella regional unit, in the Central Macedonia region of Greece. It was also the capital of the defunct province of the same name. Edessa holds a special place in the history of the Greek world as, according to some ancient sources, it was here that Caranus established the first capital of ancient Macedon. Later, under the Byzantine Empire, Edessa benefited from its strategic location, controlling the Via Egnatia as it enters the Pindus mountains, and became a center of medieval Greek culture, famed for its strong walls and fortifications. In the modern period, Edessa was one of Greece's industrial centers until the middle of the 20th century, with many textile factories operating in the city and its immediate vicinity. Today however its economy mainly relies on services and tourism. Edessa hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radoslav Hlapen
Radoslav Hlapen ( sr, Радослав Хлапен; 1350–1383) was a Serbian magnate who served Serbian Emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–1355) and Stefan Uroš V (r. 1355–71) as '' vojvoda'' (military commander). He took part in the conquest of Byzantine lands, and was given a region north of Thessaly to govern in the early 1350s. Origin It is believed that Radoslav Hlapen is the same person as ''župan'' (count) Hlapen ( la, Clapen) who governed Konavle and the wider Trebinje region in the 1330s. He was possibly the son of ''župan'' Radoslav, and thus named Radoslav after his father. Another theory is that he was the son of Syrgiannes Palaiologos. Byzantine Emperor John VI Kantakouzenos (r. 1347–54) mentioned him as among the most important nobles, and he was called a relative of Dušan. Service under Stefan Dušan Serres was captured in September 1345, Veria in the first half of 1346. Veria and the surrounding towns were recuperated by John VI Kantakuzenos. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros II Orsini
Nikephoros II Orsini - Doukas (Greek: Νικηφόρος Β΄ Δούκας, ''Nikēphoros II Doukas''), was the ruler of Epirus from 1335 to 1338 and from 1356 until his death in 1359. Life Nikephoros was the son of John Orsini of Epirus and Anna Palaiologina. When his mother allegedly poisoned his father in 1335, Nikephoros II succeeded as a 7-year-old child. His mother Anna assumed the regency for her young son but failed to allay the enmity of the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos, who invaded and annexed the Epirote part of Thessaly in 1336 and advanced on Ioannina. The Albanians took advantage of conflict to the south to raid the Byzantine possessions in the north, but were defeated by the emperor in 1337. Andronikos summoned Anna to negotiate in 1338 but refused to accept her son as Byzantine vassal and installed his governors in Epirus. Keeping Anna as hostage, Andronikos arranged for the marriage between Nikephoros and Maria Kantakouzene, the daughter of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena Of Bulgaria
Helena of Bulgaria, Empress of Serbia ( bg, Елена, sr, Јелена; c. 1315–1374) was a Bulgarian princess, and the Queen and Empress consort of Serbia by marriage to Serbian King and later Emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55). She was a regent of Serbia between 1355 and 1356 for her son Stefan Uroš V. Life She was the daughter of despot Sratsimir and Keratsa Petritsa of the Shishman family, a descendant of Tsar Ivan Asen II. She was the sister of tsar (emperor) Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria, Ivan-Alexander, John Komnenos, Michael and Theodora. Stefan Dušan was crowned King of Serbia at Svrčin on 8 September 1331 (Nativity of the Theotokos). A year later, most likely 26 April 1332 (Thomas Sunday), Dušan married Helena. Previously, it was erroneously assumed that the marriage took place on Easter (19 April), however, marriages are not instituted on Easter in the Orthodox Church. Their wedding night was held at the royal court in Skopje. The marriage was arran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Uroš IV Dušan Of Serbia
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Thessaly
The history of Thessaly covers the history of the region of Thessaly in north-central Greece from antiquity to the present day. Topography Thessaly is characterized by the large Thessalian plain, formed by the Pineios River, which is surrounded by mountains, most notably the Pindus mountain range to the west, which separates Thessaly from Epirus. Only two passes, the Porta pass and, in the summer, the pass of Metsovo, connect the two regions. From the south, the narrow coastal pass of Thermopylae connects Thessaly with southern Greece. In the north Thessaly borders on Macedonia, either through the coast or the pass of Servia towards Thessalonica, or in the northwest towards western Macedonia. Antiquity The first evidence of human habitation in Thessaly dates to the late Paleolithic, but in the early Neolithic this expanded rapidly. Over 400 archaeological sites dating to the period are known, including fortified ones. The most notable of these is at Sesklo. During the Mycenaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_3.jpg)

.jpg)