|
The Coolin
The Coolin, or The Coolun, is an Irish air often characterised as one of the most beautiful in the traditional repertoire. In Irish, its name has been given as ''An Chúileann'' or ''An Chúilfhionn'' ("the fair haired girl" or "the fair lady") depending on the text used. The tune is also known as "The Lady of the Desert". History The air, and the texts fitted to it, have a long and very complex history. Its exact provenance is unknown, but it has been variously asserted by different authors as dating from the 13th century, from the time of Henry VIII, or from the 17th century, though the latter is the most credible.Donnellan, L. "Traditional Irish and Highland Airs", in Quinn (ed.), ''Journal of the County Louth Archaeological Society'', vol 3, no. 1 (1912), 11-12 There are at least two main Irish language texts and a number of later English translations, or interpretations of both; there are also English words (such as those by Moore) which are not a translation of either Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Traditional Music
Irish traditional music (also known as Irish trad, Irish folk music, and other variants) is a genre of folk music that developed in Ireland. In ''A History of Irish Music'' (1905), W. H. Grattan Flood wrote that, in Gaelic Ireland, there were at least ten instruments in general use. These were the ''cruit'' (a small harp) and '' clairseach'' (a bigger harp with typically 30 strings), the ''timpan'' (a small string instrument played with a bow or plectrum), the ''feadan'' (a fife), the ''buinne'' (an oboe or flute), the ''guthbuinne'' (a bassoon-type horn), the ''bennbuabhal'' and ''corn'' ( hornpipes), the ''cuislenna'' (bagpipes – see Great Irish warpipes), the ''stoc'' and ''sturgan'' (clarions or trumpets), and the ''cnamha'' (bones).''A History of Irish Music: Chapter II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Ferguson
Sir Samuel Ferguson (10 March 1810 – 9 August 1886) was an Irish poet, barrister, antiquarian, artist and public servant. He was an acclaimed 19th-century Irish poet, and his interest in Irish mythology and early Irish history can be seen as a forerunner of William Butler Yeats and the other poets of the Irish Literary Revival. Early life Ferguson was born in Belfast, Ireland the third son of John Ferguson and Agnes Knox. His father was a spendthrift and his mother was a conversationalist and lover of literature, who read out the works of Shakespeare, Walter Scott, Keats, Shelley and other English-language authors to her six children. Ferguson lived at a number of addresses, including Glenwhirry, where he later said he acquired a love of nature that inspired his works. He studied at the Belfast Academy and the Belfast Academical Institution. Later, he moved to Dublin, for law education at Trinity College, obtaining his BA in 1826 and his MA in 1832. His father ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Václav Voříšek
Jan Václav Hugo Voříšek (; ''Johann Hugo Worzischek'', 11 May 1791, in Vamberk, Bohemia – 19 November 1825, in Vienna, Austria) was a Czech composer, pianist, and organist. Life Voříšek was born in the town of Vamberk, Bohemia, where his father was schoolmaster, choirmaster and organist. As a child prodigy, he started to perform publicly in Bohemian towns at the age of nine. His father taught him music, encouraged his playing the piano and helped him get a scholarship to attend the University of Prague, where he studied philosophy. He also had lessons in piano and composition from Václav Tomášek. He found it impossible to obtain sufficient work as a musician in Prague, so in 1813 at the age of 22, Voříšek moved to Vienna to study law and, he hoped, to meet Beethoven. In Vienna he was able to greatly improve his piano technique under Johann Nepomuk Hummel, but once more failed to gain full-time employment as a musician. Although Voříšek was enthralled by the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Clancy (musician)
Willie Clancy (24 December 1918 – 24 January 1973)Sleeve notes by Peter Brown, from ''The Gold Ring'' CD, (RTÉ 276CD), RTÉ 2009 was an Irish uilleann piper, flute player and whistle player. Early life Clancy was born into a musical family in the outskirts of Milltown Malbay, County Clare. His parents (Gilbert Clancy and Ellen Killeen) both sang and played concertina, and his father also played the flute. Clancy's father had been heavily influenced by local blind piper Garret Barry and passed much of Barry's music on to Willie.Mac Mathúna, Ciarán (1980) "Willie Clancy" (sleeve notes from ''The Pipering of Willie Clancy''; volume I). Career Willie started playing the whistle at age 5, and later took up the flute. He first saw a set of pipes in 1936 when he saw Johnny Doran playing locally. He obtained his first set of pipes two years later. His influences included Leo Rowsome, Séamus Ennis, John Potts, and Andy Conroy. Clancy won the Oireachtas competition i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnny Doran
Johnny Doran (1908 – 19 January 1950)Sleeve notes compiled by Jackie Small and published with ''The Bunch of Keys'' audio tape, Comhairle Bhéaloideas Éireann (CBÉ 001), 1988 was an Irish uilleann piper. Life and family Johnny Doran was born around 1908 in Rathnew, County Wicklow. His family were Travellers with a distinguished musical heritage; his father John Doran and brother Felix Doran were also pipers, and his great-grandfather was the celebrated Wexford piper John Cash. By his early twenties, Doran was working as an itinerant musician, travelling with his family from town to town in a horse-drawn caravan and playing for money at fairs, races and sporting events. His playing is said to have inspired the young Willie Clancy and Martin Talty to take up piping as a career. On 30 January 1948, Doran's caravan was parked on waste ground near Back Lane in Dublin's Cornmarket area. It was very windy, and a brick wall collapsed on the caravan, and also on Doran, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Rowsome
Leo Rowsome (5 April 1903 - 20 September 1970) was the third generation of an unbroken line of uilleann pipers. He was a performer, manufacturer and teacher of the uilleann pipes throughout his life. Samuel Rowsome, Leo’s grandfather sent his sons, John, Thomas and William to a German teacher of music who lived in Ferns, near their home in County Wexford to learn the theory of music and how to play various instruments. This knowledge was passed on through William to his son, Leo who made good use of it in his teaching, writing music for his many pupils. Leo was born in Harold's Cross, Dublin in 1903. His father, William realised that his son had the ability to become a talented musician and craftsman. Constantly watching his father making and repairing instruments, Leo learned the art of pipe making and instrument repair. So rapid was his progress at piping that in 1919 at the age of sixteen he was appointed teacher of the uilleann pipes at Dublin’s Municipal School of Musi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uilleann Pipes
The uilleann pipes ( or , ) are the characteristic national bagpipe of Ireland. Earlier known in English as "union pipes", their current name is a partial translation of the Irish language terms (literally, "pipes of the elbow"), from their method of inflation. There is no historical record of the name or use of the term ''uilleann pipes'' before the 20th century. It was an invention of Grattan Flood and the name stuck. People mistook the term 'union' to refer to the 1800 Act of Union; this is incorrect as Breandán Breathnach points out that a poem published in 1796 uses the term 'union'. The bag of the uilleann pipes is inflated by means of a small set of bellows strapped around the waist and the right arm (in the case of a right-handed player; in the case of a left-handed player the location and orientation of all components are reversed). The bellows not only relieve the player from the effort needed to blow into a bag to maintain pressure, they also allow relatively dry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granard
Granard () is a town in the north of County Longford, Ireland, and has a traceable history going back to AD 236. It is situated just south of the boundary between the watersheds of the Shannon and the Erne, at the point where the N55 national secondary road and the R194 regional road meet. History The town has been a centre of population since Celtic times, probably because of its elevated position offering a view over the surrounding countryside. It is mentioned in the ancient Irish epic, the '' Táin Bó Cuailgne'', as being one of the places where Queen Medb and her army stopped on their journey to take the ''Donn Cuailnge'' (the ''Brown Bull of Cooley''). The name of the village is itself so ancient as to be unclear even in Irish; the 11th-century writers of the ''Lebor na hUidre'' (containing the oldest written version of the ''Táin'') refer to it by means of a gloss as "''Gránairud Tethba tuaiscirt .i. Gránard indiu''" ("Gránairud of northern Teathbha, i.e. Grán ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast Harp Festival
The Belfast Harp Festival, called by contemporary writers The Belfast Harpers Assembly,Sara C. Lanier, «"It is new-strung and shan't be heard": nationalism and memory in the Irish harp tradition». in: ''British Journal of Ethnomusicology''; Vol. 8, 1999 11–14 July 1792, was a three-day musical and patriotic event organised in Belfast, Ireland, by leading members of the local Society for Promoting Knowledge ( the Linen Hall Library): Dr. James MacDonnell, Robert Bradshaw, Henry Joy, and Robert Simms. Edward Bunting, a young classically trained organist, was commissioned to notate the forty tunes performed by ten harpists attending, work that was to form the major part of his ''General Collection of the Ancient Irish Music'' (1796). The venue of the contest was in The Assembly Room on Waring Street in Belfast which was opened as a market house in 1769. It was staged for the benefit of the Belfast Charitable Society but coincided with the town's Bastille Day celebrations with whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Fanning (harper)
Charles Fanning, Irish harper, born Foxford, County Mayo, 1736, died after 1792. A son of a comfortable farmer and notable harper named Loughlin Fanning, he was taught by County Roscommon harper, Thady Smith. A friend and rival of Arthur O'Neill, Fanning performed at the Granard Harp Festivals of 1781, 82 and 83, each time winning first prize. He accomplished the same feat at Belfast in 1792. Captain Francis O'Neill said of him: "Charles Fanning preferred Ulster to his native province, and although certain important episodes in his life happened at Tyrone, his chief haunts were in the County of Cavan Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Bally .... The mistake of his life was marrying the kitchen maid of one of his early patrons, a Mrs. Baillie who was a good performer on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
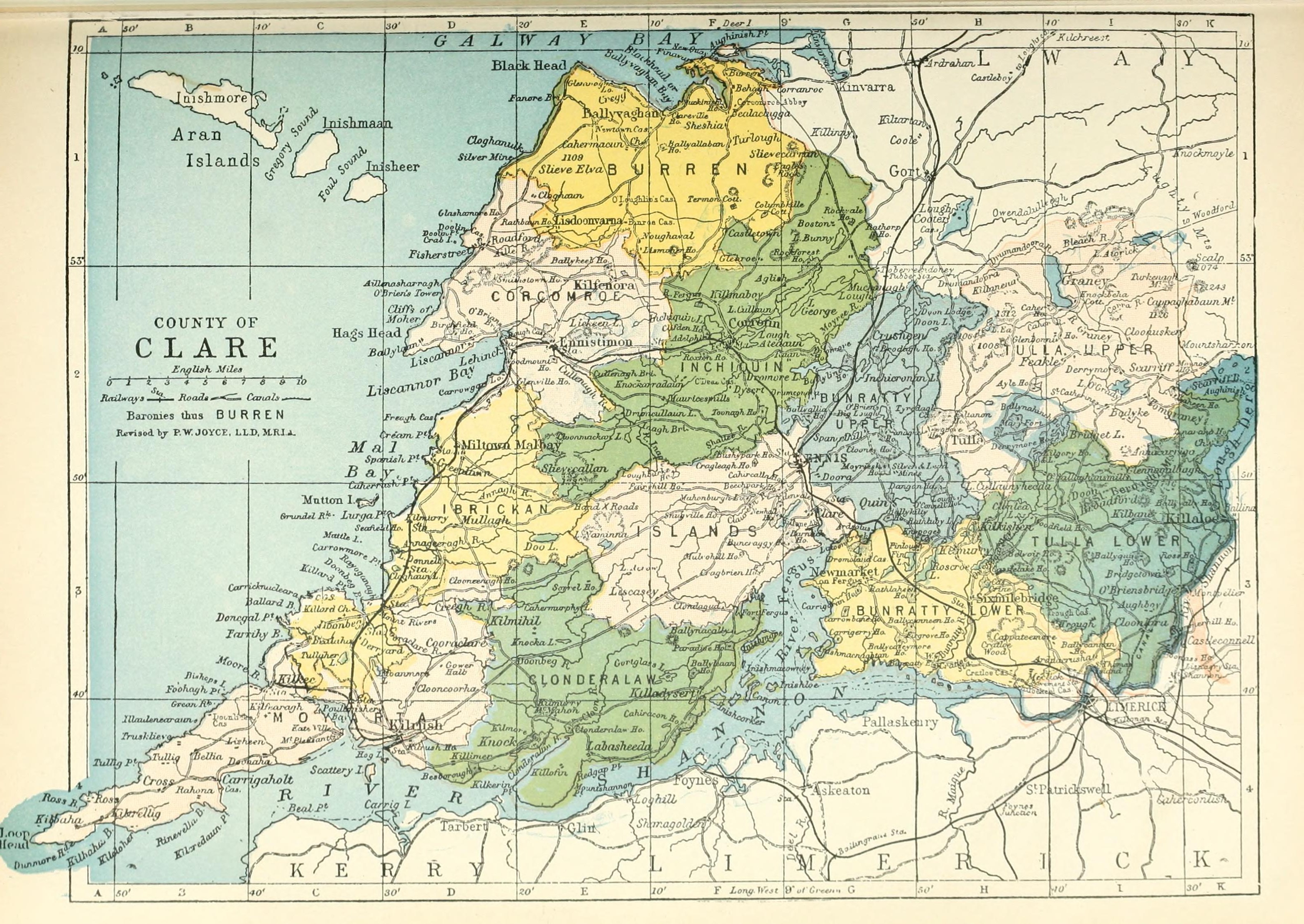
County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an Chláir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,817 at the 2016 census. The county town and largest settlement is Ennis. Geography and subdivisions Clare is north-west of the River Shannon covering a total area of . Clare is the seventh largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties in area and the 19th largest in terms of population. It is bordered by two counties in Munster and one county in Connacht: County Limerick to the south, County Tipperary to the east and County Galway to the north. Clare's nickname is ''the Banner County''. Baronies, parishes and townlands The county is divided into the baronies of Bunratty Lower, Bunratty Upper, Burren, Clonderalaw, Corcomroe, Ibrickan, Inchiquin, Islands, Moyarta, Tulla Lower and Tulla Upper. These in turn are divided into civil parishes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enabled widespread Hiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)