|
The Enemy Stars
''The Enemy Stars'', is a science fiction novel by American writer Poul Anderson, published in 1959 by J.B Lippincott in the US and by Longmans in Canada. Originally published in ''Astounding Science Fiction'' under the title ''We Have Fed Our Sea__'', it was a nominee for the 1959 Hugo Award for Best Novel. The original title refers to a line in a poem by Rudyard Kipling. Premise In the scientific speculation that underlies the story, humanity has reached out to the stars in ships that move at half the speed of light. At that speed the ships will take years, decades, even centuries to reach their destinations. And yet the ships' crews serve month-long tours of duty, teleporting to and from their bases on Earth and other worlds instantaneously through what Anderson calls a mattercaster. At the end of Chapter 5 Anderson provides a description of how a mattercaster works. In 1967, Gerald Feinberg hypothesized the existence of tachyons as particles represented by the imaginary sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poul Anderson
Poul William Anderson (November 25, 1926 – July 31, 2001) was an American fantasy and science fiction author who was active from the 1940s until the 21st century. Anderson wrote also historical novels. His awards include seven Hugo Awards and three Nebula Awards. Biography Poul Anderson was born on November 25, 1926, in Bristol, Pennsylvania to Scandinavian parents. Soon after his birth, his father, Anton Anderson relocated the family to Texas, where they lived for more than ten years. After Anton Anderson's death, his widow took the children to Denmark. The family returned to the United States after the beginning of World War II, settling eventually on a Minnesota farm. While he was an undergraduate student at the University of Minnesota, Anderson's first stories were published by editor John W. Campbell in the magazine ''Astounding Science Fiction'': "Tomorrow's Children" by Anderson and F. N. Waldrop in March 1947 and a sequel, "Chain of Logic" by Anderson alone, in July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Carle
Eric Carle (June 25, 1929 – May 23, 2021) was an American author, designer and illustrator of children's books. His picture book ''The Very Hungry Caterpillar'', first published in 1969, has been translated into more than 66 languages and sold more than 50 million copies. His career as an illustrator and children's book author took off after he collaborated on '' Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See?''. He illustrated more than 70 books, most of which he also wrote, and more than 145 million copies of his books have been sold around the world. In 2003, the American Library Association awarded Carle the biennial Laura Ingalls Wilder Medal (now called the Children's Literature Legacy Award), a prize for writers or illustrators of children's books published in the U.S. who have made lasting contributions to the field. Carle was also a U.S. nominee for the biennial, international Hans Christian Andersen Award in 2010. Early life Carle was born on June 25, 1929, in Syracuse, Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Award For Best Novel
The Hugo Award for Best Novel is one of the Hugo Awards given each year for science fiction or fantasy stories published in, or translated to, English during the previous calendar year. The novel award is available for works of fiction of 40,000 words or more; awards are also given out in the short story, novelette, and novella categories. The Hugo Awards have been described as "a fine showcase for speculative fiction", and "the best known literary award for science fiction writing". The Hugo Award for Best Novel has been awarded annually by the World Science Fiction Society since 1953, except in 1954 and 1957. In addition, beginning in 1996, Retrospective Hugo Awards or "Retro-Hugos" have been available for works published 50, 75, or 100 years prior. Retro-Hugos may only be awarded for years after 1939 in which no awards were originally given. To date, Retro-Hugo awards have been given for novels for 1939, 1941, 1943–1946, 1951, and 1954. Hugo Award nominees and winners ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work. Kipling's works of fiction include the ''Jungle Book'' duology ('' The Jungle Book'', 1894; '' The Second Jungle Book'', 1895), ''Kim'' (1901), the '' Just So Stories'' (1902) and many short stories, including "The Man Who Would Be King" (1888). His poems include " Mandalay" (1890), " Gunga Din" (1890), "The Gods of the Copybook Headings" (1919), " The White Man's Burden" (1899), and "If—" (1910). He is seen as an innovator in the art of the short story.Rutherford, Andrew (1987). General Preface to the Editions of Rudyard Kipling, in "Puck of Pook's Hill and Rewards and Fairies", by Rudyard Kipling. Oxford University Press. His children's books are classics; one critic noted "a versatile and luminous narrative gift".Rutherford, Andrew ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Feinberg
Gerald Feinberg (27 May 1933 – 21 April 1992) was a Columbia University physicist, futurist and populist author. He spent a year as a Member of the Institute for Advanced Study, and two years at the Brookhaven Laboratories. Feinberg went to Bronx High School of Science with Steven Weinberg and Sheldon Glashow and obtained his bachelor's and graduate degrees from Columbia University. His father was Yiddish poet and journalist Leon Feinberg. Among his students were Scott Dodelson, physicist at Carnegie Mellon University. Research He coined the term tachyon for hypothetical faster-than-light particles and analysed their quantum field properties, predicted the existence of the muon neutrino and advocated cryonics as a public service. He was a member of the Foresight Institute's advisory panel. Parapsychology Feinberg wrote a foreword to Edgar Mitchell's book ''Psychic Explorations'' (1974) in which he endorsed psychic phenomena. His concept of a tachyon, a theoretical particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. Physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics. If such particles did exist they could be used to send signals faster than light. According to the theory of relativity this would violate causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow down to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realized that Feinberg's model did not in fact allow for superluminal (faster-than-light) particles or signals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klein–Gordon Equation
The Klein–Gordon equation (Klein–Fock–Gordon equation or sometimes Klein–Gordon–Fock equation) is a relativistic wave equation, related to the Schrödinger equation. It is second-order in space and time and manifestly Lorentz-covariant. It is a quantized version of the relativistic energy–momentum relation E^2 = (pc)^2 + \left(m_0c^2\right)^2\,. Its solutions include a quantum scalar or pseudoscalar field, a field whose quanta are spinless particles. Its theoretical relevance is similar to that of the Dirac equation. Electromagnetic interactions can be incorporated, forming the topic of scalar electrodynamics, but because common spinless particles like the pions are unstable and also experience the strong interaction (with unknown interaction term in the Hamiltonian,) the practical utility is limited. The equation can be put into the form of a Schrödinger equation. In this form it is expressed as two coupled differential equations, each of first order in time. The so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
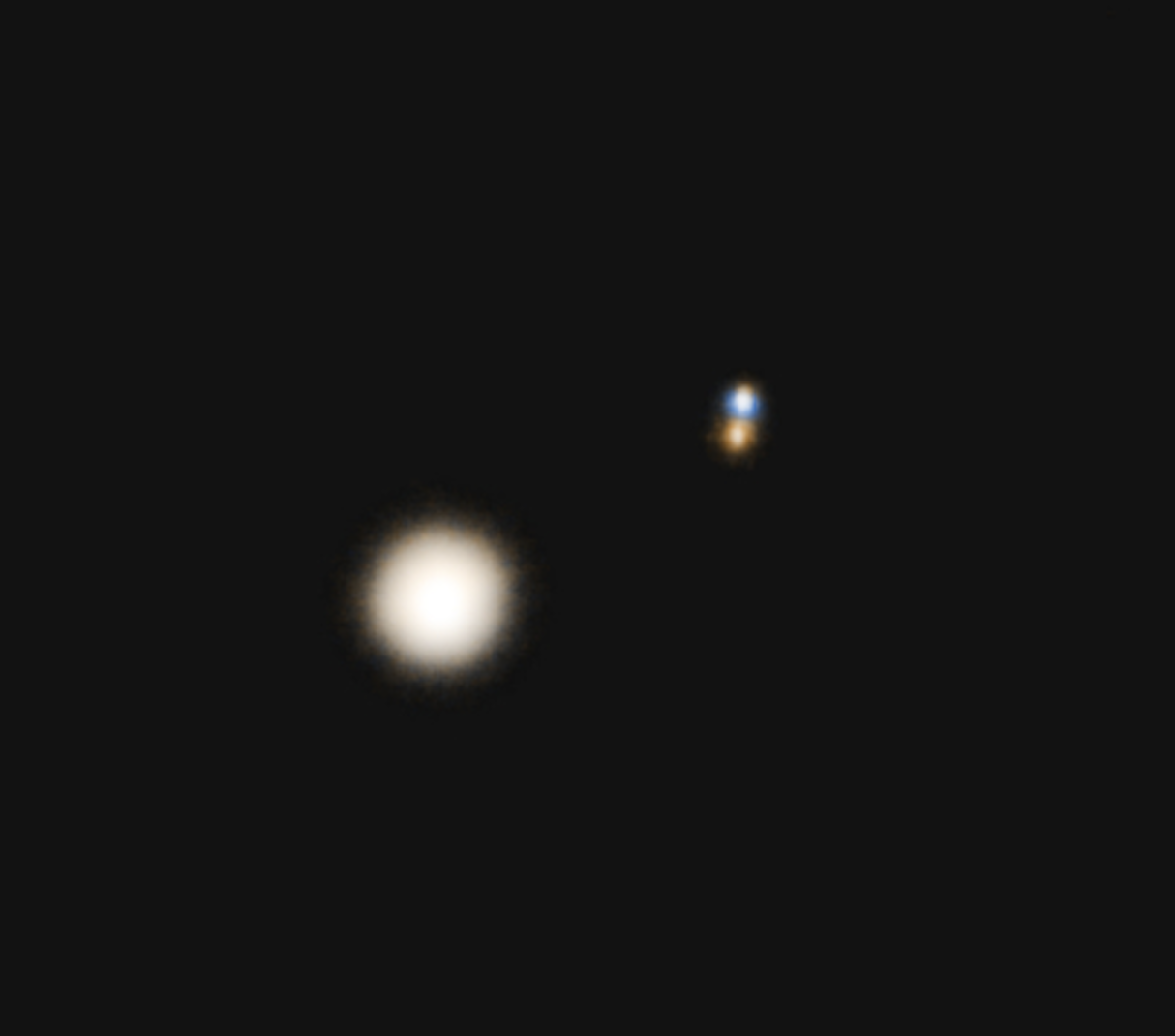
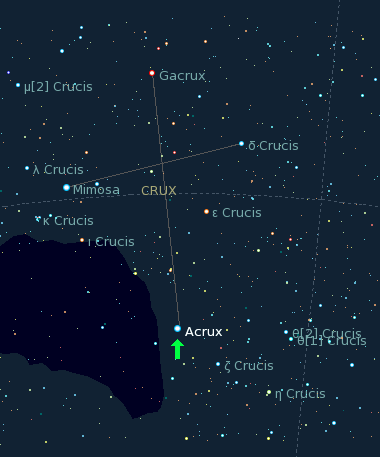
Alpha Crucis
Acrux is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux. It has the Bayer designation α Crucis, which is Latinised to Alpha Crucis and abbreviated Alpha Cru or α Cru. With a combined visual magnitude of +0.76, it is the 13th-brightest star in the night sky. It is the most southerly star of the asterism known as the Southern Cross and is the southernmost first-magnitude star, 2.3 degrees more southerly than Alpha Centauri. This system is located at a distance of 321 light-years from the Sun. To the naked eye Acrux appears as a single star, but it is actually a multiple star system containing six components. Through optical telescopes, Acrux appears as a triple star, whose two brightest components are visually separated by about 4 arcseconds and are known as Acrux A and Acrux B, α1 Crucis and α2 Crucis, or α Crucis A and α Crucis B. Both components are B-type stars, and are many times more massive and luminous than the Sun. α1 Crucis is itself a spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40 Eridani
40 Eridani is a triple star system in the constellation of Eridanus, abbreviated 40 Eri. It has the Bayer designation Omicron2 Eridani, which is Latinized from ο2 Eridani and abbreviated Omicron2 Eri or ο2 Eri. Based on parallax measurements taken by the Gaia mission, it is about 16.3 light-years from the Sun. The primary star of the system, designated 40 Eridani A and named Keid, is easily visible to the naked eye. It is orbited by a binary pair whose two components are designated 40 Eridani B and C, and which were discovered on January 31, 1783, by William Herschel. It was again observed by Friedrich Struve in 1825 and by Otto Struve in 1851. In 1910, it was discovered that although component B was a faint star, it was white in color. This meant that it had to be a small star; in fact it was a white dwarf, the first discovered.''White Dwarfs'', E. Schatzman, Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1958. , p. 1 Although it is neither the closest white dwarf, nor the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Ceti
Tau Ceti, Latinized from τ Ceti, is a single star in the constellation Cetus that is spectrally similar to the Sun, although it has only about 78% of the Sun's mass. At a distance of just under from the Solar System, it is a relatively nearby star and the closest solitary G-class star. The star appears stable, with little stellar variation, and is metal-deficient relative to the Sun. It can be seen with the unaided eye with an apparent magnitude of 3.5. As seen from Tau Ceti, the Sun would be in the northern hemisphere constellation Boötes with an apparent magnitude of about 2.6.From Tau Ceti the Sun would appear on the diametrically opposite side of the sky at the coordinates RA = , Dec = , which is located near Tau Boötis. The absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.8, so, at a distance of , the Sun would have an apparent magnitude m = M_v + 5 \cdot (\log_ 3.64 - 1) = 2.6. Observations have detected more than ten times as much dust surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germanium is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Critical Guide To Science Fiction
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |