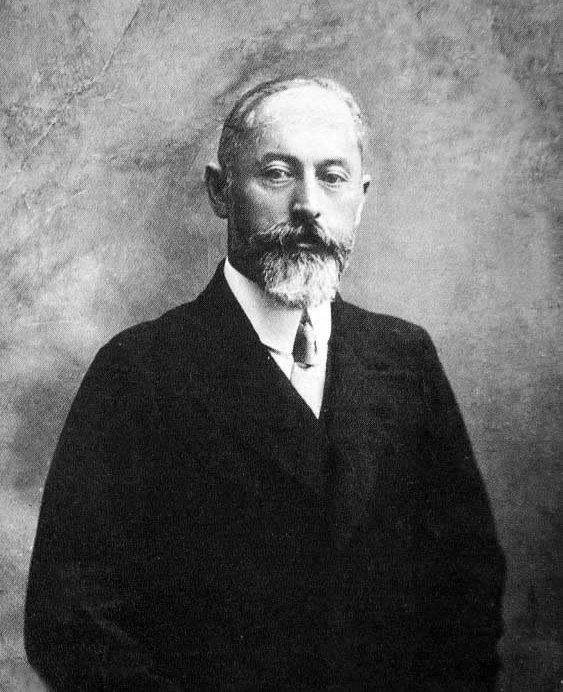|
Third Zimmerwald Conference
The Third Zimmerwald Conference or the Stockholm Conference of 1917 was the third and final of the anti-war socialist conferences that had included Zimmerwald (1915) and Kienthal (1916). It was held in Stockholm on September 5–12, 1917. Background The Third Zimmerwald Conference was originally called so that the Zimmerwald parties could discuss their attitude toward a proposed general conference of socialist parties in Stockholm that had been called by Petrograd Soviet and Dutch-Scandinavian Committee that had included the members of the old International Socialist Bureau. As this conference kept being postponed, so was the Zimmerwald meeting that was supposed to assemble before it, until late July 1917 when the International Socialist Commission decided to hold its own meeting regardless of what happened to the plans for the proposed general conference for September 5–12, 1917. Delegates The following delegates attended the conference. Neutral countries * Social Dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimmerwald Conference
The Zimmerwald Conference was held in Zimmerwald, Switzerland, from September 5 to 8, 1915. It was the first of three international socialist conferences convened by anti-militarist socialist parties from countries that were originally neutral during World War I. The individuals and organizations participating in this and subsequent conferences held at Kienthal and Stockholm are known jointly as the Zimmerwald movement. The Zimmerwald Conference began the unraveling of the coalition between revolutionary socialists (the so-called Zimmerwald Left) and reformist socialists in the Second International. Background Socialist discussions on war When the Second International, the primary international socialist organization before World War I, was founded in 1889, internationalism was one of its central tenets. "The workers have no Fatherland", Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels had declared in ''The Communist Manifesto''. Paul Lafargue, Marx's son-in-law, in his keynote address at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Nobs
Ernst Nobs (14 July 1886, in Seedorf, Bern – 15 March 1957) was a Swiss politician. He was the mayor of Zürich from 1942 to 1944. He was elected to the Swiss Federal Council on 15 December 1943, as the first member of the Social Democratic Party. He handed over office on 31 December 1951. During his time in office he was responsible for the Department of Finance and he was President of the Confederation The president of the Swiss Confederation, also known as the president of the Confederation or colloquially as the president of Switzerland, is the head of Switzerland's seven-member Federal Council, the country's executive branch. Elected by ... in 1949. References External links * * * 1886 births 1957 deaths People from Seeland District Swiss Calvinist and Reformed Christians Social Democratic Party of Switzerland politicians Members of the Federal Council (Switzerland) Finance ministers of Switzerland Members of the National Council (Switzerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy Of The Kingdom Of Poland And Lithuania
The Social Democracy of the Kingdom of Poland and Lithuania ( pl, Socjaldemokracja Królestwa Polskiego i Litwy, SDKPiL), , LKLSD), originally the Social Democracy of the Kingdom of Poland (SDKP), was a Marxist political party founded in 1893 and later served as an autonomous section of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. It later merged into the Communist Workers Party of Poland. Its most famous member was Rosa Luxemburg. Leading members The leading cadre of the SDKPiL were a famous group, many of whom would play a role in the Russian Revolution of October 1917. Chief among them was Rosa Luxemburg, the leading theoretician of the movement. Other notable figures included Leo Jogiches, Julian Marchlewski, Adolf Warski, Felix Dzerzhinsky, Stanisław Pestkowski, Karl Sobelson, Józef Unszlicht, Kazimierz Cichowski and Jakob Fürstenberg. Internationalists, many of them would play leading roles in Germany as well as in Russia. History 1893: Formation The party was fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yrjö Sirola
Yrjö Elias Sirola (born Yrjö Elias Sirén; 8 November 1876 – 18 March 1936) was a Finnish socialist politician, writer, teacher, and newspaper editor. He was prominent as an elected official in Finland, as minister of foreign affairs in the 1918 Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic, a founder of the Communist Party of Finland, and as a functionary of the Communist International. Background Yrjö Esias Sirén was born 8 November 1876 in Piikkiö, Finland, then part of the Russian Empire. His father, Karl Gustaf Sirén, worked as a clergyman.David Kirby, "Yrjö Esias Sirola," in A. Thomas Lane (ed.), ''Biographical Dictionary of European Labor Leaders: M-Z.'' Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 1995; pg. 899. Yrjö attended a lycée in Viipuri and then attended Rauma teachers' training college, from which he graduated in 1902. Career Following completion of his studies he took a post as a teacher in Hattula. Social Democratic Party (Finland) Yrjö joined the Social Democratic P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Party Of Finland
The Social Democratic Party of Finland (SDP, fi, Suomen sosialidemokraattinen puolue ; sv, Finlands socialdemokratiska parti), shortened to the Social Democrats ( fi, link=no, Sosiaalidemokraatit; sv, link=no, Socialdemokrater) and commonly known in Finnish as Demarit ( sv, link=no, Socialdemokraterna), is a social-democratic political party in Finland. It is currently the largest party in the Parliament of Finland with 40 seats. Founded in 1899 as the Finnish Labour Party ( fi, link=no, Suomen työväenpuolue; sv, link=no, Finska arbetarpartiet), the SDP is Finland's oldest active political party and has a close relationship with the Central Organisation of Finnish Trade Unions. It is also a member of the Party of European Socialists, Progressive Alliance, Socialist International and SAMAK. Following the resignation of Antti Rinne in December 2019, Sanna Marin became the country's 76th Prime Minister. SDP formed a new coalition government on the basis of its predecessor, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osip Ermansky
Osip (Russian ''О́сип'') is a Russian male given name, a variant of the name Joseph. Notable people with the name include: * Osip Abdulov (1900–1953), Soviet actor * Osip Aptekman, Russian revolutionary * Ossip Bernstein (1882-1962), Russian-French chess player * Osip Bilchansky (1858-1879), Russian terrorist hanged for using a gun to resist arrest * Osip Bodyansky (1808-1877), Russian Imperial Slavist of Ukrainian Cossack descent * Osip Braz (1873-1936), Russian-Jewish realist painter * Osip Brik, Russian writer and literary critic, a futurist * Osip Dymov (writer), pseudonym for Yosif (Osip) Isidorovich Perelman (1878-1959), Russian writer * Osip Gelfond (1868-1942), Russian physician and Marxist philosopher * Osip Komissarov, hatter's apprentice famous for thwarting the assassination of Alexander II of Russia * Osip Kozodavlev (1754–1819), Russian statesman, politician and Minister of the Interior * Osip Mikhailovich Lerner (1847–1907), also known as Y. Y. (Yosef Yehud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menshevik Internationalists
The Menshevik-Internationalists were a faction inside the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Mensheviks). The faction, representing the left-wing inside the party, emerged in May 1917. It was joined by a number of political leaders returning from exile, the most notable being Julius Martov. The Menshevik-Internationalist opposed the pro-war line of Dan and Tsereli. The Menshevik-Internationalists hoped to sway the Menshevik Party over to an anti-war stance. The Menshevik-Internationalists dominated the Menshevik Party Organizations in Kharkov, Tula and some other places. They had some control over the Petrograd branch of the party. At the Menshevik Party congress in August 1917, the Menshevik-Internationalists represented about a third of the gathered delegates. A major chunk of the Menshevik-Internationalist faction broke away and joined the Bolsheviks in August 1917. This group included Yuri Larin. At the election for the All-Russian Central Executive Committee held at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Makadziub
Mark may refer to: Currency * Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, the currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina * East German mark, the currency of the German Democratic Republic * Estonian mark, the currency of Estonia between 1918 and 1927 * Finnish markka ( sv, finsk mark, links=no), the currency of Finland from 1860 until 28 February 2002 * Mark (currency), a currency or unit of account in many nations * Polish mark ( pl, marka polska, links=no), the currency of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Republic of Poland between 1917 and 1924 German * Deutsche Mark, the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until 2002 * German gold mark, the currency used in the German Empire from 1873 to 1914 * German Papiermark, the German currency from 4 August 1914 * German rentenmark, a currency issued on 15 November 1923 to stop the hyperinflation of 1922 and 1923 in Weimar Germany * Lodz Ghetto mark, a special currency for Lodz Ghetto. * R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Axelrod
Pavel Borisovich Axelrod (russian: Па́вел Бори́сович Аксельро́д; 25 August 1850 – 16 April 1928) was an early Russian Marxist revolutionary. Along with Georgi Plekhanov, Vera Zasulich, and Leo Deutsch, he was one of the members of the first organization of Russian Marxists, Emancipation of Labor. After the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, he was part of the Menshevik faction, with which he was identified until his death. Early life and career Pavel Axelrod was the son of a Jewish innkeeper. His parents lived in the Jewish poorhouse. He was forced to work for a living from a young age; though while still in his early teens, he produced his first political essay, on the condition of the Jewish poor in the Mogilev Region, in modern-day Belarus. At the age of 16, he discovered the writings of the German socialist Ferdinand Lasalle, which had a major influence on him. Later, he obtained a place at Kiev University, with fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Semashko (medicine)
Dr. Nikolai Aleksandrovich Semashko (russian: Никола́й Алекса́ндрович Сема́шко; – May 18, 1949), was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet statesman and academic who became People's Commissar of Public Health in 1918, and served in that role until 1930. He was one of the organizers of the health system in the Soviet Union (often called the Semashko system), an academician of the Academy of Medical Sciences (1944) and of the Russian SFSR (1945). Life and career Early life Nikolai Semashko was born to a teacher in the village of Livenskoe in Yelets uyezd of Oryol guberniya (in present-day Lipetsk Oblast). His mother was a sister of Georgi Plekhanov. In 1891, after graduating from the Yelets gymnasium (where he studied with Mikhail Prishvin), Semashko entered the medical faculty of Moscow University. In 1893 he became a member of a Marxist group. In 1895, for his participation in the revolutionary movement, he was arrested and exiled to his home in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatslav Vatslavovich Vorovsky
Vatslav Vatslavovich Vorovsky (Russian: Ва́цлав Ва́цлавович Воро́вский; Polish: Wacław Worowski) (27 October Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 15 October1871 – 10 May 1923) was a Russian Bolsheviks">Bolshevik, Marxist revolutionary, literary critic, publicist and Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, Soviet diplomat. One of the first Soviet diplomats, Vorovsky is best remembered as the victim of a May 1923 political assassination in Lausanne, Switzerland, where he was the official representative of the Soviet government to the Conference of Lausanne. Biography Early years Vatslav Vorovsky was born on 27 October 1871 (n.s.) in Moscow, the son of an ethnically Polish but Russified noble and engineer.Branko Lazitch with Milorad M. Drachkovitch, ''Biographical Dictionary of the Comintern: New, Revised, and Expanded Edition.'' Stanford, CA: Hoover Institution Press, 1986; pp. 498–499. His father d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |