|
The Mughal Harem
''The Mughal Harem'' is a book by historian K.S. Lal published in 1988 about the Mughal Harem. Scholars perceive the work as communal propaganda, intended to exoticize the harem. Contents Based on contemporary sources, Lal studies queens, princesses, dancing girls, and slaves who belonged to Mughal harem from 15th to 18th century. The political roles of Nur Jahan, Jahanara and Roshanara are described in detail. Reception A. Jan Qaiser of Aligarh Muslim University was very dismissive of the book. Ruby Lal noted Lal's work to be one of the few academic accounts on the topic but laden with oriental tropes of sexuality and seclusion. Karuna Sharma shared Ruby Lal's concerns; K. S. Lal's was the first comprehensive study of the subject but it exoticized the Harem and failed to account for members, who did not have any sexual role. Gianna Carotenuto found the work to be laced with "salacious tales and the sexy exploits of mythic heroes and heroines"; Lal's approach was intended t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Harem
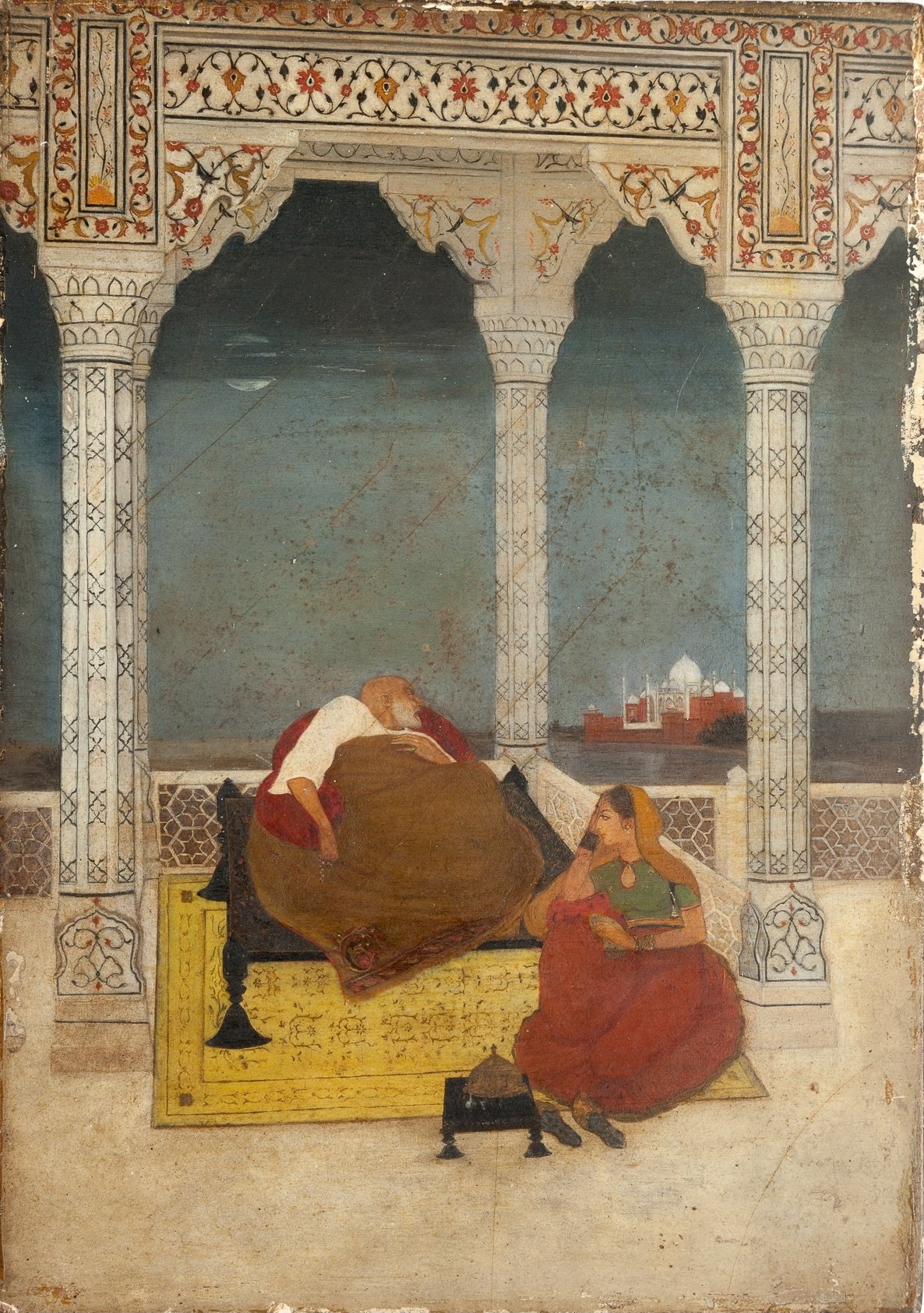
The Mughal Harem was the harem of Mughal emperors of the Indian subcontinent. The term originated with the Near East, meaning a "forbidden place; sacrosanct, sanctum", and etymologically related to the Arabic ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; female members of the family" and ''ḥarām'', "forbidden; sacred". It has the same meaning as the Turkish word ''seraglio'' and the Persian word ''zenana''. It is also similar to the Sanskrit word anthapura, meaning ‘the inner apartment’ of the household. It came to mean the sphere of women in what was usually a polygynous household and their segregated quarters which were forbidden to men. The Harem, being a forbidden place, was constant topic of speculation and curiosity. It was a vibrant and a big physical space where women were arranged in regard to their proximity to the Emperor. History The women Harems were composed of wives and female relatives of the Mughals. Most women usually entered the Harem through marriage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nur Jahan
Nur Jahan, born Mehr-un-Nissa P ersian: نورجهان (; – 18 December 1645) was the wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Jahangir from 1620 until his death in 1627. Nur Jahan was born Mehr-un-Nissa, as the daughter of a Mirza Ghiyas Beg, who served under Jahangir's father, Emperor Akbar. Nur Jahan was the most powerful empress in the Mughal Empire. More decisive and proactive than her husband, she is considered by historians to have been the real power behind the throne for more than a decade. Nur Jahan was granted certain honours and privileges which were never enjoyed by any Mughal empress before or after like having coinage struck in her name. Jahangir's addiction to alcohol and opium made it easier for Nur Jahan to exert her influence over him and exercise power. She was granted the privilege to issue farmāns (sovereign mandates). The only other empress to command such devotion from her husband was Mumtaz Mahal, for whom the Taj Mahal was built by Emperor Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahanara Begum
Jahanara Begum (23 March 1614 – 16 September 1681) was a Mughal princess and later the Padshah Begum of the Mughal Empire from 1631 to 1658 and again from 1668 until her death. She was the second and the eldest surviving child of Emperor Shah Jahan and Mumtaz Mahal. After Mumtaz Mahal's untimely death in 1631, the 17-year-old Jahanara was entrusted with the charge of the royal seal and conferred the title of ''Padshah Begum'' (First lady) of the Mughal Empire, despite the fact that her father had three surviving wives. She was Shah Jahan's favourite daughter, wielded major political influence during her father's reign, and has been described as "the most powerful woman in the empire" at the time. Jahanara was an ardent partisan of her brother, Dara Shikoh, and supported him as her father's chosen successor. During the war of succession which took place after Shah Jahan's illness in 1657, Jahanara sided with the heir-apparent Dara and ultimately joined her father in Agra Fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roshanara Begum
Roshanara Begum ( fa, , lit=Adorned in Light); 3 September 1617 – 11 September 1671) was a Mughal princess and the third daughter of Emperor Shah Jahan and his wife, Mumtaz Mahal. Roshanara was a brilliant woman and a talented poet. She was a partisan of her younger brother, Aurangzeb, and supported him during the war of succession which took place after Shah Jahan's illness in 1657. After Aurangzeb's accession to the throne in 1658, Roshanara was given the title of Padshah Begum by her brother and became the First Lady of the Mughal Empire, when she became a powerful political figure. Today, however, Roshanara is best known for the Roshanara Bagh, a pleasure garden located in present-day north Delhi. The present-day Roshanara Club which was constructed in the late 19th century by the British is a country club that was actually originally a part of the Roshanara Bagh. Family Of Roshanara's four brothers, the eldest, Dara Shikoh, was Shah Jahan's favourite son and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
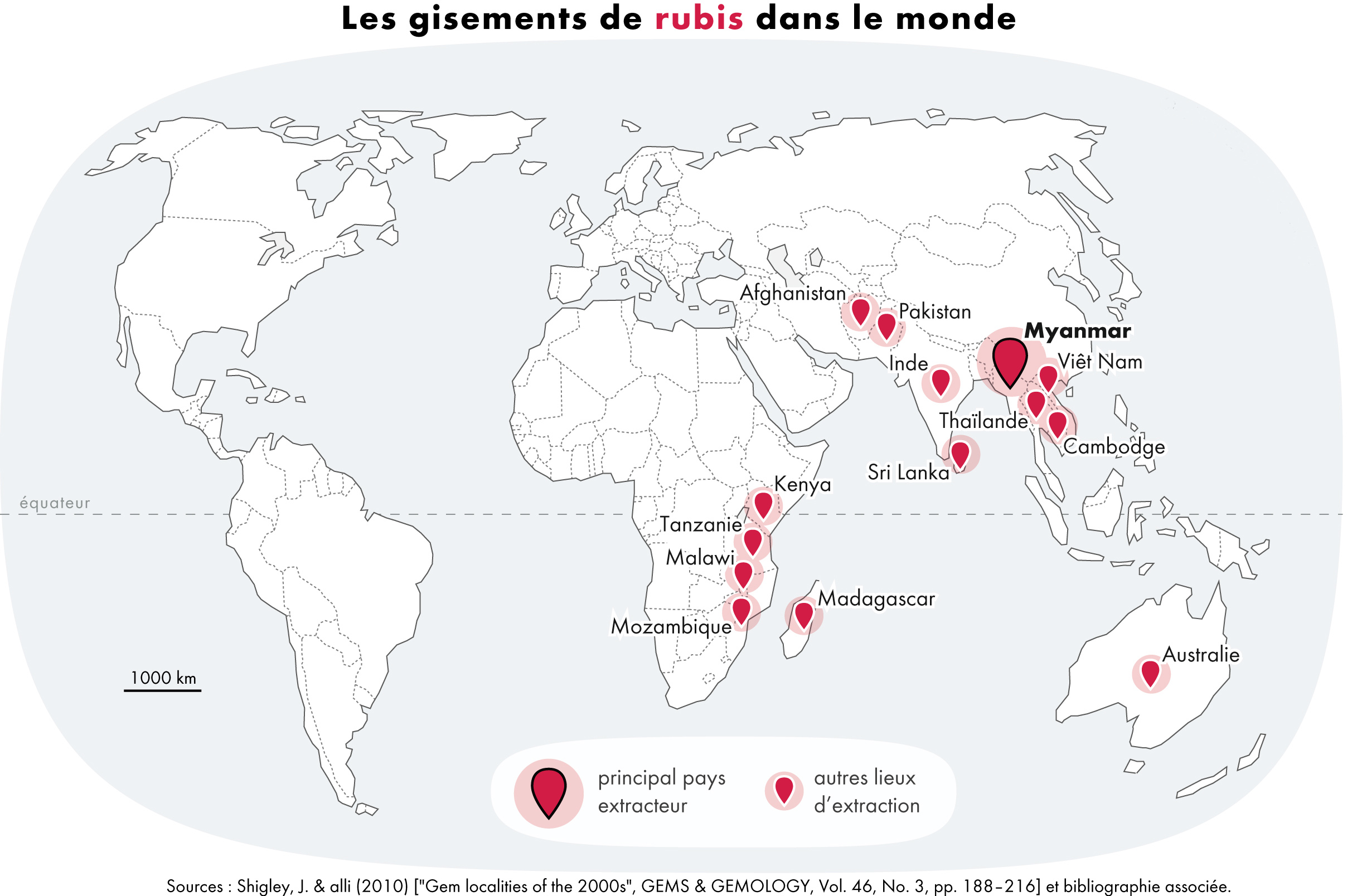
Ruby Lal
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indrani Chatterjee
Indrani Chatterjee is an Indian-American historian, academic, and author. She is the John L. Nau III Distinguished Professor of the History and Principles of Democracy at the University of Virginia. She is known for writing about underexplored themes in South Asia’s past —including slavery, the household, and monasticism. Chatterjee is the author and editor of four books, ''Gender, Slavery and Law in Colonial India'', ''Unfamiliar Relations: Family and History in South Asia'', ''Slavery and South Asian History'', and ''Forgotten Friends: Monks, Marriages, and Memories of Northeast India''. Education Chatterjee studied at Delhi University, and received her Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in History at St. Stephen's College of the University of Delhi in 1982 and 1984, respectively. She earned an M. Phil. Degree in History at Jawaharlal Nehru University in 1987. She earned her Ph.D. in History at the University of London in 1996. Her doctoral dissertation was titled "Slavery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communalism (South Asia)
Communalism is a term used to denote attempts to construct religious or ethnic identity, incite strife between people identified as different communities, and to stimulate communal violence between those groups. It derives from history, differences in beliefs, and tensions between the communities. Communalism is a significant social issue in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Communal conflicts between religious communities in India, especially Hindus and Muslims have occurred since the period of British colonial rule, occasionally leading to serious inter-communal violence. The term communalism was coined by the British colonial government as it wrestled to manage Hindu-Muslim riots and other violence between religious, ethnic and disparate groups in its colonies, particularly in British West Africa and the Cape Colony, in early 20th century. Communalism is not unique to South Asia. It is found in Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Australia. History The term ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbans Mukhia
Harbans Mukhia (born 1939) is an Indian historian whose principal area of study is medieval India. Biography He received his Bachelors in Arts (BA) in history in 1958 from Kirori Mal College, Delhi University and then earned his doctorate from Department of History, Delhi University in 1969. Mukhia worked at Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), New Delhi as Professor of Medieval History at the Centre for Historical Studies. He was rector of JNU from 1999 to 2002 and retired in February 2004.. Honors and awards * Fellowship of the Indian Institute of Advanced Study, Simla (1971) * Homi Bhabha Fellowship (1979–1981) * Directeur d’Étude Associé, EHESS, Paris, 1980-2003 (a month every year)1980-2003. * UGC National Lecturer (1985–1986) * UGC National Fellow (1991–1993) * Visiting Professor, The British Academy, London, February–March, 1993. * Senior Visiting Fellow, International Institute for Asian Studies, Leiden (1997) * Fellow, IDPAD, University of Amsterdam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulletin Of The School Of Oriental & African Studies
The ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', founded in 1917 (one year after the foundation of the School) as ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies,'' is an interdisciplinary journal of Asian and African studies, published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the School of Oriental and African Studies. The first editor was also the first director of the School, Edward Denison Ross. The name changed in 1940 as a consequence of the change in the School's name (changed 1938) to incorporate African Studies. Later editors have included Dennis Twitchett (1964–68) and Robert Mayer and its current editors are Ayman Shihadeh and Nathan W. Hill Nathan Wayne Hill (born July 8, 1979) is an American historical linguist and Tibetologist specializing in languages of the Sino-Tibetan family, in particular Tibetic languages. He is Sam Lam Professor in Chinese Studies and director of the Trin .... References * * Area studies journals Publications establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1988 Non-fiction Books
File:1988 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The oil platform Piper Alpha explodes and collapses in the North Sea, killing 165 workers; The USS Vincennes (CG-49) mistakenly shoots down Iran Air Flight 655; Australia celebrates its Australian Bicentenary, Bicentennial on January 26; The 1988 Summer Olympics are held in Seoul, South Korea; Soviet Union, Soviet troops begin their Soviet-Afghan War, withdrawal from Afghanistan, which is completed the 1989, next year; The 1988 Armenian earthquake kills between 25,000-50,000 people; The 8888 Uprising in Myanmar, led by students, protests the Burma Socialist Programme Party; A bomb explodes on Pan Am Flight 103, causing the plane to crash down on the town of Lockerbie, Scotland- the event kills 270 people., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Piper Alpha rect 200 0 400 200 Iran Air Flight 655 rect 400 0 600 200 Australian Bicentenary rect 0 200 300 400 Pan Am Flight 103 rect 300 200 600 400 1988 Summer Olympics rect 0 400 200 600 8888 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |