|
Tessys Method
The TESSYS method (transforaminal endoscopic surgical system) is a minimally-invasive, endoscopic spinal procedure for the treatment of a herniated disc. It was a further development of the YESS method by the Dutch Dr Thomas Hoogland in the Alpha Klinik in Munich in 1989 and was first called THESSYS (Thomas Hoogland EndoScopic SYStem). The procedure involves performing a small foramenotomy and removal of soft tissue compressing the nerve root. Concept With the Tessys method, the surgeon removes the herniated portions of the disc using posterior lateral endoscopic access. This surgical method for spinal disc herniations is especially gentle for the patient. During the procedure, the patient is positioned either in the lateral or prone position, and local anesthetic is administered, usually in combination with sedation. The patient remains responsive, and typically general anesthesia is not necessary. The surgeon removes the herniated disc tissue through an access tube of mere m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally-invasive Procedure
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologists were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
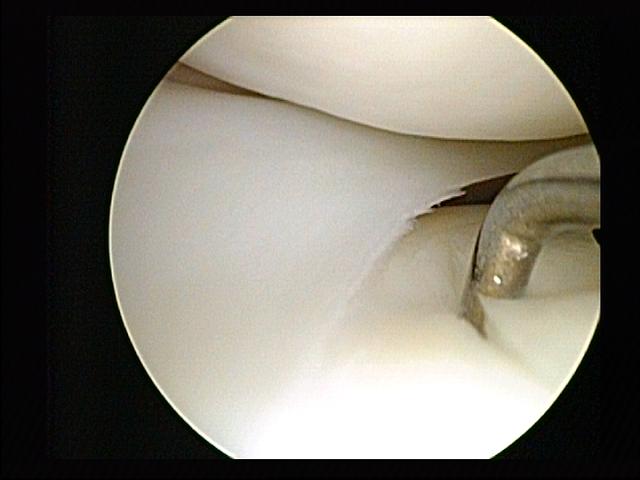
Endoscopic Spinal Surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery, also known as MISS, has no specific meaning or definition. It implies a lack of severe surgical invasion. The older style of open-spine surgery for a relatively small disc problem used to require a 5-6 inch incision and a month in the hospital. MISS techniques utilize more modern technology, advanced imaging techniques and special medical equipment to reduce tissue trauma, bleeding, radiation exposure, infection risk, and decreased hospital stays by minimizing the size of the incision. Modern endoscopic procedures (see below) can be done through a 2 to 5 mm skin opening. By contrast, procedures done with a microscope require skin openings of approximately one inch, or more. MISS can be used to treat a number of spinal conditions such as degenerative disc disease, disc herniation, fractures, tumors, infections, instability, and deformity. It also makes spine surgery possible for patients who were previously considered too high-risk for tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Disc Herniation
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture. When a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings, the disc is said to be herniated. Disc herniation is frequently associated with age-related degeneration of the outer ring, known as the '' annulus fibrosus'', but is normally triggered by trauma or straining by lifting or twisting. Tears are almost always posterolateral (on the back sides) owing to relative narrowness of the posterior longitudinal lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as physicians before specializing in surgery. There are also surgeons in podiatry, dentistry, and veterinary medicine. It is estimated that surgeons perform over 300 million surgical procedures globally each year. History The first person to document a surgery was the 6th century BC Indian physician-surgeon, Sushruta. He specialized in cosmetic plastic surgery and even documented an open rhinoplasty procedure.Ira D. Papel, John Frodel, ''Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery'' His magnum opus ''Suśruta-saṃhitā'' is one of the most important surviving ancient treatises on medicine and is considered a foundational text of both Ayurveda and surgery. The treatise addresses all aspects of general medicine, but the translator G. D. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by either a doctor or a surgeon. A patient may be fully conscious or anaesthesia, anaesthetised during the procedure. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. For nonmedical use, similar instruments are called borescopes. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a camera, the next problem to solve was how to insert a source of light, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Disc Herniation
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture. When a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings, the disc is said to be herniated. Disc herniation is frequently associated with age-related degeneration of the outer ring, known as the '' annulus fibrosus'', but is normally triggered by trauma or straining by lifting or twisting. Tears are almost always posterolateral (on the back sides) owing to relative narrowness of the posterior longitudinal lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Computed Tomography
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
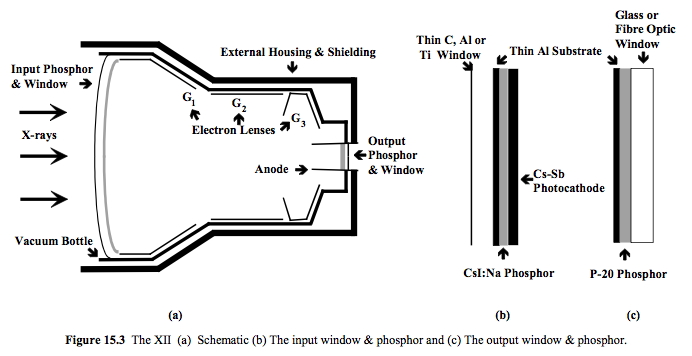
C-Arm
An X-ray image intensifier (XRII) is an image intensifier that converts X-rays into visible light at higher intensity than the more traditional fluorescent screens can. Such intensifiers are used in X-ray imaging systems (such as fluoroscopes) to allow low-intensity X-rays to be converted to a conveniently bright visible light output. The device contains a low absorbency/scatter input window, typically aluminum, input fluorescent screen, photocathode, electron optics, output fluorescent screen and output window. These parts are all mounted in a high vacuum environment within glass or, more recently, metal/ceramic. By its intensifying effect, It allows the viewer to more easily see the structure of the object being imaged than fluorescent screens alone, whose images are dim. The XRII requires lower absorbed doses due to more efficient conversion of X-ray quanta to visible light. This device was originally introduced in 1948. Operation The overall function of an image intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parviz Kambin
Parviz Kambin (May 21, 1931 - March 29, 2020) was an American-Iranian medical doctor and orthopaedic surgeon. He was a Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery and has established an Endowed Chair of Spinal Surgery Research at Drexel University College of Medicine. He published more than 55 articles in peer-reviewed journals, edited two textbooks and contributed chapters in spinal surgery textbooks. He lectured worldwide in the field of minimally invasive spinal surgery. His research and development in this specialty began in 1970. Biography Kambin was born in Tehran, Iran on May 21, 1931. He received his doctorate degree in medicine from Tehran University Faculty of Medicine in 1956. He continued his post-graduate training as an intern at St. Joseph's Regional Medical Center. He then did a four-year residency at New Jersey Orthopaedic Hospital and New York University, and received his American Board Certification in Orthopaedic Surgery in 1965. Kambin was a Professor of Orthopae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bones Of The Vertebral Column
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralized matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |