|
Thermometer Code
Unary coding, or the unary numeral system, is an entropy encoding that represents a natural number, ''n'', with ''n'' ones followed by a zero (if the term ''natural number'' is understood as ''non-negative integer'') or with ''n'' − 1 ones followed by a zero (if the term ''natural number'' is understood as ''strictly positive integer''). A unary number's code length would thus be ''n'' + 1 with that first definition, or ''n'' with that second definition. Unary code when vertical behaves like mercury in a thermometer that gets taller or shorter as ''n'' gets bigger or smaller, and so is sometimes called thermometer code. An alternative representation uses ''n'' or ''n'' − 1 zeros followed by a one, effectively swapping the ones and zeros, without loss of generality. For example, the first ten unary codes are: Unary coding is an ''optimally efficient'' encoding for the following discrete probability distribution :\operatorname(n) = 2^\, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unary Numeral System
The unary numeral system is the simplest numeral system to represent natural numbers: to represent a number ''N'', a symbol representing 1 is repeated ''N'' times. In the unary system, the number 0 (zero) is represented by the empty string, that is, the absence of a symbol. Numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ... are represented in unary as 1, 11, 111, 1111, 11111, 111111, ... Unary is a bijective numeral system. However, although it has sometimes been described as "base 1", it differs in some important ways from positional notations, in which the value of a digit depends on its position within a number. For instance, the unary form of a number can be exponentially longer than its representation in other bases. The use of tally marks in counting is an application of the unary numeral system. For example, using the tally mark (𝍷), the number 3 is represented as . In East Asian cultures, the number 3 is represented as 三, a character drawn with three strokes. (One and two are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coding Theory
Coding theory is the study of the properties of codes and their respective fitness for specific applications. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography, error detection and correction, data transmission and computer data storage, data storage. Codes are studied by various scientific disciplines—such as information theory, electrical engineering, mathematics, linguistics, and computer science—for the purpose of designing efficient and reliable data transmission methods. This typically involves the removal of redundancy and the correction or detection of errors in the transmitted data. There are four types of coding: # Data compression (or ''source coding'') # Error detection and correction, Error control (or ''channel coding'') # Cryptography, Cryptographic coding # Line code, Line coding Data compression attempts to remove unwanted redundancy from the data from a source in order to transmit it more efficiently. For example, DEFLATE data compression makes files small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elsevier
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ''Trends (journals), Trends'', the ''Current Opinion (Elsevier), Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services include digital tools for Data management platform, data management, instruction, research analytics, and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group, known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier, a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2022 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,800 journals. As of 2018, its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 Ebook, e-books, with over one b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BCD Code
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise four-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named ''pseudo-tetrad(e)s'', ''pseudo-decimals'', or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Binary-coded Decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise four-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named ''pseudo-tetrad(e)s'', ''pseudo-decimals'', or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unary Numeral System
The unary numeral system is the simplest numeral system to represent natural numbers: to represent a number ''N'', a symbol representing 1 is repeated ''N'' times. In the unary system, the number 0 (zero) is represented by the empty string, that is, the absence of a symbol. Numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ... are represented in unary as 1, 11, 111, 1111, 11111, 111111, ... Unary is a bijective numeral system. However, although it has sometimes been described as "base 1", it differs in some important ways from positional notations, in which the value of a digit depends on its position within a number. For instance, the unary form of a number can be exponentially longer than its representation in other bases. The use of tally marks in counting is an application of the unary numeral system. For example, using the tally mark (𝍷), the number 3 is represented as . In East Asian cultures, the number 3 is represented as 三, a character drawn with three strokes. (One and two are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subhash Kak
Subhash Kak is an Indian-American computer scientist and historical revisionist. He is the Regents Professor of Computer Science Department at Oklahoma State University–Stillwater, an honorary visiting professor of engineering at Jawaharlal Nehru University, and a member of the Indian Prime Minister's Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC). Kak has published on the history of science, the philosophy of science, ancient astronomy, and the history of mathematics. Kak has also published on archaeoastronomy, and advocated the idea of Indigenous Aryans. Many scholars have rejected his theories on these topics in entirety, and his writings have been heavily criticized. In 2019, the Government of India awarded him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award in India, for his contributions on the history of mathematics, science, ancient astronomy and philosophy of science. Early life and education Kak was born to Ram Nath Kak, a government veteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
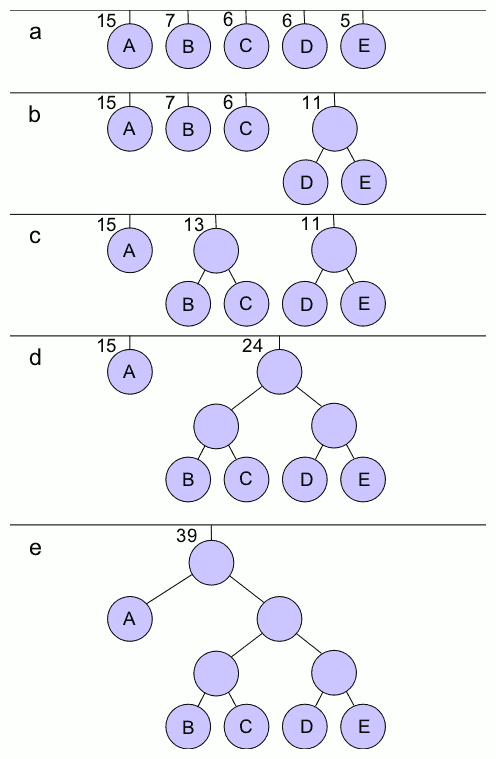
Huffman Encoding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear to the number of input weights if these weights are sorted. However, although optimal among met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Canonical Huffman Code
In computer science and information theory, a canonical Huffman code is a particular type of Huffman code with unique properties which allow it to be described in a very compact manner. Rather than storing the structure of the code tree explicitly, canonical Huffman codes are ordered in such a way that it suffices to only store the lengths of the codewords, which reduces the overhead of the codebook. Motivation Data compressors generally work in one of two ways. Either the decompressor can infer what codebook the compressor has used from previous context, or the compressor must tell the decompressor what the codebook is. Since a canonical Huffman codebook can be stored especially efficiently, most compressors start by generating a "normal" Huffman codebook, and then convert it to canonical Huffman before using it. In order for a symbol code scheme such as the Huffman code to be decompressed, the same model that the encoding algorithm used to compress the source data must be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prefix Code
A prefix code is a type of code system distinguished by its possession of the prefix property, which requires that there is no whole Code word (communication), code word in the system that is a prefix (computer science), prefix (initial segment) of any other code word in the system. It is trivially true for fixed-length codes, so only a point of consideration for variable-length code, variable-length codes. For example, a code with code has the prefix property; a code consisting of does not, because "5" is a prefix of "59" and also of "55". A prefix code is a uniquely decodable code: given a complete and accurate sequence, a receiver can identify each word without requiring a special marker between words. However, there are uniquely decodable codes that are not prefix codes; for instance, the reverse of a prefix code is still uniquely decodable (it is a suffix code), but it is not necessarily a prefix code. Prefix codes are also known as prefix-free codes, prefix condition codes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uniquely Decodable Code
In coding theory, a variable-length code is a code which maps source symbols to a ''variable'' number of bits. The equivalent concept in computer science is ''bit string''. Variable-length codes can allow sources to be compressed and decompressed with ''zero'' error (lossless data compression) and still be read back symbol by symbol. With the right coding strategy, an independent and identically-distributed source may be compressed almost arbitrarily close to its entropy. This is in contrast to fixed-length coding methods, for which data compression is only possible for large blocks of data, and any compression beyond the logarithm of the total number of possibilities comes with a finite (though perhaps arbitrarily small) probability of failure. Some examples of well-known variable-length coding strategies are Huffman coding, Lempel–Ziv coding, arithmetic coding, and context-adaptive variable-length coding. Codes and their extensions The extension of a code is the mapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |