|
The New Female Coterie
The New Female Coterie was an 18th-century London social club. The exact founding date is unknown, though it is assumed to be circa 1770, when Caroline Stanhope, Countess of Harrington was blackballed from joining the Female Coterie, a club for aristocrats, though its name was probably derived from the press. The New Female Coterie became a social outlet for "demi-reps", a word Henry Fielding coined in 1749 in his nove''l Tom Jones'' to refer to a woman ‘who intrigues with every Man she likes, under the Name and Appearance of Virtue’. The members came to include high-status women who had been publicly shamed for promiscuity or adultery, such as Henrietta Grosvenor, Seymour Dorothy Fleming, Penelope Ligonier Penelope Ligonier, née Penelope Pitt (1749–1827), was an English aristocrat and socialite, and first wife of Edward Ligonier, Earl Ligonier of Clonmell. She was the eldest daughter of Penelope Atkins () and George Pitt, 1st Baron Rivers. Bo ..., Lady Margaret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century London
The 18th century was a period of rapid growth for London, reflecting an increasing national population, the early stirrings of the Industrial Revolution, and London's role at the centre of the evolving British Empire. By the end of the century nearly one million people lived in London, about one tenth of the population of Great Britain. By 1715, London's population reached an estimated 630,000 people, roughly equaling that of Europe's largest city until that time, Paris. Within a few years London itself was the largest city in Europe, reaching 750,000 people by 1760 and 1 million by the end of the century. The average height of a male Londoner was 5'7¼" (171cm) and the average height of a female Londoner was 5'1¾" (157cm). Extent and population London's growth in the 18th century was marked above all by the westward shift of the population away from the City of London. Westminster was intensively developed, with new districts like Mayfair housing Britain's wealthiest aristo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Club
A social club may be a group of people or the place where they meet, generally formed around a common interest, occupation, or activity. Examples include: book discussion clubs, chess clubs, anime clubs, country clubs, charity work, criminal headquarters (e.g., the Cage Documentary featuring the work of ex-New Jersey State Trooper Mike Russell, whose undercover work for the New Jersey State Police led to the arrests of 41 members of the Genovese crime family, and of corrupt prison officials, and a state senator or the Ravenite Social Club), final club, fishing club, gaming club, gentlemen's clubs (known as private clubs in the US), hunting clubs, military officers' clubs, political clubs, science clubs, university clubs, Christian fellowships and other religious clubs. This article covers only three distinct types of social clubs: the historic gentlemen's clubs, the modern activities clubs, and an introduction to fraternities and sororities. This article does not cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroline Stanhope, Countess Of Harrington
Caroline Stanhope, Countess of Harrington (née Lady Caroline FitzRoy; 8 April 1722 – 26 June 1784) was a British socialite and ''demimondaine''. After being blackballed by the English social group The Female Coterie, she founded The New Female Coterie, a social club of courtesans and " fallen women" that met in a brothel. Known for her infidelity and bisexuality, she was nicknamed the "Stable Yard Messalina" due to her adulterous lifestyle. Her "colourful" life is often contrasted with that of her daughter-in-law, Jane Stanhope, Countess of Harrington, who was viewed as a respectable member of British high society. Family Lady Caroline was born on 8 April 1722, the fifth child of Charles FitzRoy, 2nd Duke of Grafton and Lady Henrietta Somerset, the daughter of Charles Somerset, Marquess of Worcester. Lady Caroline married William Stanhope, 2nd Earl of Harrington on 11 August 1746. Together they had seven children, including Isabella Molyneux, Countess of Sefton and Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackballing
Blackballing is a rejection in a traditional form of secret ballot, where a white ball or ballot constitutes a vote in support and a black ball signifies opposition. The system is typically used where an organization's rules provide that one or two objections, rather than an at-least-50% share of votes, are sufficient to defeat a proposition. Since the seventeenth century, these rules have commonly applied to elections to membership of many gentlemen's clubs and similar institutions such as Masonic lodges and fraternities. A large supply of black and white balls is provided for voters. Each voter audibly casts a single ball into the ballot box under cover of the box, or of a combination of a cloth and the box itself, so that observers can see who votes but not how they are voting. When all voting is complete, the box is opened and the balls displayed: all present can immediately see the result, without any means of knowing which members are objecting. Process The principle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Female Coterie
The Female Coterie was the title given to a group of "ladies of quality" in 18th century London. Horace Walpole described their activities as meeting every morning "either to play cards, chat or do whatever else they please". Dinner and supper were provided, followed by the card game loo. The founding members were Mrs Fitzroy, Lady Pembroke, Mrs Meynell, Lady Molyneux, Miss Pelham and Miss Lloyd. History The society was founded in 1769 by William Almack, already proprietor of the clubs later to become Boodle's and Brooks's, then based at his houses in Nos. 49 and 50 Pall Mall, and of the famous Assembly Rooms on King Street. The society first met on 17 December 1769 and soon attracted a great deal of attention. On 6 May 1770 Horace Walpole recorded that: : "There is a new institution that begins to make, and if it proceeds, will make a considerable noise. It is a club of both sexes to be erected at Almack's, on the model of that of the men of White's...I am ashamed to sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
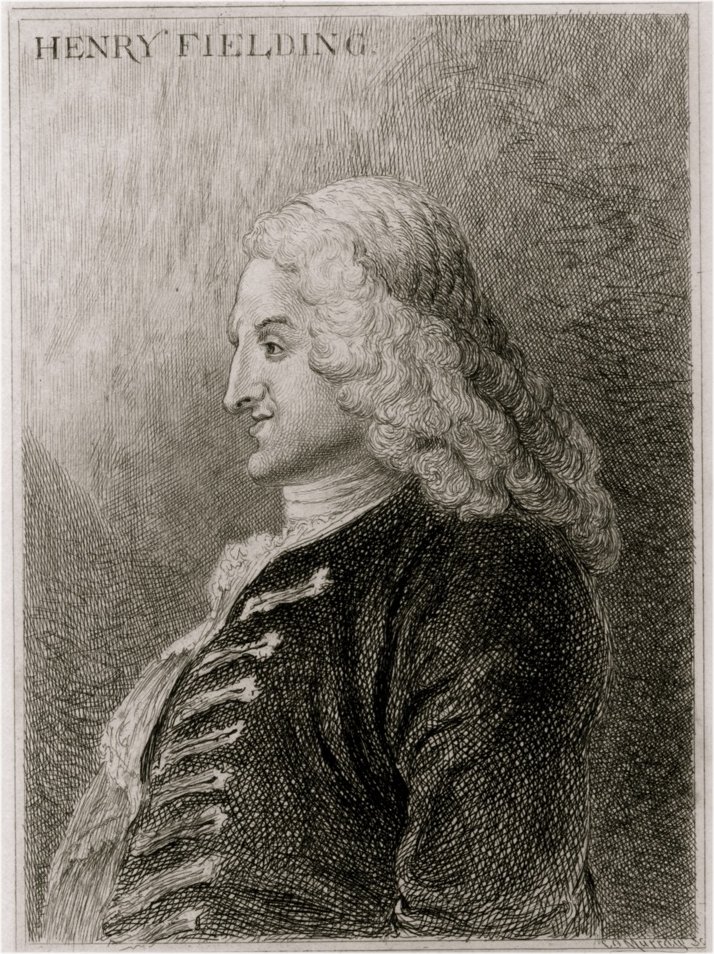
Henry Fielding
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English novelist, irony writer, and dramatist known for earthy humour and satire. His comic novel '' Tom Jones'' is still widely appreciated. He and Samuel Richardson are seen as founders of the traditional English novel. He also holds a place in the history of law enforcement, having used his authority as a magistrate to found the Bow Street Runners, London's first intermittently funded, full-time police force. Early life Fielding was born 22 April 1707 at Sharpham, Somerset, and educated at Eton College, where he began a lifelong friendship with William Pitt the Elder. His mother died when he was 11. A suit for custody was brought by his grandmother against his charming but irresponsible father, Lt Gen. Edmund Fielding. The settlement placed Henry in his grandmother's care, but he continued to see his father in London. In 1725, Henry tried to abduct his cousin Sarah Andrews (with whom he was infatuated) while she was on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The History Of Tom Jones, A Foundling
''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'', often known simply as ''Tom Jones'', is a comic novel by English playwright and novelist Henry Fielding. It is a ''Bildungsroman'' and a picaresque novel. It was first published on 28 February 1749 in London and is among the earliest English works to be classified as a novel. It is the earliest novel mentioned by W. Somerset Maugham in his 1948 book '' Great Novelists and Their Novels'' among the ten best novels of the world. The novel is highly organised despite its length. Samuel Taylor Coleridge argued that it has one of the "three most perfect plots ever planned", alongside ''Oedipus Tyrannus'' and ''The Alchemist''. It became a best seller with four editions published in its first year alone. It is generally regarded as Fielding's greatest book and as an influential English novel. Plot The novel's events occupy eighteen books. It opens with the narrator stating that the purpose of the novel will be to explore "human nature". The k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrietta, Lady Grosvenor
Henrietta de Hochepied, Baroness de Hochepied (née Vernon; formerly Baroness Grosvenor) – 1828) was an English aristocrat, socialite, and courtesan. Early life She was one of four daughters born to Lady Henrietta ( née Wentworth) Vernon (third daughter of Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford) and Henry Vernon of Hilton Hall, former Member of Parliament for Lichfield and Newcastle-under-Lyme. New Female Coterie After her separation from the Baron Grosvenor (who was made Earl Grosvenor in 1784), Henrietta lived in Paris and London in the subsequent years, with the emotional and financial support of several men, and the press continued to report on her lovers and her appearances at social occasions for decades. She was a member of the social club for the 'demi-reps' nicknamed the New Female Coterie by the English press, whose members comprised fellow elite women publicly shamed for infidelity such as Caroline Stanhope, Countess of Harrington and Seymour Fleming. Janine Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymour Fleming
Seymour Dorothy Fleming (5 October 1758 – 9 September 1818), styled Lady Worsley from 1775 to 1805, was a member of the British gentry, notable for her involvement in a high-profile criminal conversation trial. Early life and family Fleming was the younger daughter and coheir of the Irish-born Sir John Fleming, 1st Baronet (d. 1763), of Brompton Park (aka Hale House, Cromwell House), Middlesex, and his wife, Jane Coleman (d. 1811). She was probably named after her maternal grandmother, Jane Seymour, a daughter of Sir Edward Seymour, 5th Baronet. Her father and two of her sisters died when she was five, and she and her surviving sister were then brought up by their mother, who remarried in 1770 to Edwin Lascelles, 1st Baron Harewood, a rich sexagenarian whose wealth derived from sugar plantations in the West Indies. Her elder sister, Jane Stanhope, Countess of Harrington, was noted for being an "epitome of virtue". Marriage to Worsley On 20 September 1775, at the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penelope Ligonier
Penelope Ligonier, née Penelope Pitt (1749–1827), was an English aristocrat and socialite, and first wife of Edward Ligonier, Earl Ligonier of Clonmell. She was the eldest daughter of Penelope Atkins () and George Pitt, 1st Baron Rivers. Both her parents were 'noted for their extraordinary physical beauty', but their family life was unhappy due to her parents' turbulent marriage. Horace Walpole, an admirer of Penelope Atkins, alleged that George Pitt 'had heaped on her every possible cruelty and provoking outrage', and alleged that after their separation he prevented her from seeing their four children. During the 1760s, while George Pitt was serving as envoy-extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary to Turin, Penelope was enrolled in a convent school in Lyon, where she met Edward Ligonier. They were married at the British Embassy in Paris on 16 December 1766. When they relocated to Cobham Park after their marriage they continued to entertain an international circle of fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1770 Establishments In England
Year 177 ( CLXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Commodus and Plautius (or, less frequently, year 930 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 177 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Lucius Aurelius Commodus Caesar (age 15) and Marcus Peducaeus Plautius Quintillus become Roman Consuls. * Commodus is given the title ''Augustus'', and is made co-emperor, with the same status as his father, Marcus Aurelius. * A systematic persecution of Christians begins in Rome; the followers take refuge in the catacombs. * The churches in southern Gaul are destroyed after a crowd accuses the local Christians of practicing cannibalism. * Forty-seven Christians are martyred in Lyon (Saint Blandina and Pothinus, bishop o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Era
The Georgian era was a period in British history from 1714 to , named after the Hanoverian Kings George I, George II, George III and George IV. The definition of the Georgian era is often extended to include the relatively short reign of William IV, which ended with his death in 1837. The subperiod that is the Regency era is defined by the regency of George IV as Prince of Wales during the illness of his father George III. The transition to the Victorian era was characterized in religion, social values, and the arts by a shift in tone away from rationalism and toward romanticism and mysticism. The term ''Georgian'' is typically used in the contexts of social and political history and architecture. The term ''Augustan literature'' is often used for Augustan drama, Augustan poetry and Augustan prose in the period 1700–1740s. The term ''Augustan'' refers to the acknowledgement of the influence of Latin literature from the ancient Roman Republic. The term ''Georgian era'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)