|
Test Assertion
In computer software testing, a test assertion is an expression which encapsulates some testable logic specified about a target under test. The expression is formally presented as an assertion, along with some form of identifier, to help testers and engineers ensure that tests of the target relate properly and clearly to the corresponding specified statements about the target. Usually the logic for each test assertion is limited to one single aspect specified. A test assertion may include prerequisites which must be true for the test assertion to be valid. See also * Test driven *Conformance testing Conformance testing and also known as compliance testing or type testing, is testing or other activities that determine whether a process, product, or service complies with the requirements of a specification, technical standard, contract, or reg ... References * Green, Stephen D. (Editor) et al. (2012) "Test Assertions Guidelines Committee Note 1.0" ''OASIS-open.org'' * Durand, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assertion (computing)
In computer programming, specifically when using the imperative programming paradigm, an assertion is a predicate (a Boolean-valued function over the state space, usually expressed as a logical proposition using the variables of a program) connected to a point in the program, that always should evaluate to true at that point in code execution. Assertions can help a programmer read the code, help a compiler compile it, or help the program detect its own defects. For the latter, some programs check assertions by actually evaluating the predicate as they run. Then, if it is not in fact true – an assertion failure – the program considers itself to be broken and typically deliberately crashes or throws an assertion failure exception. Details The following code contains two assertions, x > 0 and x > 1, and they are indeed true at the indicated points during execution: x = 1; assert x > 0; x++; assert x > 1; Programmers can use assertions to help specify programs and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Identifier
An identifier is a name that identifies (that is, labels the identity of) either a unique object or a unique ''class'' of objects, where the "object" or class may be an idea, person, physical countable object (or class thereof), or physical mass noun, noncountable substance (or class thereof). The abbreviation ID often refers to identity, identification (the process of identifying), or an identifier (that is, an instance of identification). An identifier may be a word, number, letter, symbol, or any combination of those. The words, numbers, letters, or symbols may follow an code, encoding system (wherein letters, digits, words, or symbols ''stand for'' [represent] ideas or longer names) or they may simply be arbitrary. When an identifier follows an encoding system, it is often referred to as a code or id code. For instance the ISO/IEC 11179 metadata registry standard defines a code as ''system of valid symbols that substitute for longer values'' in contrast to identifiers wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
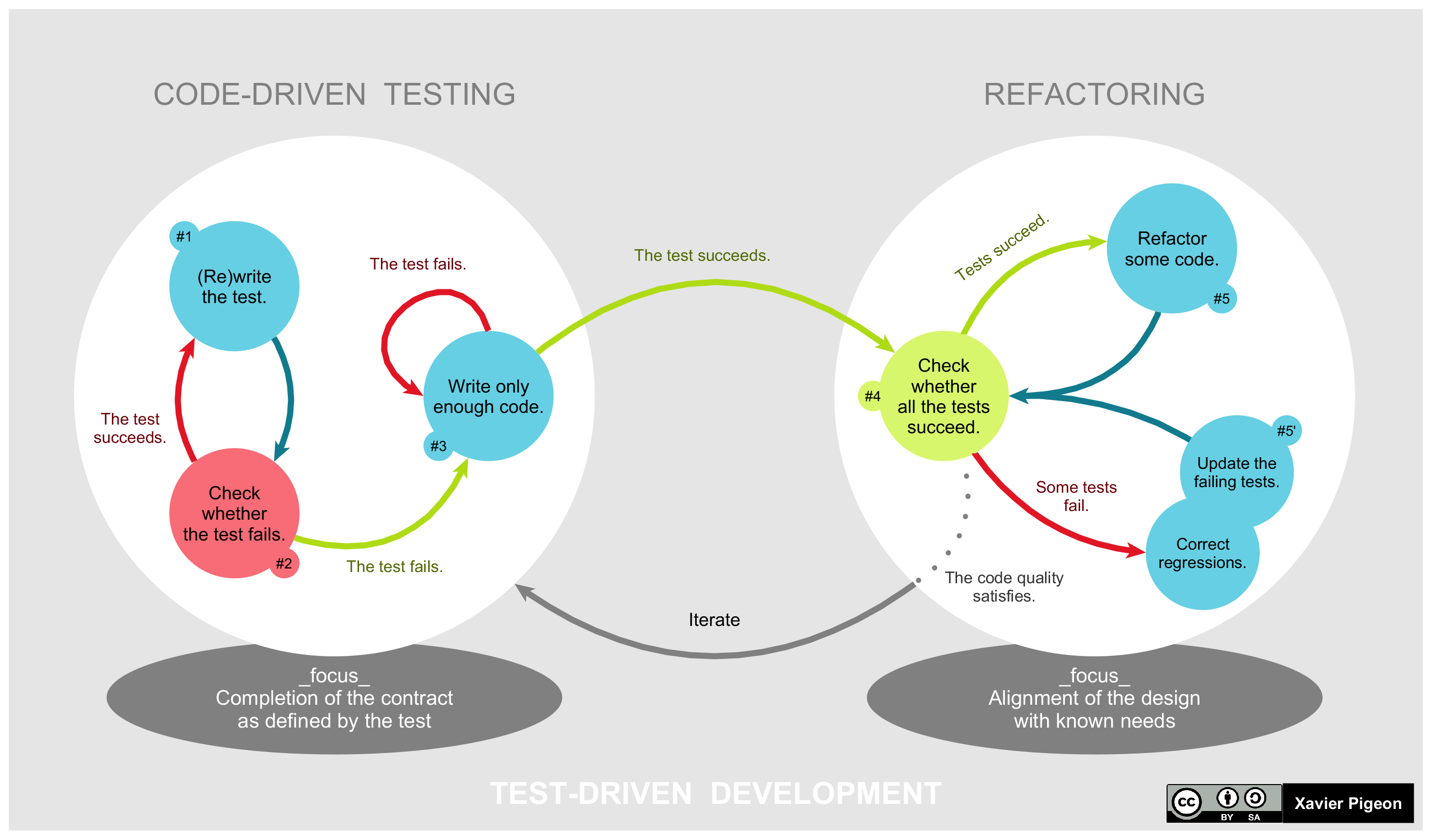
Test Driven
Test-driven development (TDD) is a way of writing code that involves writing an automated unit-level test case that fails, then writing just enough code to make the test pass, then refactoring both the test code and the production code, then repeating with another new test case. Alternative approaches to writing automated tests is to write all of the production code before starting on the test code or to write all of the test code before starting on the production code. With TsDD, both are written together, therefore shortening debugging time necessities. TDD is related to the test-first programming concepts of extreme programming, begun in 1999, but more recently has created more general interest in its own right.Newkirk, JW and Vorontsov, AA. ''Test-Driven Development in Microsoft .NET'', Microsoft Press, 2004. Programmers also apply the concept to improving and debugging legacy code developed with older techniques.Feathers, M. Working Effectively with Legacy Code, Prentice H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conformance Testing
Conformance testing and also known as compliance testing or type testing, is testing or other activities that determine whether a process, product, or service complies with the requirements of a specification, technical standard, contract, or regulation. It is an element of the more general conformity assessment. Testing is often either logical testing or physical testing. The test procedures may involve other criteria from mathematical testing or chemical testing. Beyond simple conformance, other requirements for efficiency, interoperability, or compliance may apply. Conformance testing may be undertaken by the producer of the product or service being assessed, by a user, or by an accredited independent organization, which can sometimes be the author of the standard being used. When testing is accompanied by certification, the products or services may then be advertised as being certified in compliance with the referred technical standard. Manufacturers and suppliers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |