|
Thomas Linley The Younger
Thomas Linley the younger (7 May 17565 August 1778), also known as Thomas Linley Junior or Tom Linley, was the eldest son of the composer Thomas Linley and his wife Mary Johnson. He was one of the most precocious composers and performers that have been known in England. A highly talented violinist, Tom Linley was also the most promising of all native English composers between Purcell and Elgar, combining prodigious talent with a delightful personality. He is sometimes referred to as the "English Mozart". His early promise was cut short when he drowned in a boating accident, aged just 22 years. Early life Outside of London, Bath was the most fashionable city in late 18th century England and, in Bath, the Linleys were the most influential musical family. Originally from Gloucestershire and of a modest background (Tom's grandfather was a carpenter/builder whose business later flourished thanks to Bath's urban development), the Linleys quickly became the most prominent artists amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
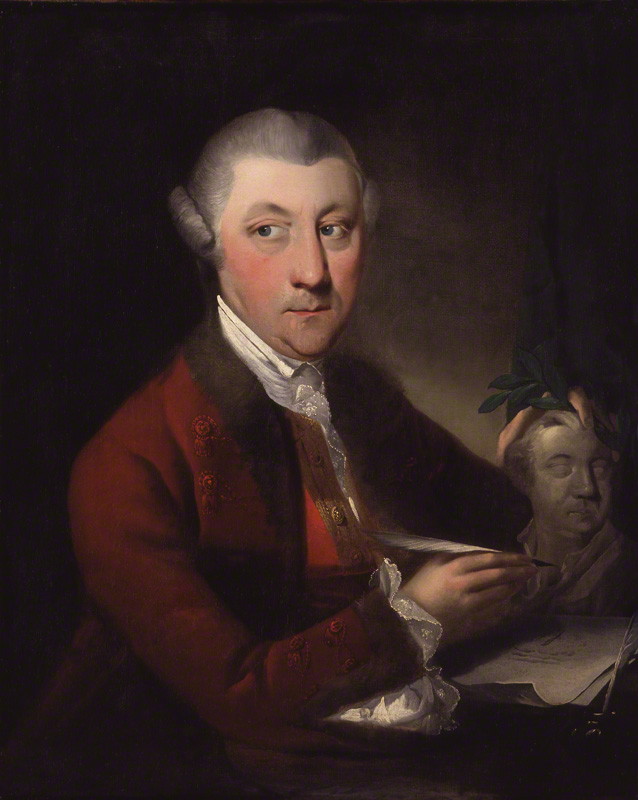
Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of the second half of the 18th century. He painted quickly, and the works of his maturity are characterised by a light palette and easy strokes. Despite being a prolific portrait painter, Gainsborough gained greater satisfaction from his landscapes. He is credited (with Richard Wilson) as the originator of the 18th-century British landscape school. Gainsborough was a founding member of the Royal Academy. Youth and training He was born in Sudbury, Suffolk, the youngest son of John Gainsborough, a weaver and maker of woollen goods, and his wife Mary, the sister of the Reverend Humphry Burroughs. One of Gainsborough's brothers, Humphrey, had a faculty for mechanics and was said to have invented the method of condensing steam in a separate ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Assembly Rooms
The Bath Assembly Rooms, designed by John Wood the Younger in 1769, are a set of assembly rooms located in the heart of the World Heritage City of Bath in England which are now open to the public as a visitor attraction. They are designated as a Grade I listed building. During the Georgian era Bath became fashionable, and the architects John Wood, the Elder, and his son laid out new areas of housing for residents and visitors. Assembly rooms had been built early in the 18th century, but a new venue for balls, concerts and gambling was envisaged in the area between Queen Square, The Circus and the Royal Crescent. Robert Adam submitted a proposal that was rejected as too expensive. John Wood, the Younger raised funding through a tontine, and construction started in 1769. The new or upper assembly rooms opened with a grand ball in 1771 and became the hub of fashionable society, being frequented by Jane Austen and Charles Dickens, along with the nobility of the time. The bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson Of Exeter
William Jackson (29 May 1730 – 5 July 1803), referred to as Jackson of Exeter, was an English organist and composer. Life Jackson was born and died in Exeter, England, the son of an Exeter grocer, who later became master of the city workhouse. After receiving some musical instruction from John Silvester, organist of Exeter Cathedral, Jackson was sent in 1748 to London, to become a pupil of John Travers, organist to the Chapel Royal. In 1767 Jackson wrote the music for an adaptation of Milton's ''Lycidas'', which was produced at Covent Garden on 4 November of the same year, on the occasion of the death of Prince Edward, Duke of York and Albany, brother to George III. While in London, he was a visitor at the meetings of the Madrigal Society. On his return to Exeter Jackson devoted himself to teaching music until Michaelmas 1777, when he was appointed subchanter, organist, lay vicar, and master of choristers to the cathedral, in succession to Richard Langdon. Jackson's pupils in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd's Evening Post
''Lloyd's Evening Post'', also known as ''The London Packet'' and ''Lloyd's Evening Post and British Chronicle'', was a British evening newspaper published tri-weekly in London from 1757 to 1808. Founded shortly after the ''London Chronicle'' and similar in format, it came out on Monday, Wednesday and Friday, alternating in "friendly rivalry" with the ''London Chronicle'' which came out on Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday. History The ''Lloyd's Evening Post'' was founded in July 1757 by James Emonson (a former partner of William Bowyer), and was published from Emonson's printing office in St John's Square, Clerkenwell. According to the colophon of the July 14–16, 1762 edition, copies of the paper could be purchased from W. Nicoll in St. Paul's Church Yard, and letters to the editor and advertisements were accepted at Lloyd's Coffee House and at the publisher's. John Rivington (1756–1785), a member of the Rivington publishing family, began working for Emonson in 1777 and too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornpipe
The hornpipe is any of several dance forms played and danced in Britain and Ireland and elsewhere from the 16th century until the present day. The earliest references to hornpipes are from England with Hugh Aston's Hornepype of 1522 and others referring to Lancashire hornpipes in 1609 and 1613. It is suggested that the hornpipe as a dance began around the 16th century on English sailing vessels. However, the dance does not seem to have become associated with sailors until after 1740 when the dancer Yates performed 'a hornpipe in the character of a Jack Tar' at Drury Lane Theatre, after which, in 1741 at Covent Garden we hear of "a hornpipe by a gentleman in the character of a sailor". Movements were those familiar to sailors of that time: "looking out to sea" with the right hand to the forehead, then the left, lurching as in heavy weather, and giving the occasional rhythmic tug to their breeches both fore and aft. Folk hornpipes The hornpipe is an Irish, Scottish and English d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten years later. At the time of his accession to the throne, he was acting as Prince Regent, having done so since 5 February 1811, during his father's final mental illness. George IV was the eldest child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. He led an extravagant lifestyle that contributed to the fashions of the Regency era. He was a patron of new forms of leisure, style and taste. He commissioned John Nash to build the Royal Pavilion in Brighton and remodel Buckingham Palace, and commissioned Jeffry Wyatville to rebuild Windsor Castle. George's charm and culture earned him the title "the first gentleman of England", but his dissolute way of life and poor relationships with his parents and his wife, Caroline of Brunswick, earned him the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masque
The masque was a form of festive courtly entertainment that flourished in 16th- and early 17th-century Europe, though it was developed earlier in Italy, in forms including the intermedio (a public version of the masque was the pageant). A masque involved music, dancing, singing and acting, within an elaborate stage design, in which the architectural framing and costumes might be designed by a renowned architect, to present a deferential allegory flattering to the patron. Professional actors and musicians were hired for the speaking and singing parts. Masquers who did not speak or sing were often courtiers: the English queen Anne of Denmark frequently danced with her ladies in masques between 1603 and 1611, and Henry VIII and Charles I of England performed in the masques at their courts. In the tradition of masque, Louis XIV of France danced in ballets at Versailles with music by Jean-Baptiste Lully. Development The masque tradition developed from the elaborate pageants and cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hull (actor)
Thomas Hull (1728–1808) was an English actor and dramatist. Early life Born in 1728 in Strand, London, where his father practised as an apothecary, he was educated at Charterhouse School, with a view to a career in the church. He made an unsuccessful attempt to follow his father's profession. Stage career According to ''Biographia Dramatica'', Hull first appeared at the Smock Alley Theatre in Dublin; and then moved on to Bath, Somerset, where he managed the theatre for John Palmer. His first recorded appearance was, however, at Covent Garden Theatre, 5 October 1759, as Elder Wou'dbe in George Farquhar's ''Twin Rivals''. At Covent Garden Hull stayed without a break, apparently, till the end of his career, a period of forty-eight years. He was the original Harpagus in John Hoole's ''Cyrus'' (3 December 1768), Edwin in William Mason's ''Elfrida'' (21 November 1772), Pizarro in Arthur Murphy's ''Alzuma'' (23 February 1773), Mador in Mason's ''Caractacus'' (6 December 1776), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covent Garden Theatre
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is an opera house and major performing arts venue in Covent Garden, central London. The large building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. It is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet, and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. The first theatre on the site, the Theatre Royal (1732), served primarily as a playhouse for the first hundred years of its history. In 1734, the first ballet was presented. A year later, the first season of operas, by George Frideric Handel, began. Many of his operas and oratorios were specifically written for Covent Garden and had their premieres there. The current building is the third theatre on the site, following disastrous fires in 1808 and 1856 to previous buildings. The façade, foyer, and auditorium date from 1858, but almost every other element of the present complex dates from an extensive reconstruction in the 1990s. The main auditorium seats 2,256 people, maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oratorio
An oratorio () is a large musical composition for orchestra, choir, and soloists. Like most operas, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguishable characters, and arias. However, opera is musical theatre, while oratorio is strictly a concert piece – though oratorios are sometimes staged as operas, and operas are sometimes presented in concert form. In an oratorio, the choir often plays a central role, and there is generally little or no interaction between the characters, and no props or elaborate costumes. A particularly important difference is in the typical subject matter of the text. Opera tends to deal with history and mythology, including age-old devices of romance, deception, and murder, whereas the plot of an oratorio often deals with sacred topics, making it appropriate for performance in the church. Protestant composers took their stories from the Bible, while Catholic composers looked to the lives of saints, as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charity Concert
A benefit concert or charity concert is a type of musical benefit performance (e.g., concert, show, or gala) featuring musicians, comedians, or other performers that is held for a charitable purpose, often directed at a specific and immediate humanitarian crisis. Benefit concerts can have both subjective and concrete objectives. Subjective objectives include raising awareness about an issue such as misery in Africa (such as Live 8) and uplifting a nation after a disaster (such as America: A Tribute to Heroes). Concrete objectives include raising funds (such as Live Aid) and influencing legislation (such as Live 8 or Farm Aid). The two largest benefit concerts of all time, in size, were the Live 8 and the Live Earth events, which both attracted billions of spectators. Scholars theorize that the observed increase on concert size since the Live Aid is happening because organizers strive to make their events as big as the tragedy at hand, thus hoping to gain legitimization that wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of The King's Musick
Master of the King's Music (or Master of the Queen's Music, or earlier Master of the King's Musick) is a post in the Royal Household of the United Kingdom. The holder of the post originally served the monarch of England, directing the court orchestra and composing or commissioning music as required. The post is broadly comparable to that of poet laureate. It is given to people eminent in the field of classical music; they have almost always been composers. Duties are not clearly stated, though it is generally expected the holder of the post will write music to commemorate important royal events, such as coronations, birthdays, anniversaries, marriages and deaths, and to accompany other ceremonial occasions. The individual may also act as the sovereign's adviser in musical matters. Since 2004 the appointment has been for a fixed term of ten years rather than for life, as previously. The King's Musick In the 14th century professional music-making in England was theoretically regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
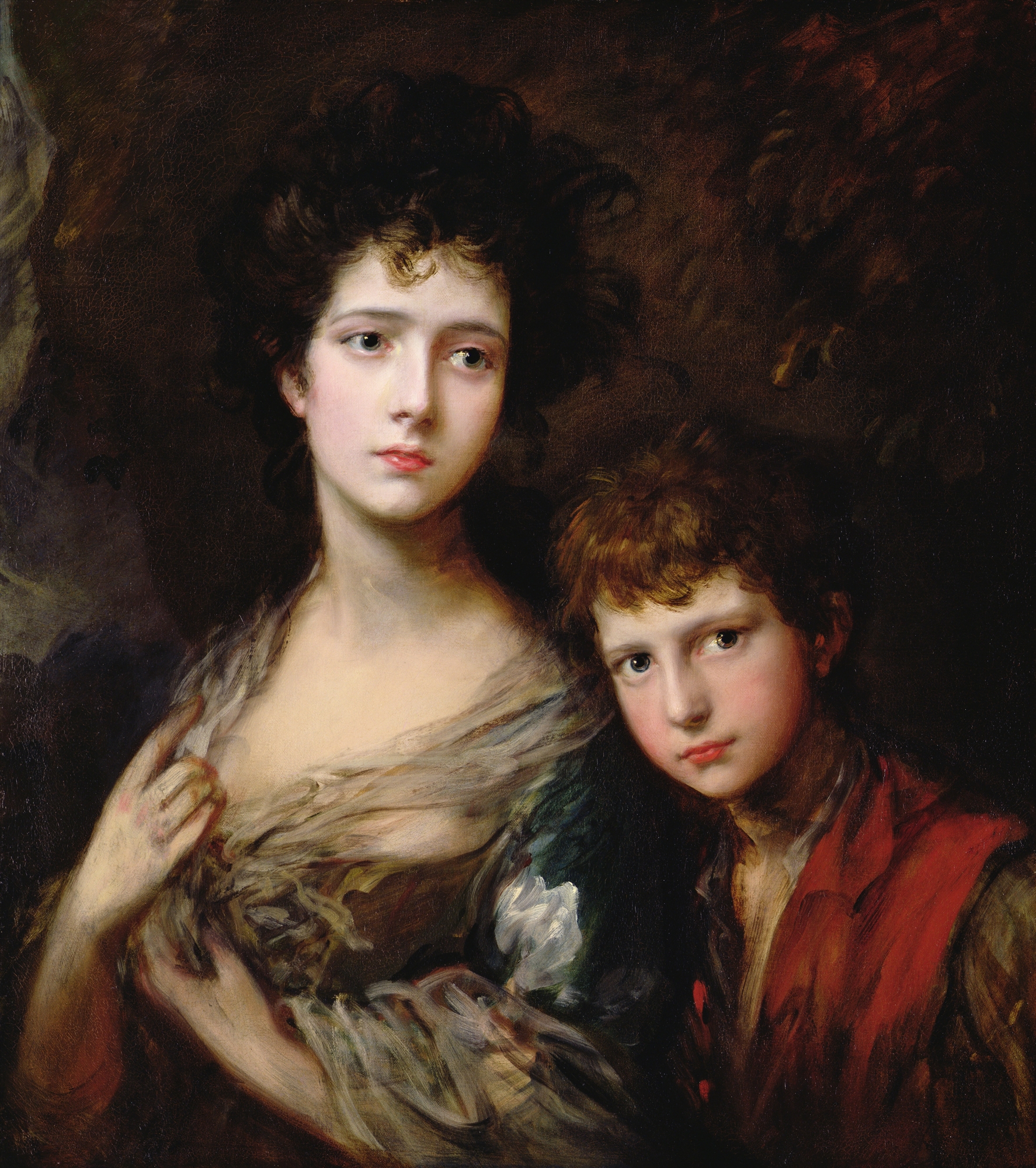
.jpg)