|
The Songs Of Distant Earth
''The Songs of Distant Earth'' is a 1986 science fiction novel by British writer Arthur C. Clarke, based upon his 1958 short story of the same title. He stated that it was his favourite of all his novels. Clarke also wrote a short step outline with the same title, published in ''Omni'' magazine and anthologized in '' The Sentinel'' in 1983. The novel tells of a utopian human colony in the far future that is visited by travellers from a doomed Earth, as the Sun has gone nova.'' The Songs of Distant Earth'' explores apocalyptic, atheistic, and utopian ideas, as well as the effects of long-term interstellar travel and extra-terrestrial life. Plot summary The novel is set in the early 3800s and takes place almost entirely on the faraway oceanic planet of Thalassa. Thalassa has a small human population sent there by way of an embryonic seed pod, one of many sent out from Earth in an attempt to continue the human race before the Earth was destroyed. The story begins w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mike Oldfield
Mike may refer to: Animals * Mike (cat), cat and guardian of the British Museum * Mike the Headless Chicken, chicken that lived for 18 months after his head had been cut off * Mike (chimpanzee), a chimpanzee featured in several books and documentaries Arts * Mike (miniseries), a 2022 Hulu limited series based on the life of American boxer Mike Tyson * Mike (2022 film), a Malayalam film produced by John Abraham * ''Mike'' (album), an album by Mike Mohede * ''Mike'' (1926 film), an American film * MIKE (musician), American rapper, songwriter and record * ''Mike'' (novel), a 1909 novel by P. G. Wodehouse * "Mike" (song), by Elvana Gjata and Ledri Vula featuring John Shahu * Mike (''Twin Peaks''), a character from ''Twin Peaks'' * "Mike", a song by Xiu Xiu from their 2004 album ''Fabulous Muscles'' Businesses * Mike (cellular network), a defunct Canadian cellular network * Mike and Ike, a candies brand Military * MIKE Force, a unit in the Vietnam War * Ivy Mike, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheistic
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no deities. Atheism is contrasted with theism, which in its most general form is the belief that at least one deity exists. The first individuals to identify themselves as atheists lived in the 18th century during the Age of Enlightenment. The French Revolution, noted for its "unprecedented atheism", witnessed the first significant political movement in history to advocate for the supremacy of human reason.Extract of page 22 In 1967, Albania declared itself the first official atheist coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mores
Mores (, sometimes ; , plural form of singular , meaning "manner, custom, usage, or habit") are social norms that are widely observed within a particular society or culture. Mores determine what is considered morally acceptable or unacceptable within any given culture. A folkway is what is created through interaction and that process is what organizes interactions through routine, repetition, habit and consistency. William Graham Sumner (1840–1910), an early United States of America, U.S. sociologist, introduced both the terms "mores" (1898) and "folkways" (1906) into modern sociology. Mores are strict in the sense that they determine the difference between right and wrong in a given society, people may be punished for their immorality which is common place in many societies in the world, at times with disapproval or ostracizing. The main examples of traditional customs and conventions that are mores may include; lying, cheating, harm, causing harm, sobriety, alcohol use, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan (; ; November 9, 1934December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, planetary scientist, cosmologist, astrophysicist, astrobiologist, author, and science communicator. His best known scientific contribution is research on extraterrestrial life, including experimental demonstration of the production of amino acids from basic chemicals by radiation. Sagan assembled the first physical messages sent into space, the Pioneer plaque and the Voyager Golden Record, universal messages that could potentially be understood by any extraterrestrial intelligence that might find them. Sagan argued the hypothesis, accepted since, that the high surface temperatures of Venus can be attributed to, and calculated using, the greenhouse effect.Extract of page 14 Initially an assistant professor at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procrastinate
Procrastination is the action of unnecessarily and voluntarily delaying or postponing something despite knowing that there will be negative consequences for doing so. The word has originated from the Latin word ''procrastinatus'', which itself evolved from the prefix ''pro-'', meaning "forward," and ''crastinus'', meaning "of tomorrow." Oftentimes, it is a habitual human behaviour. It is a common human experience involving delay in everyday chores or even putting off salient tasks such as attending an appointment, submitting a job report or academic assignment, or broaching a stressful issue with a partner. Although typically perceived as a negative trait due to its hindering effect on one's productivity often associated with depression, low self-esteem, guilt and inadequacy, it can also be considered a wise response to certain demands that could present risky or negative outcomes or require waiting for new information to arrive. From a cultural and a social perspective, stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean World
An ocean world, ocean planet, panthalassic planet, maritime world, water world or aquaplanet, is a type of planet that contains a substantial amount of water in form of oceans, either beneath the surface, as subsurface oceans, or on the surface with a hydrosphere, potentially submerging all dry land. The term ''ocean world'' is also used sometimes for astronomical bodies with an ocean composed of a different fluid or thalassogen, such as lava (the case of Io), ammonia (in a eutectic mixture with water, as is likely the case of Titan's inner ocean) or hydrocarbons like on Titan's surface (which could be the most abundant kind of exosea). Earth is the only astronomical object known to have bodies of liquid water on its surface, although several exoplanets have been found with the right conditions to support liquid water. For exoplanets, current technology cannot directly observe liquid surface water, so atmospheric water vapor may be used as a proxy. The characteristics of oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
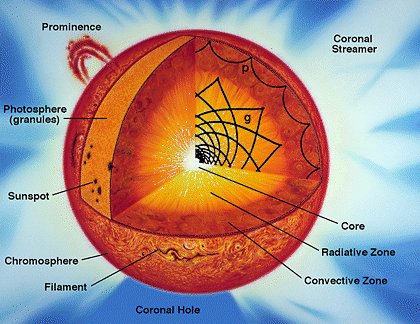
Solar Neutrino Problem
The solar neutrino problem concerned a large discrepancy between the flux of solar neutrinos as predicted from the Sun's luminosity and as measured directly. The discrepancy was first observed in the mid-1960s and was resolved around 2002. The flux of neutrinos at Earth is several tens of billions per square centimetre per second, mostly from the Sun's core. They are nevertheless hard to detect, because they interact very weakly with matter, traversing the whole Earth. Of the three types ( flavors) of neutrinos known in the Standard Model of particle physics, the Sun produces only electron neutrinos. When neutrino detectors became sensitive enough to measure the flow of electron neutrinos from the Sun, the number detected was much lower than predicted. In various experiments, the number deficit was between one half and two thirds. Particle physicists knew that a mechanism, discussed back in 1957 by Bruno Pontecorvo, could explain the deficit in electron neutrinos. However, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Emissions From The Sun
A solar neutrino is a neutrino originating from nuclear fusion in the Sun's core, and is the most common type of neutrino passing through any source observed on Earth at any particular moment. Neutrinos are elementary particles with extremely small rest mass and a neutral electric charge. They only interact with matter via the weak interaction and gravity, making their detection very difficult. This has led to the now-resolved solar neutrino problem. Much is now known about solar neutrinos, but the research in this field is ongoing. History and background Homestake experiment The timeline of solar neutrinos and their discovery dates back to the 1960s, beginning with the two astrophysicists John N. Bahcall and Raymond Davis Jr. The experiment, known as the Homestake experiment, named after the town in which it was conducted (Homestake, South Dakota), aimed to count the solar neutrinos arriving at Earth. Bahcall, using a solar model he developed, came to the conclusion that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryonic Suspension
Cryonics (from el, κρύος ''kryos'' meaning 'cold') is the low-temperature freezing (usually at ) and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future. Cryonics is regarded with skepticism within the mainstream scientific community. It is generally viewed as a pseudoscience, and its practice has been characterized as quackery. Cryonics procedures can begin only after the "patients" are clinically and legally dead. Cryonics procedures may begin within minutes of death, and use cryoprotectants to prevent ice formation during cryopreservation. It is, however, not possible for a corpse to be reanimated after undergoing vitrification, as this causes damage to the brain including its neural circuits. The first corpse to be frozen was that of James Bedford in 1967. As of 2014, about 250 dead bodies had been cryopreserved in the United States, and 1,500 people had made arrangements for cryopreservation of their corpses. Critics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo Space Colonization
Embryo space colonization is a theoretical interstellar space colonization concept that involves sending a robotic mission to a habitable terrestrial planet, dwarf planet, minor planet or natural satellite transporting frozen early-stage human embryos or the technological or biological means to create human embryos. The proposal circumvents the most severe technological problems of other mainstream interstellar colonization concepts. In contrast to the sleeper ship proposal, it does not require the more technically challenging 'freezing' of fully developed humans (see ''cryonics)''. Various concepts Embryo space colonization concepts involve various concepts of delivering the embryos from Earth to an extrasolar planet around another star system. * The most straightforward concept is to make use of embryo cryopreservation. Modern medicine has made it possible to store frozen embryos in various low-development stages (up to several weeks into the development of the embryo). * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |