|
Text Retrieval Conference
The Text REtrieval Conference (TREC) is an ongoing series of workshops focusing on a list of different information retrieval (IR) research areas, or ''tracks.'' It is co-sponsored by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (part of the office of the Director of National Intelligence), and began in 1992 as part of the TIPSTER Text program. Its purpose is to support and encourage research within the information retrieval community by providing the infrastructure necessary for large-scale ''evaluation'' of text retrieval methodologies and to increase the speed of lab-to-product transfer of technology. TREC's evaluation protocols have improved many search technologies. A 2010 study estimated that "without TREC, U.S. Internet users would have spent up to 3.15 billion additional hours using web search engines between 1999 and 2009." Hal Varian the Chief Economist at Google wrote that "The TREC data revitaliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user or searcher enters a query into the system. Queries are formal statements of information needs, for example search strings in web search engines. In inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TREC Genomics
The TREC Genomics track was a workshop held under the auspices of NIST for the purpose of evaluating systems for information retrieval and related technologies in the genomics domain. The TREC Genomics track took place annually from 2003 to 2007, with some modifications to the task set every year; tasks included information retrieval, document classification, GeneRIF prediction, and question answering Question answering (QA) is a computer science discipline within the fields of information retrieval and natural language processing (NLP), which is concerned with building systems that automatically answer questions posed by humans in a natural l .... See also * TREC, the Text Retrieval Conference External links The TREC Genomics track web site Genomics organizations {{genetics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microblog
Microblogging is a form of social network that permits only short posts. They "allow users to exchange small elements of content such as short sentences, individual images, or video links",. Retrieved June 5, 2014 which may be the major reason for their popularity. These small messages are sometimes called ''micro posts''. As with traditional blogging, users post about topics ranging from the simple, such as "what I'm doing right now," to the thematic, such as "sports cars." Commercial microblogs also exist to promote websites, services, and products and to promote collaboration within an organization. Some microblogging services offer privacy settings, which allow users to control who can read their microblogs or alternative ways of publishing entries besides the web-based interface. These may include text messaging, instant messaging, e-mail, digital audio, or digital video. Origin The first micro-blogs were known as ''tumblelogs''. The term was coined by why the lucky stiff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Document
An electronic document is any electronic media content (other than computer programs or system files) that is intended to be used in either an electronic form or as printed output. Originally, any computer data were considered as something internal — the final data output was always on paper. However, the development of computer networks has made it so that in most cases it is much more convenient to distribute electronic documents than printed ones. The improvements in electronic visual display technologies made it possible to view documents on screen instead of printing them (thus saving paper and the space required to store the printed copies). However, using electronic documents for final presentation instead of paper has created the problem of multiple incompatible file formats. Even plain text computer files are not free from this problem — e.g. under MS-DOS, most programs could not work correctly with UNIX-style text files (see newline), and for non-English s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery (law)
Discovery, in the law of common law jurisdictions, is a pre-trial procedure in a lawsuit in which each party, through the law of civil procedure, can obtain evidence from the other party or parties by means of discovery devices such as interrogatories, requests for production of documents, requests for admissions and depositions. Discovery can be obtained from non-parties using subpoenas. When a discovery request is objected to, the requesting party may seek the assistance of the court by filing a motion to compel discovery. History Discovery evolved out of a unique feature of early equitable pleading procedure before the English Court of Chancery: among various requirements, a plaintiff's bill in equity was required to plead "positions". These were statements of evidence that the plaintiff assumed to exist in support of his pleading and which he believed lay within the knowledge of the defendant. They strongly resembled modern requests for admissions, in that the defen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffeo (company)
Diffeo, Inc. ( ), is a software company that developed a collaborative intelligence text mining product for defense, intelligence and financial services customers. The Diffeo product is a recommender engine that analyzes text in a user's working documents, such as draft emails and web pages, identifying named entities and proposing related entities. Diffeo was founded in 2012 and was acquired by Salesforce in 2019. The company grew out of NIST's Text Retrieval Conference where the founding team organized the Knowledge Base Acceleration (KBA) evaluation to measure the effectiveness of recommender engines. History Founding The company was founded by three Hertz Fellows, Dan Roberts, Max Kleiman-Weiner, and John Frank, a co-founder of MetaCarta. The name Diffeo comes from a shortening of diffeomorphism, which two of the cofounders were learning about in a class about blackholes by Andrew Strominger. Diffeo was one of the first residents in hack/reduce. Funding In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Need
The term information need is often understood as an individual or group's desire to locate and obtain information to satisfy a conscious or unconscious need. Rarely mentioned in general literature about needs, it is a common term in information science. According to Hjørland (1997) it is closely related to the concept of relevance: If something is relevant for a person in relation to a given task, we might say that the person needs the information for that task. Information needs are related to, but distinct from information requirements. They are studied for: # The explanation of observed phenomena of information use or expressed need; # The prediction of instances of information uses; # The control and thereby improvement of the utilization of information manipulation of essential conditions. Background The concept of information needs was coined by an American information journalisRobert S. Taylorin his 1962 articl"The Process of Asking Questions"published in ''American D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federated Search
Federated search retrieves information from a variety of sources via a search application built on top of one or more search engines. A user makes a single query request which is distributed to the search engines, databases or other query engines participating in the federation. The federated search then aggregates the results that are received from the search engines for presentation to the user. Federated search can be used to integrate disparate information resources within a single large organization ("enterprise") or for the entire web. Federated search, unlike distributed search, requires centralized coordination of the searchable resources. This involves both coordination of the queries transmitted to the individual search engines and fusion of the search results returned by each of them. Purpose Federated search came about to meet the need of searching multiple disparate content sources with one query. This allows a user to search multiple databases at once in real time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
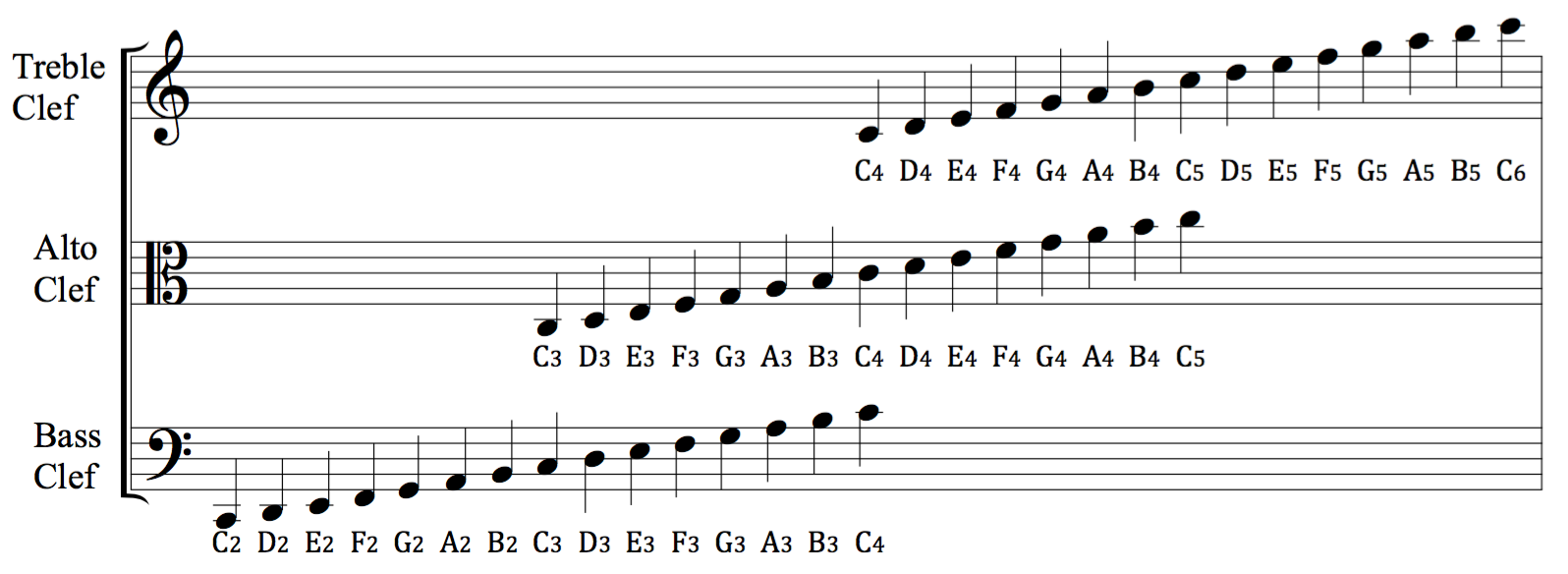
CLEF
A clef (from French: 'key') is a Musical notation, musical symbol used to indicate which Musical note, notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff (music), stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the #G-clefs, G-clef, #F-clefs, F-clef, and #C-clefs, C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing Scientific pitch notation, G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-language Information Retrieval
Cross-language information retrieval (CLIR) is a subfield of information retrieval dealing with retrieving information written in a language different from the language of the user's query. The term "cross-language information retrieval" has many synonyms, of which the following are perhaps the most frequent: cross-lingual information retrieval, translingual information retrieval, multilingual information retrieval. The term "multilingual information retrieval" refers more generally both to technology for retrieval of multilingual collections and to technology which has been moved to handle material in one language to another. The term Multilingual Information Retrieval (MLIR) involves the study of systems that accept queries for information in various languages and return objects (text, and other media) of various languages, translated into the user's language. Cross-language information retrieval refers more specifically to the use case where users formulate their information nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |