|
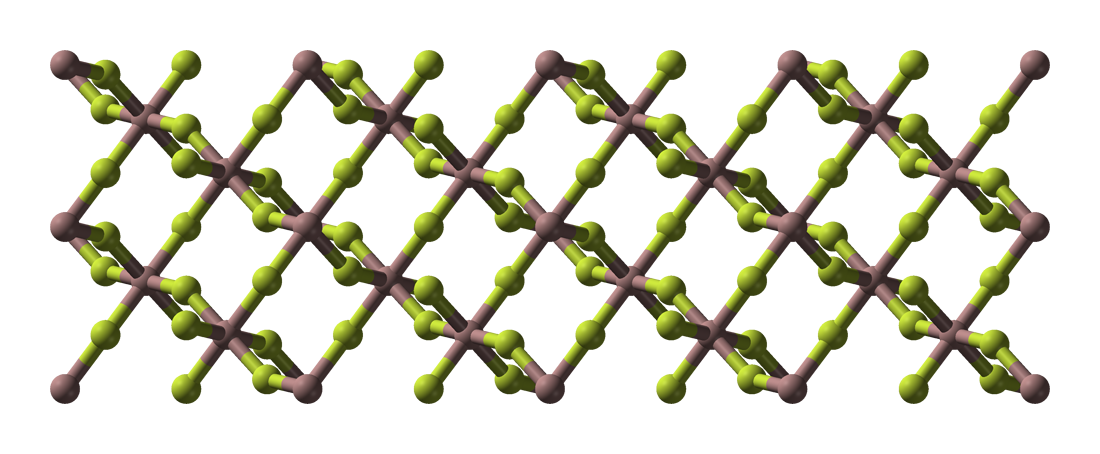
Thallium(III) Fluoride
Thallium trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TlF3. It is a white solid. Aside from being one of two thallium fluorides, the compound is only of theoretical interest. It adopts the same structure as bismuth trifluoride Bismuth(III) fluoride or bismuth trifluoride is a chemical compound of bismuth and fluorine. The chemical formula is BiF3. It is a grey-white powder melting at 649 °C. It occurs in nature as the rare mineral gananite. Synthesis Bismuth flu ..., featuring eight-coordinate Tl(III) centers. Some evidence exists for a second polymorph. References {{fluorine compounds Thallium compounds Fluorides Metal halides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium(III) Chloride
The thallium halides include monohalides, where thallium has oxidation state +1, trihalides in which thallium generally has oxidation state +3, and some intermediate halides containing thallium with mixed +1 and +3 oxidation states. These materials find use in specialized optical settings, such as focusing elements in research spectrophotometers. Compared to the more common zinc selenide-based optics, materials such as thallium bromoiodide enable transmission at longer wavelengths. In the infrared, this allows for measurements as low as 350 cm−1 (28 μm), whereas zinc selenide is opaque by 21.5 μm, and ZnSe optics are generally only usable to 650 cm−1 (15 μm). Monohalides The monohalides all contain thallium with oxidation state +1. Parallels can be drawn between the thallium(I) halides and their corresponding silver salts; for example, thallium(I) chloride and bromide are light-sensitive, and thallium(I) fluoride is more soluble in water than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum Fluoride
Aluminium fluoride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula AlF3·''x''H2O. They are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium metal. Several occur as minerals. Occurrence and production Aside from anhydrous AlF3, several hydrates are known. With the formula AlF3·''x''H2O, these compounds include monohydrate (''x'' = 1), two polymorphs of the trihydrate (''x'' = 3), a hexahydrate (''x'' = 6), and a nonahydrate (''x'' = 9). The majority of aluminium fluoride is produced by treating alumina with hydrogen fluoride at 700 °C: Hexafluorosilicic acid may also be used make aluminum fluoride. :H2SiF6 + Al2O3 + 3 H2O → 2 AlF3 + SiO2 + 4 H2O Alternatively, it is manufactured by thermal decomposition of ammonium hexafluoroaluminate. For small scale laboratory preparations, AlF3 can also be prepared by treating aluminium hydroxide or aluminium metal with hydrogen fluoride. Aluminium fluoride trihydrate is found in nature as the rare miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium(III) Fluoride
Gallium(III) fluoride ( Ga F3) is a chemical compound. It is a white solid that melts under pressure above 1000 °C but sublimes around 950 °C. It has the FeF3 structure where the gallium atoms are 6-coordinate. GaF3 can be prepared by reacting F2 or HF with Ga2O3 or by thermal decomposition of (NH4)3GaF6.Anthony John Downs, (1993), ''Chemistry of Aluminium, Gallium, Indium, and Thallium'', Springer, GaF3 is virtually insoluble in water. Solutions of GaF3 in HF can be evaporated to form the trihydrate, GaF3·3H2O, which on heating gives a hydrated form of GaF2(OH). Gallium(III) fluoride reacts with mineral acids to form hydrofluoric acid Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th .... References Further reading * Fluorides Gallium compounds Metal halides [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium(I) Fluoride
Thallium(I) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula TlF. It is a white solid, forming orthorhombic crystals. The solid slightly deliquescence, deliquescent. It has a distorted sodium chloride (rock salt) crystal structure, due to the 6s2 Inert pair effect, inert pair on Tl+. This salt is unusual among the thallium halides, thallium(I) halides in that it is very soluble in water. Reactions Thallium(I) fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of thallium(I) carbonate with hydrofluoric acid. References {{fluorine compounds Thallium(I) compounds Fluorides Metal halides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Trifluoride
Bismuth(III) fluoride or bismuth trifluoride is a chemical compound of bismuth and fluorine. The chemical formula is BiF3. It is a grey-white powder melting at 649 °C. It occurs in nature as the rare mineral gananite. Synthesis Bismuth fluoride can be prepared by reacting bismuth(III) oxide with hydrofluoric acid: :Bi2O3 + 6 HF → 2 BiF3 + 3 H2O Structure α-BiF3 has a cubic crystalline structure (Pearson symbol cF16, space group Fm-3m, No. 225). BiF3 is the prototype for the D03 structure, which is adopted by several intermetallics, including Mg3Pr, Cu3Sb, Fe3Si, and AlFe3, as well as by the hydride LaH3.0. The unit cell is face-centered cubic with Bi at the face centers and vertices, and F at the octahedral site (mid-edges, center), and tetrahedral sites (centers of the 8 sub cubes) - thus the primitive cell contains 4 Bi and 12 F. Alternatively, with the unit cell shifted (1/4,1/4,1/4) the description can be of a fcc cell with face, edge, corner, and centers filled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium Compounds
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek , , meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862; Lamy by electrolysis, and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the international exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year. Thallium tends to form the +3 and +1 oxidation states. The +3 state resembles that of the other elements in group 13 (boron, aluminium, gallium, indium). However, the +1 state, which is far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorides
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin. Fluoride is the simplest fluorine anion. In terms of charge and size, the fluoride ion resembles the hydroxide ion. Fluoride ions occur on Earth in several minerals, particularly fluorite, but are present only in trace quantities in bodies of water in nature. Nomenclature Fluorides include compounds that contain ionic fluoride and those in which fluoride does not dissociate. The nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |