|
Theodore Schultz
Theodore William Schultz (; 30 April 1902 – 26 February 1998) was an American Agricultural economist and chairman of the University of Chicago Department of Economics. Schultz rose to national prominence after winning the 1979 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Early life and education Theodore William Schultz was born on April 30, 1902 in a small town ten miles northwest of Badger, South Dakota on a 560-acre farm. When Schultz was in the eighth grade, his father Henry decided to pull him out of attending Kingsbury County Schoolhouse. His father's view was that if his eldest son continued to get an education he would be less inclined to continue working on the farm. Schultz subsequently did not have any formal post-secondary education. He eventually enrolled in the Agriculture College at South Dakota State, in a three-year program that met for four months a year during the winter. After being recognized for having great potential as a student, Schultz moved on to a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago School Of Economics
The Chicago school of economics is a neoclassical school of economic thought associated with the work of the faculty at the University of Chicago, some of whom have constructed and popularized its principles. Milton Friedman and George Stigler are considered the leading scholars of the Chicago school. Chicago macroeconomic theory rejected Keynesianism in favor of monetarism until the mid-1970s, when it turned to new classical macroeconomics heavily based on the concept of rational expectations. The freshwater–saltwater distinction is largely antiquated today, as the two traditions have heavily incorporated ideas from each other. Specifically, new Keynesian economics was developed as a response to new classical economics, electing to incorporate the insight of rational expectations without giving up the traditional Keynesian focus on imperfect competition and sticky wages. Chicago economists have also left their intellectual influence in other fields, notably in pioneerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifford Hardin
Clifford Morris Hardin (October 9, 1915April 4, 2010) was an American politician and was the Chancellor of the University of Nebraska. He served as the United States Secretary of Agriculture from 1969 to 1971 under President Richard Nixon. Biography Hardin was born in Knightstown, Indiana, on October 9, 1915, to J. Alvin and Mabel (née Macy) Hardin. He earned a B.S. (1937), M.S. (1939) and Ph.D. (1941) from Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana. On June 28, 1939, Hardin married the former Martha Love Wood. They had two sons and three daughters. He taught Agricultural Economics at the Michigan State University of Lansing from 1944 to 1948, when he became the assistant director and then the director of the Agricultural Experiment Station. He did some post-doctoral work during the 1940s at the University of Chicago where he did research in agricultural economics with future Nobel Prize winner, Theodore Schultz.Sumner, Daniel A. Agricultural Economics at Chicago, in David G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Financial Institutions
An international financial institution (IFI) is a financial institution that has been established (or chartered) by more than one country, and hence is subject to international law. Its owners or shareholders are generally national governments, although other international institutions and other organizations occasionally figure as shareholders. The most prominent IFIs are creations of multiple nations, although some bilateral financial institutions (created by two countries) exist and are technically IFIs. The best known IFIs were established after World War II to assist in the reconstruction of Europe and provide mechanisms for international cooperation in managing the global financial system. Types Multilateral Development Banks A multilateral development bank (MDB) is an institution, created by a group of countries, that provides financing and professional advice to enhance development. An MDB has many members, including developed donor countries and developing borrower cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bretton Woods System
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretton Woods system was the first example of a fully negotiated monetary order intended to govern monetary relations among independent states. The Bretton Woods system required countries to guarantee convertibility of their currencies into U.S. dollars to within 1% of fixed parity rates, with the dollar convertible to gold bullion for foreign governments and central banks at US$35 per troy ounce of fine gold (or 0.88867 gram fine gold per dollar). It also envisioned greater cooperation among countries in order to prevent future competitive devaluations, and thus established the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to monitor exchange rates and lend reserve currencies to nations with balance of payments deficits. Preparing to rebuild the interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Development
International development or global development is a broad concept denoting the idea that societies and countries have differing levels of economic or human development on an international scale. It is the basis for international classifications such as developed country, developing country and least developed country, and for a field of practice and research that in various ways engages with international development processes. There are, however, many schools of thought and conventions regarding which are the exact features constituting the "development" of a country. Historically, development was largely synonymous with economic development, and especially its convenient but flawed quantification (see parable of the broken window) through readily gathered (for developed countries) or estimated monetary proxies (estimated for severely undeveloped or isolationist countries) such as gross domestic product (GDP), often viewed alongside actuarial measures such as life expectancy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
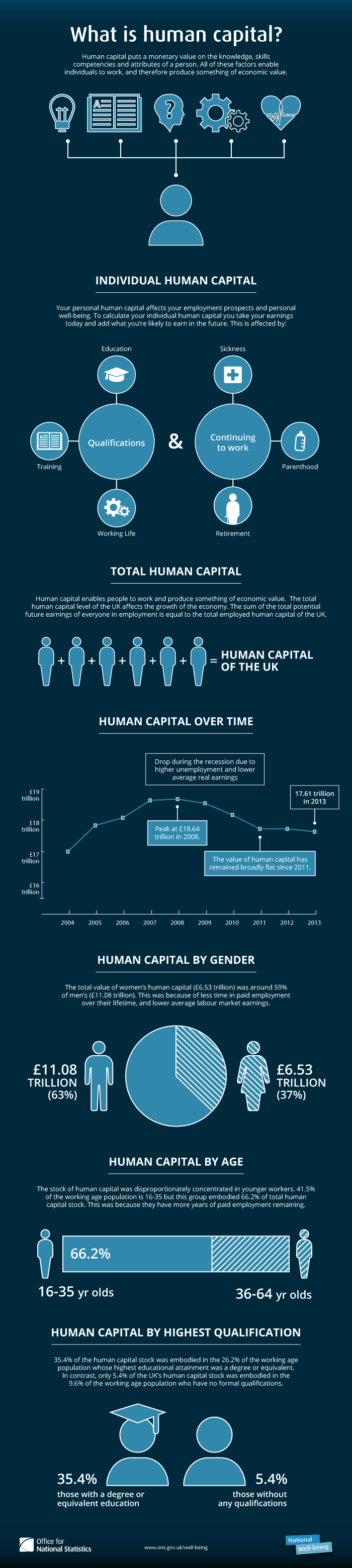
Human Capital Theory
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skill, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons (economist), Robert Gibbons, an economist at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, and Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Schultz Receiving The Nobel Prize
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory * Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), includes the etymology of the given name and a list of people * Theodore (surname), a list of people Fictional characters * Theodore "T-Bag" Bagwell, on the television series ''Prison Break'' * Theodore Huxtable, on the television series ''The Cosby Show'' Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One racing team See also * Principality of Theodoro, a principality in the south-west Crimea from the 13th to 15th centuries * Thoros (other), Armenian for Theodore * James Bass Mullinger James Bass Mullinger (1834 or 1843 – 22 November 1917), sometimes known by his pen name Theodorus, was a British author, historian, lecturer and scholar. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and objectives. The term has been used frequently in the 20th and 21st centuries, but the concept has existed in the West for far longer. " Modernization", "Westernization", and especially "industrialization" are other terms often used while discussing economic development. Historically, economic development policies focused on industrialization and infrastructure; since the 1960s, it has increasingly focused on poverty reduction. Whereas economic development is a policy intervention aiming to improve the well-being of people, economic growth is a phenomenon of market productivity and increases in GDP; economist Amartya Sen describes economic growth as but "one aspect of the process of economic development". Economists primarily focus on the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Capital Theory
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skill, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons (economist), Robert Gibbons, an economist at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, and Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |