|
Thecocoelurus
''Thecocoelurus'' is a nomen dubium, dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of England. The phylogenetic placement of this genus is uncertain, and it has been referred to an oviraptosaur, an ornithomimosaur, or a therizinosaur by different researchers throughout its history. Discovery and naming ''Thecocoelurus'' is known only from half of a single neck, cervical vertebra, discovered by the Rev. William Darwin Fox on the Isle of Wight during the 19th century. After his death the ''Fox Collection'' was acquired by the British Museum of Natural History. William Davies (palaeontologist), William Davies was the first to notice the specimen and assumed a close affinity with ''Coelurus''. It was described by Harry Govier Seeley in 1888. Seeley named the fossil ''Thecospondylus daviesi'', referring it to a genus he had named earlier for the incomplete cast of a sacrum. However, in 1901 Baron Franz Nopcsa renamed it ''Coelurus daviesi''. In 1923 Friedrich vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex Formation
The Wessex Formation is a fossil-rich English geological formation that dates from the Berriasian to Barremian stages (about 145–125 million years ago) of the Early Cretaceous. It forms part of the Wealden Group and underlies the younger Vectis Formation and overlies the Durlston Formation. The dominant lithology of this unit is mudstone with some interbedded sandstones. It is part of the strata of the Wessex Basin, exposed in both the Isle of Purbeck and the Isle of Wight. While the Purbeck sections are largely barren of vertebrate remains, the Isle of Wight sections are well known for producing the richest and most diverse fauna in Early Cretaceous Europe. Nomenclatural History The Wessex Formation has historically alternately been called the "Variegated Marls And Sandstones", a name used by W. J. Arkell in his 1947 map of the Isle of Purbeck as well as the "Wealden Marls" It was given its current formal name by Daley and Stewart in 1979 Stratigraphy and Lithology In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
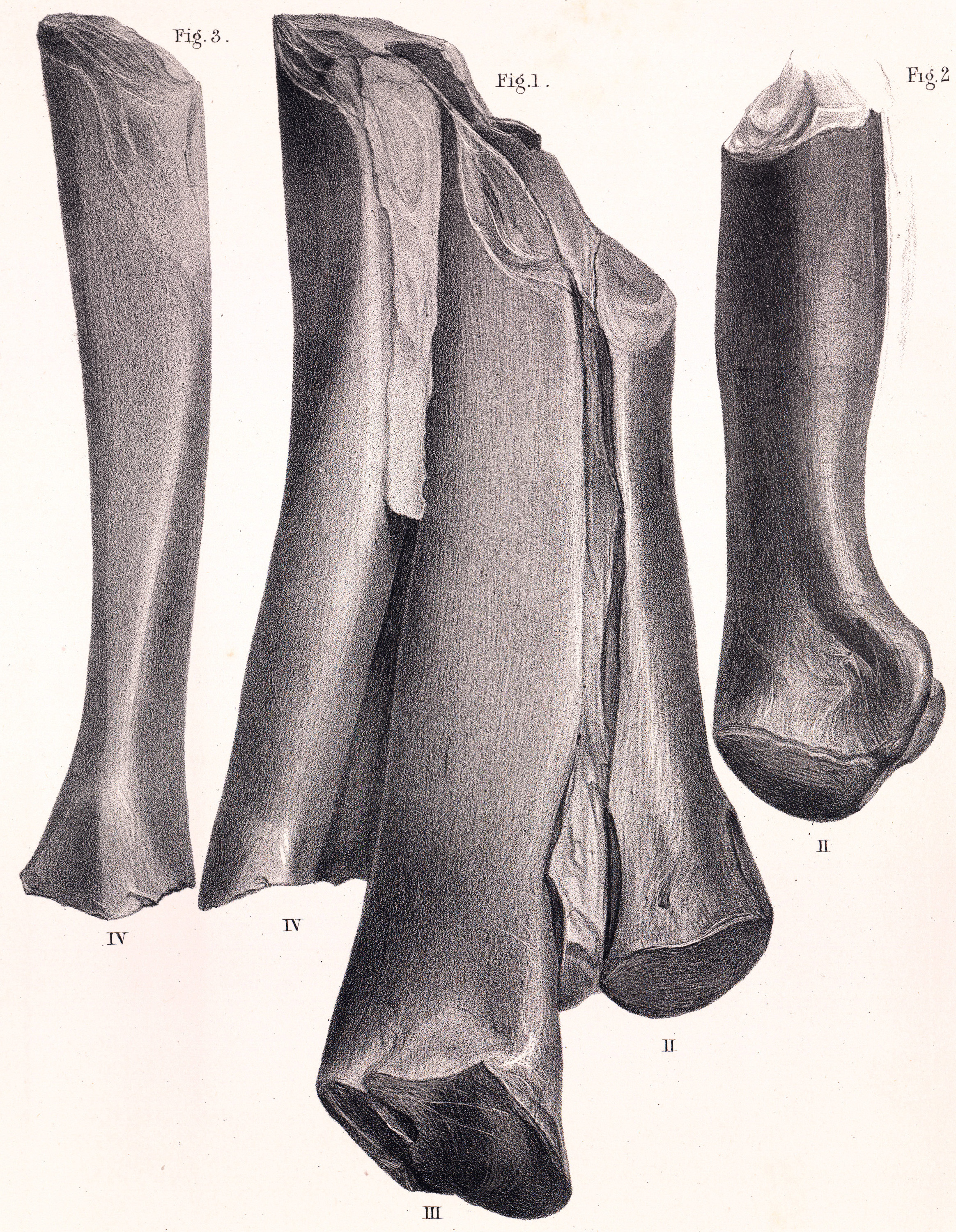
Thecospondylus
''Thecospondylus'' (THEEK-o-SPON-di-lus, "sheath vertebra") is a dubious genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of England. Scientists are unsure as to whether ''Thecospondylus'' was a saurischian or an ornithischian. History Dr. A.C. Horner, an amateur geologist living at Tonbridge, in the nineteenth century acquired a fossil found in the quarry of Southborough. He sent it to paleontologist Harry Govier Seeley who in 1882 described and named it as the type species ''Thecospondylus horneri''. The genus name is derived from Greek ''theke'' meaning 'sheath' and ''spondylos'' meaning 'vertebra', a reference to the "extremely thin" bone forming the vertebrae. The specific name honours Horner. The holotype, BMNH R.291, was found in a layer of the Hastings Sand, sandstone dating from the Valanginian - Hauterivian. It consist of an elongated natural internal cast or endocast of the neural canal of the sacrum, about sixty centimetres long. It shows the divisions of at least fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviraptosaur
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like skulls, with or without bony crests atop the head. They ranged in size from '' Caudipteryx'', which was the size of a turkey, to the 8-meter-long, 1.4-ton ''Gigantoraptor''. The group (along with all maniraptoran dinosaurs) is close to the ancestry of birds. Some researchers such as Maryanska ''et al'' (2002) and Osmólska ''et al.'' (2004) have proposed that they may represent primitive flightless birds.Osmólska, Halszka, Currie, Philip J., Brasbold, Rinchen (2004) "The Dinosauria" Weishampel, Dodson, Osmólska. "Chapter 8 Oviraptorosauria" University of California Press. The most complete oviraptorosaur specimens have been found in Asia. The North American oviraptorosaur record is sparse.Varricchio, D. J. 2001. Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Theropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1923 In Paleontology
Arthropoda newly named insects Archosauromorpha Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology 1920s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurus
''Coelurus'' ( ) is a genus of coelurosaurian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period (mid-late Kimmeridgian faunal stage, 155–152 million years ago). The name means "hollow tail", referring to its hollow tail vertebrae (Greek κοῖλος, ''koilos'' = hollow + οὐρά, ''oura'' = tail). Although its name is linked to one of the main divisions of theropods (Coelurosauria), it has historically been poorly understood, and sometimes confused with its better-known contemporary ''Ornitholestes''. Like many dinosaurs studied in the early years of paleontology, it has had a confusing taxonomic history, with several species being named and later transferred to other genera or abandoned. Only one species is currently recognized as valid: the type species, ''C. fragilis'', described by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1879. It is known from one partial skeleton found in the Morrison Formation of Wyoming, United States. It was a small bipedal carnivore with elongate legs. Description ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valdoraptor
''Valdoraptor'' (meaning "Wealden plunderer") is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. Its fossils were found in England. It is known only from bones of the feet. The holotype, BMNH R2559 (incorrectly given by Owen as BMNH R2556), was found near Cuckfield in layers of the Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation dating from the late Valanginian. The specimen is damaged lacking parts of the upper and lower ends. It has a conserved length of and an estimated length of . This genus is paleontologically significant for being the first ornithomimosaur specimen known from England and represents the earliest record of ornithomimosaurs. Discovery In 1858 Richard Owen referred a fossil consisting of a set of three metatarsals, foot bones, part of the collection of the British Museum of Natural History, to the herbivorous dinosaur genus ''Hylaeosaurus'' because of its size and bone texture. Owen had a lithograph made of the bones that gave a mirrored image: although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therizinosaur
Therizinosaurs (once called segnosaurs) were large herbivorous Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs whose fossils have been found across the Early Cretaceous, Early to Late Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Various features of the forelimbs, skull and pelvis unite these finds as both theropods and maniraptorans, close relatives to birds. The name of the representative genus, ''Therizinosaurus'', is derived from the Ancient Greek , Greek (, 'to reap' or 'scythe')Translated paper and (, 'lizard'). The older representative, ''Segnosaurus'', is derived from the Latin ('slow') and the Greek . History of research [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum Of Natural History
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus'' cast that domin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Darwin Fox
The Reverend William Darwin Fox (23 April 1805 – 8 April 1880) was an English clergyman, naturalist, and a second cousin of Charles Darwin. Early life Fox was born in 1805 and initially raised at Thurleston Grange near Elvaston, Derbyshire and from 1814 at Osmaston Hall, Osmaston about 2.5 miles (4 km) south of Derby. Fox was the son of Samuel Fox (1765–1851) and his second wife, Ann Darwin (1777–1859). Ann was the daughter of William Alvey Darwin (1726–1783) and Jane Brown (1746–1835), and niece of Erasmus Darwin (1731–1802). Fox attended Repton School from 1816 to 1823, when the headmaster was William Boultbee Sleath. Like his second cousin Charles Darwin, Fox prepared for the church at Christ's College, Cambridge. He was also a naturalist and entomologist, particularly collecting butterflies Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the Order (biology), order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of Wight has resorts that have been popular holiday destinations since Victorian times. It is known for its mild climate, coastal scenery, and verdant landscape of fields, downland and chines. The island is historically part of Hampshire, and is designated a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. The island has been home to the poets Algernon Charles Swinburne and Alfred, Lord Tennyson. Queen Victoria built her summer residence and final home, Osborne House at East Cowes, on the Isle. It has a maritime and industrial tradition of boat-building, sail-making, the manufacture of flying boats, hovercraft, and Britain's space rockets. The island hosts annual music festivals, including the Isle of Wight Festival, which in 1970 was the largest rock music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |