|
Thomas Greene (governor)
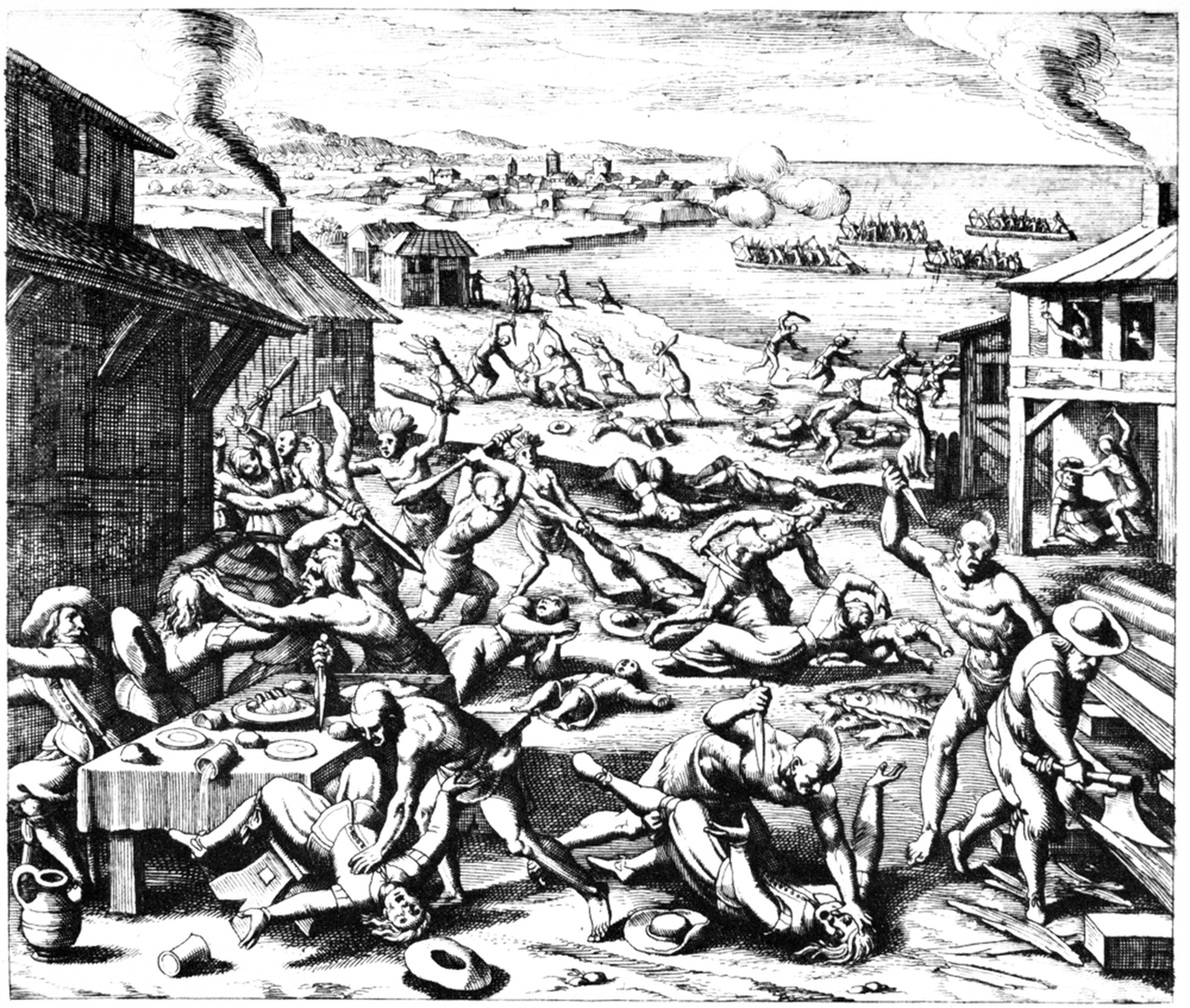
Thomas Greene of Bobbing, Kent, 2nd Proprietary Governor of Maryland (1610, Bobbing, Kent, England – shortly before 20 January 1652 St. Mary's County, Maryland) was an early settler of the Maryland colony and second Provincial Governor of the colony from 1647 to 1648. Biography He was the son of Sir Thomas Greene and Lady Margaret Webb. His father was created Knight Bachelor of the Realm by James I in 1622 at Windsor Castle. Thomas came over from England on the ''Ark'' and ''Dove'' expedition in 1634. Greene was among the earliest settlers of the colony after its founding in 1634 as a haven of religious tolerance for English Catholics among other groups. He was already prominent in the politics of the colony by 1637 or 1638, when he became a prominent leader of moderate Catholics. More radical Catholics led by Thomas Cornwaleys resisted attempts by the colony's proprietor, Cecilius Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore to ensure a broader religious tolerance by, for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Colonial Governors Of Maryland
Maryland began as a proprietary colony of the Catholic Calvert family, the Lords Baltimore under a royal charter, and its first eight governors were appointed by them. When the Catholic King of England, James II, was overthrown in the Glorious Revolution, the Calverts lost their charter and Maryland became a royal colony. It was governed briefly by local Protestants before the arrival of the first of 12 governors appointed directly by the English crown. The royal charter was restored to the Calverts in 1715 and governors were again appointed by the Calverts through the American Revolution. Colonial period This list only includes legally appointed governors, and excludes those who, during brief periods of rebellion, claimed themselves as governors of the colony. See also *List of governors of Maryland Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Maryland, List of colonial governors of Maryland Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Claiborne
William Claiborne also, spelled Cleyburne (c. 1600 – c. 1677) was an English pioneer, surveyor, and an early settler in the colonies/provinces of Virginia and Maryland and around the Chesapeake Bay. Claiborne became a wealthy merchant and planter, as well as a major political figure in the mid-Atlantic colonies. He featured in disputes between the colonists of Virginia and the later settling of Maryland, partly because of his earlier trading post on Kent Island in the mid-way of the Chesapeake Bay, which provoked the first naval military battles in North American waters. Claiborne repeatedly attempted and failed to regain Kent Island from the Maryland Calverts, sometimes by force of arms, after its inclusion in the lands that were granted by a 1632 Royal Charter to the Calvert family. Kent Island had become Maryland territory after the surrounding lands were granted to Sir George Calvert, first Baron and Lord Baltimore (1579–1632) by the reigning King of England, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Brandon, 1st Duke Of Suffolk
Charles Brandon, 1st Duke of Suffolk, 1st Viscount Lisle, (22 August 1545) was an English military leader and courtier. Through his third wife, Mary Tudor, he was brother-in-law to King Henry VIII. Biography Charles Brandon was the second but only surviving son of Sir William Brandon, Henry Tudor's standard-bearer at the Battle of Bosworth Field, where Richard III was slain. His mother, Elizabeth Bruyn (d. March 1494), was daughter and co-heiress of Sir Henry Bruyn (died 1461). Charles Brandon was brought up at the court of Henry VII, and became Henry VIII's closest friend. He is described by Dugdale as "a person comely of stature, high of courage and conformity of disposition to King Henry VIII, with whom he became a great favourite." Brandon held a succession of offices in the royal household, becoming Master of the Horse in 1513, and received many valuable grants of land. On 15 May 1513, he was created Viscount Lisle, having entered into a marriage contract wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotney Castle
Scotney Castle is an English country house with formal gardens south-east of Lamberhurst in the valley of the River Bewl in Kent, England. It belongs to the National Trust. The gardens, which are a Site of Special Scientific Interest and a celebrated example of the Picturesque style, are open to the public. The central feature is the ruins of a medieval, moated manor house, Scotney Old Castle, which is on an island on a small lake. The lake is surrounded by sloping, wooded gardens with fine collections of rhododendrons, azaleas and kalmia for spring colour, summer wisteria and roses, and spectacular autumn colour. At the top of the garden stands a house which was built to replace the Old Castle between 1835 and 1843. This is known as Scotney New Castle, or simply Scotney Castle, and was designed by Anthony Salvin. It is an early and unusually restrained example of Tudor Revival architectural style in 19th-century Britain. Following the death of the resident, Elizabeth Huss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
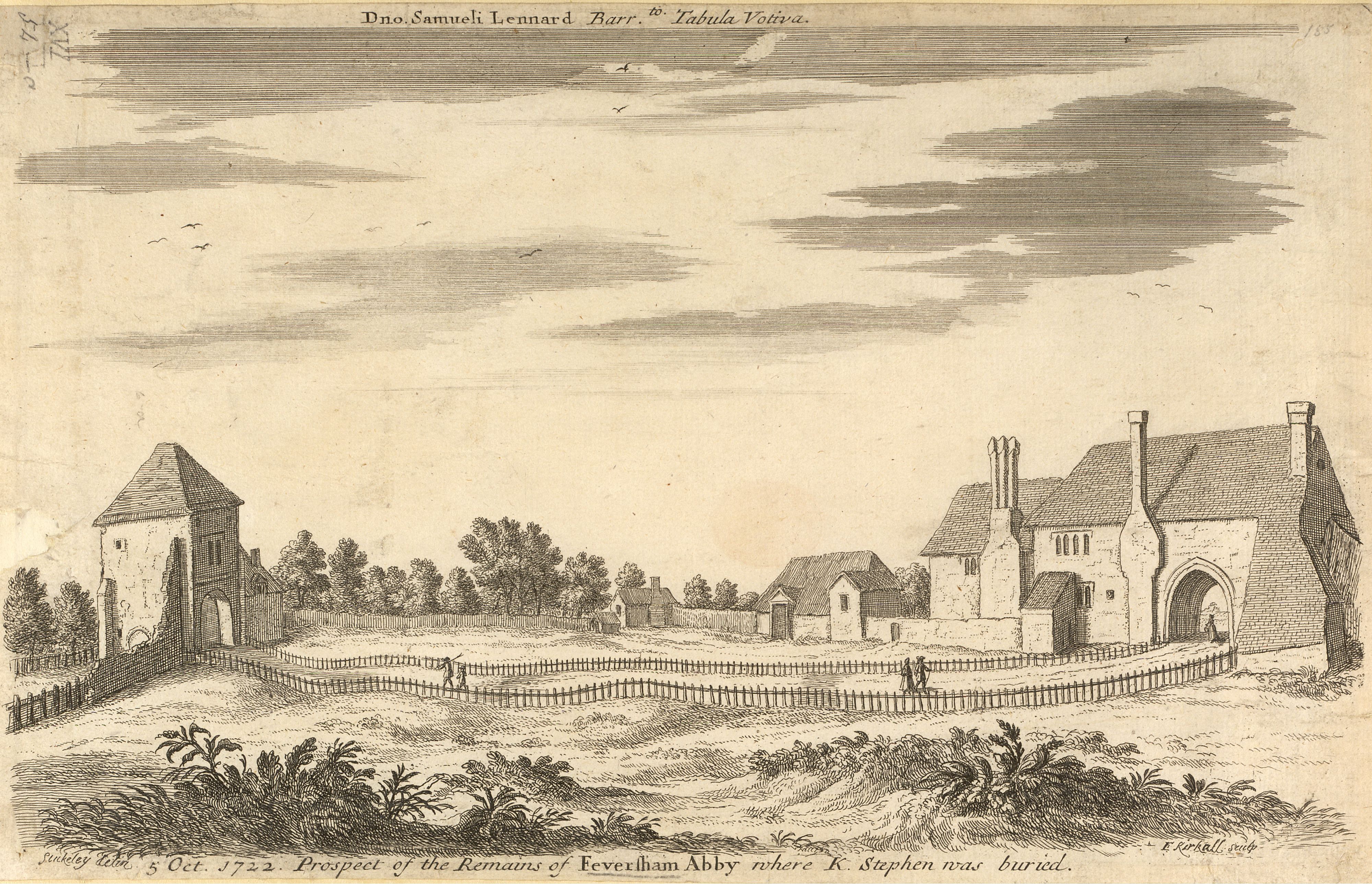
Faversham
Faversham is a market town in Kent, England, from London and from Canterbury, next to the Swale, a strip of sea separating mainland Kent from the Isle of Sheppey in the Thames Estuary. It is close to the A2, which follows an ancient British trackway which was used by the Romans and the Anglo-Saxons, and known as Watling Street. The name is of Old English origin, meaning "the metal-worker's village". There has been a settlement at Faversham since pre-Roman times, next to the ancient sea port on Faversham Creek. It was inhabited by the Saxons and mentioned in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Favreshant''. The town was favoured by King Stephen who established Faversham Abbey, which survived until the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1538. Subsequently, the town became an important seaport and established itself as a centre for brewing, and the Shepherd Neame Brewery, founded in 1698, remains a significant major employer. The town was also the centre of the explosives industry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen, King Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne ''jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William Ade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Severn
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland Toleration Act
The Maryland Toleration Act, also known as the Act Concerning Religion, the first law in North America requiring religious tolerance for Christians. It was passed on April 21, 1649, by the assembly of the Maryland colony, in St. Mary's City in St. Mary's County, Maryland. It created one of the pioneer statutes passed by the legislative body of an organized colonial government to guarantee any degree of religious liberty. Specifically, the bill, now usually referred to as the Toleration Act, granted freedom of conscience to all Christians. (The colony which became Rhode Island passed a series of laws, the first in 1636, which prohibited religious persecution including against non-Trinitarians; Rhode Island was also the first government to separate church and state.) Historians argue that it helped inspire later legal protections for freedom of religion in the United States. The Calvert family, who founded Maryland partly as a refuge for English Catholics, sought enactment of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of religious freedom. It was part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. The first (1642–1646) and second (1648–1649) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–1651) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The wars also involved the Scottish Covenanters and Irish Confederates. The war ended with Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651. Unlike other civil wars in England, which were mainly fought over who should rule, these conflicts were also concerned with how the three Kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland should be governed. The outcome was threefold: the trial of and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundheads
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive administration of the country/kingdom. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. Puritanism played a significant role in English history, especially during the Protectorate. Puritans were dissatisfied with the limited extent of the English Reformation and with the Church of England's toleration of certain practices associated with the Roman Catholic Church. They formed and identified with various religious groups advocating greater purity of worship and doctrine, as well as personal and corporate piety. Puritans adopted a Reformed theology, and in that sense they were Calvinists (as were many of their earlier opponents). In church polity, some advocated separation from all other established Christian denominations in favour of autonomous gathered churches. These English Dissenters, Separatist and Indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after his father inherited the English throne in 1603, he moved to England, where he spent much of the rest of his life. He became heir apparent to the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland in 1612 upon the death of his elder brother, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales. An unsuccessful and unpopular attempt to marry him to the Spanish Habsburg princess Maria Anna of Spain, Maria Anna culminated in an eight-month visit to Spain in 1623 that demonstrated the futility of the marriage negotiation. Two years later, he married the House of Bourbon, Bourbon princess Henrietta Maria of France. After his 1625 succession, Charles quarrelled with the Parliament of England, English Parliament, which sought to curb his royal prerogati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |