|
Thirlwall Prize
Since 1884, the Thirlwall Prize was instituted at Cambridge University in the memory of Bishop Connop Thirlwall, and has been awarded during odd-numbered years, for the best essay about British history or literature for a subject with original research. It was instituted on the condition that a foundation a medal is awarded in alternate years for the best dissertation involving original historical research, together with a sum of money to defray the expenses of publication. From 1885, the Prince Consort Prize was awarded in alternate years. Winners Winners of the Thirlwall Prize include: * 1889 The Constitutional Experiments of the Commonwealth by E. Jenks * 1891 The Doctrine of Consideration in English Law by F. Aidan Hibbert * 1897 English Democratic Ideas in the Seventeenth Century by G.P. Gooch * 1905 The Second Athenian Confederacy by F.H. Marshall * 1907 Claudian as an Historical Authority by J. H. E. Crees * 1913 To Bartolus of Sassoferrato: his Position in the His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. The First Punic War had ended in a Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awards And Prizes Of The University Of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge (formally The Chancellor, Masters, and Scholars of the University of Cambridge) is a collegiate public research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by King Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the second-oldest university in the English-speaking world and the world's fourth-oldest surviving university. The history and influence of the University of Cambridge has made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Numerous scholarships, prizes, honors, and awards specific to the university are awarded to prospective or current students. List of awards * Adam Smith Prize: awarded for best performance in the Part IIB Economics Tripos examinations and dissertation * Adams Prize: awarded for distinguished research in the Mathematical Sciences * Browne Medal: awarded for annual competitions in Latin and Greek poetry * Carus Greek Testament Prizes awarded to candidates who are given a passage in Greek fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of History Awards ...
This list of history awards covers notable awards given to persons, a group of persons, or institutions, for their contribution to the study of history. It is organized by region. The entries name the prize and sponsoring organization, give notes on the purpose or criteria, and where available give the period in which the prize was awarded. Typically a prize is first awarded in the year after it is established, and applies to work published in the previous year. Americas Canada Latin America United States Asia Europe Oceania Australia See also * Lists of awards References {{Phaleristics, state=collapsed history History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivian H
Vivian may refer to: *Vivian (name), a given name and also a surname Toponyms * Vivian, Louisiana, U.S. * Vivian, South Dakota, U.S. * Vivian, West Virginia, U.S. * Vivian Island, Nunavut, Canada * Ballantrae, Ontario, a hamlet in Stouffville, Ontario, formerly known as Vivian Other * ''Vivian'' (album), an album by Vivian Green * Vivian (''Paper Mario''), a ''Paper Mario'' character * Vivian & Sons, a British metallurgical and chemicals business based at Hafod, in the lower Swansea valley * , an Empire F type coaster originally named ''Empire Farjeon'', in service in Greece from 1966-87 See also * Saint-Vivien (other) * Vivien (other) * Vivienne, a female version of the name * Viviana (other), a female version of the name * Vivianite, a mineral * Vyvyan Vivian (and variants such as Vivien and Vivienne) is a given name, and less often a surname, derived from a Latin name of the Roman Empire period, masculine ''Vivianus'' and feminine '' Vivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical History
__NOTOC__ Church history or ecclesiastical history as an academic discipline studies the history of Christianity and the way the Christian Church has developed since its inception. Henry Melvill Gwatkin defined church history as "the spiritual side of the history of civilized people ever since our Master's coming". A. M. Renwick, however, defines it as an account of the Church's success and failure in carrying out Christ's Great Commission.A. M. Renwick and A. M. Harman, ''The Story of the Church'' (3rd ed.), p. 8. Renwick suggests a fourfold division of church history into missionary activity, church organization, doctrine and "the effect on human life". Church history is often, but not always, studied from a Christian perspective. Writers from different Christian traditions will often highlight people and events particularly relevant to their own denominational history. Catholic and Orthodox writers often highlight the achievements of the ecumenical councils, while evangel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Pecock
Reginald Pecock (or Peacock; c. 1395– c. 1461) was a Welsh prelate, scholastic, and writer. Life Pecock was probably born in Laugharne and was educated at Oriel College, Oxford. Having been ordained priest in 1421, Pecock secured a mastership at Whittington College, London, in 1431 where he was also parish priest of St. Michael Paternoster Royal, the adjacent parish church. On 14 June 1444 he was consecrated as Bishop of St Asaph,Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 296 and translated as Bishop of Chichester on 23 March 1450.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 239 In 1454 he became a member of the privy council. He wrote books of both a pedagogical and polemical nature. His pedagogical books, in which he proposes a wholly new catechism include ''The Donet'', ''The Follower to the Donet'', and ''The Rule of Christian Religion''. He joined the debate on Christian doctrine in his ''Repressing of Over Mich Wyting'' laming''the Clergie'', 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Liverpool
Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool, (7 June 1770 – 4 December 1828) was a British Tory statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1812 to 1827. He held many important cabinet offices such as Foreign Secretary, Home Secretary and Secretary of State for War and the Colonies. He was also a member of the House of Lords and served as leader. As prime minister, Liverpool called for repressive measures at domestic level to maintain order after the Peterloo Massacre of 1819. He dealt smoothly with the Prince Regent when King George III was incapacitated. He also steered the country through the period of radicalism and unrest that followed the Napoleonic Wars. He favoured commercial and manufacturing interests as well as the landed interest. He sought a compromise of the heated issue of Catholic emancipation. The revival of the economy strengthened his political position. By the 1820s he was the leader of a reform faction of "Liberal Tories" who low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
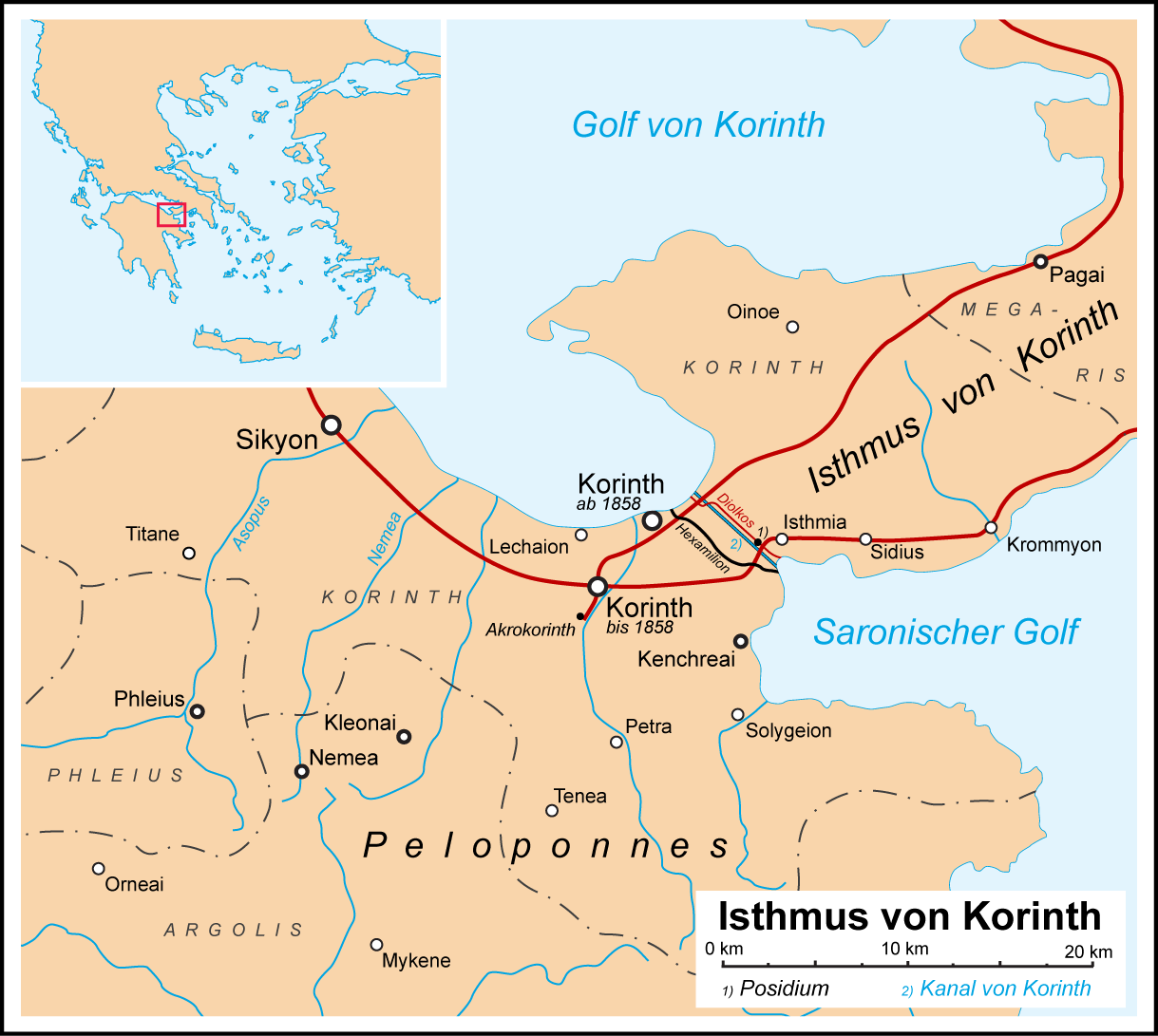
Aratos Of Sicyon
Aratus of Sicyon (Ancient Greek: Ἄρατος ὁ Σικυώνιος; 271–213 BC) was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous military campaigns including the Cleomenean War and the Social War. Aratus was exiled to Argos at the age of seven, after his father, the magistrate of Sicyon, was killed in a coup. In 251 BC, he led an expedition composed of other exiles which freed Sicyon from tyranny, and assumed power in the city. Sicyon joined the Achaean League, in which Aratus would later be elected '' strategos''. In his first major campaign as strategos, he seized the Macedonian-held citadel of Acrocorinth, previously believed impregnable. After conquering the Acrocorinth, Aratus pursued the Achaean League's expansion. When the Spartan king Cleomenes III conquered the Achaean cities of Argos and Corinth, Aratus succeeded in securing an alliance with his erstwhil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a revival movement within the 18th-century Church of England and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States, and beyond because of vigorous missionary work, today claiming approximately 80 million adherents worldwide. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist churches, focuses on sanctification and the transforming effect of faith on the character of a Christian. Distinguishing doctrines include the new birth, assurance, imparted righteousness, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Hayes Scullard
Howard Hayes Scullard (9 February 1903 – 31 March 1983) was a British historian specialising in ancient history, notable for editing the ''Oxford Classical Dictionary'' and for his many published works. Scullard's father was Herbert Hayes Scullard, a minister, and his mother Barbara Louisa Dodds. Born in Bedford, England, his early education was at Highgate School, followed by St. John's College, Cambridge. He was a tutor and then reader at New College London, from 1935 to 1959, when he became Professor of Ancient History at King's College London, retiring in 1970. He nonetheless remained active in retirement and notably wrote chapters for the re-edition of ''The Cambridge Ancient History'', but his contributions to volumes VII and VIII were published posthumously.A. E. Astin & F. W. Walbank, ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. VII, Rome and the Mediterranean to 133 B.C.'', Cambridge University Press, 1989, p. xvi. Perhaps his most widely known work is ''From the Gracchi t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the Numantine War in Spain. He oversaw the final defeat and destruction of the city of Carthage. He was a prominent patron of writers and philosophers, the most famous of whom was the Greek historian Polybius. In politics, he opposed the populist reform program of his murdered brother-in-law, Tiberius Gracchus. Family Scipio Aemilianus was the second son of Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus, the commander of the Romans' victorious campaign in the Third Macedonian War, and his first wife, Papiria Masonis. Scipio was adopted by his first cousin, Publius Cornelius Scipio P.f. P.n. Africanus, Publius Cornelius Scipio, the eldest son of his aunt Aemilia Tertia and her husband Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, the acclaimed commander who won ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
