|
Tepecano
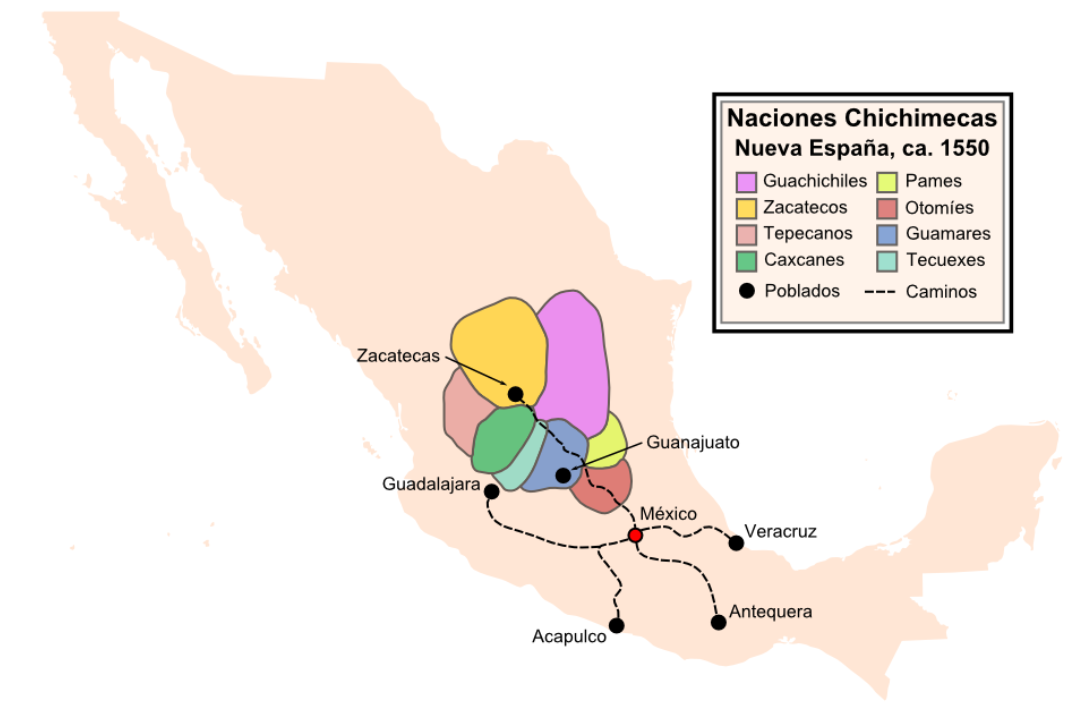
The Tepecano language is an extinct indigenous language of Mexico belonging to the Uto-Aztecan language-family. It was formerly spoken by a small group of people in Azqueltán (earlier Atzqueltlán), Jalisco, a small village on the Río Bolaños in the far northern part of the state, just east of the territory of the Huichol people. Most closely related to Southern Tepehuán of the state of Durango, Tepecano was a Mesoamerican language and evinced many of the traits that define the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area. So far as is known, the last speaker of Tepecano was Lino de la Rosa (born September 22, 1895), who was still living as of February 1980. Research on Tepecano was first carried out by the American linguistic anthropologist John Alden Mason in Azqueltán from 1911 to 1913. This work led to the publication of a monographic grammatical sketch in 1916 as well as an article on native prayers in Tepecano that Mason had collected from informants in 1918. Later field-researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huichol People
The Huichol or Wixárika are an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States living in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango, as well as in the United States in the states of California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. They are best known to the larger world as the ''Huichol'', although they refer to themselves as ''Wixáritari'' ("the people") in their native Huichol language. The adjectival form of ''Wixáritari'' and name for their own language is ''Wixárika''. The ethnonym huichol comes from the adaptation to the language Nahuatl from the ethnonym wixarika, due to that in the language wixarika the a can be spoken like o; r y l are allophones, and the pronunciation of x, that was a sibilant, was read as an affricate, tz, between the 17th and 18th centuries (time period in which the word could have been borrowed), but the loss of the syllable -ka resulted in huitzol en náhuatl, and its hispanicization, wirraricas. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azqueltán
Azqueltán is a small settlement located on the banks of the Bolaños River in the municipality of Villa Guerrero, Jalisco, Mexico. "Azqueltán" (reduced from earlier "Atzqueltlán") means "land of many ants" in the Tepehuán language. According to John Alden Mason, the village was originally settled by a group of indigenous Tepehuán who migrated to the isolated canyon location in the 13th or 14th Century AD following droughts in the northern Sierra Madre Occidental and Arizona during that time. In 1534, Spaniards arrived in the area and Huichol groups settled in the surrounding areas, most likely as a result of Spanish incursion into their homelands to the east. In the eighteenth century, historically Tepehuán lands outside of the river-canyon were taken over by Spaniards and Tlaxcaltecs brought to the region as colonizers by the Spaniards. While other historically Tepehuán settlements in the region, such as Totatiche and Temastián, lost their Tepehuán identity due to mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uto-Aztecan Languages
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family was created to show that it includes both the Ute language of Utah and the Nahuan languages (also known as Aztecan) of Mexico. The Uto-Aztecan language family is one of the largest linguistic families in the Americas in terms of number of speakers, number of languages, and geographic extension. The northernmost Uto-Aztecan language is Shoshoni, which is spoken as far north as Salmon, Idaho, while the southernmost is the Pipil language of El Salvador and Nicaragua. ''Ethnologue'' gives the total number of languages in the family as 61, and the total number of speakers as 1,900,412. Speakers of Nahuatl languages account for over 85% of these. The internal classification of the family often divides it into two branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dennis Holt
Dennis Graham Holt (born October 6, 1942) is an American poet, linguist and translator. Born in Hollywood, Los Angeles, California, Holt graduated from Van Nuys High School in Los Angeles in 1960. Holt subsequently attended the California Institute of Technology, the University of California, Berkeley, and UCLA (where his graduate advisor was William Bright), receiving from the last of these four degrees in Linguistics (B.A. 1972, M.A. 1973, C.Phil. 1975, and Ph.D. 1986). From September 1966 until November 1969, he served in the Peace Corps in Bolivia, working with cooperative coffee-processing plants in the province of Nor Yungas, and later teaching English as a second language at the Instituto Anglo-Americano in Oruro. Following his Peace Corps service, Holt returned to Los Angeles in 1970, where he soon became involved with the Venice Poetry Workshop at the Beyond Baroque Literary Arts Center in the Venice Beach District of the city, an association that continued throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piman Languages
Piman (or Tepiman) refers to a group of languages within the Uto-Aztecan family that are spoken by ethnic groups (including the Pima) spanning from Arizona in the north to Durango, Mexico in the south. The Piman languages are as follows (Campbell 1997): : 1. O'odham (also known as Pima language, Papago language) : 2. O'ob (also known as Mountain Pima, Lowland Pima) : 3. O'otham (also known as Tepehuán proper, Southwestern Tepehuán, Southeastern Tepehuán) : 4. Tepecano ''(†)'' Morphology Piman languages are agglutinative, where words use suffix complexes for a variety of purposes with several morpheme A morpheme is the smallest meaningful constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. In English, morphemes are often but not necessarily words. Morphemes that stand alone are ...s strung together. Sources Agglutinative languages Languages of the United States Indigenous languages of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bright
William O. Bright (August 13, 1928 – October 15, 2006) was an American linguist and toponymist who specialized in Native American and South Asian languages and descriptive linguistics. Biography Bright earned a bachelor's degree in linguistics in 1949 and a doctorate in the same field in 1955, both from the University of California, Berkeley. He was a professor of linguistics and anthropology at UCLA from 1959 to 1988. He then moved to the University of Colorado at Boulder, where he remained on the faculty until his death. Bright was an authority on the native languages and cultures of California, and was especially known for his work on Karuk, a Native American language from northwestern California. His study of the language was the first carried out under the auspices of the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages. He was made an honorary member of the Karuk tribe—the first outsider to be so honored—in recognition of his efforts to document and preserve their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogmios (journal)
Ogmios (also known as Ogmius; grc, Ὄγμιος; la, Ogmius, Ogimius) was the Celtic deity of eloquence. He is described as resembling a more elderly version of Heracles, and uses his powers of persuasion to bind men to himself,Ogmios - A Gaulish and Irish God, also known as Ogma, Ogmia Celtnet.org UK with stories describing thin, long chains connecting his tongue to the ears of his followers. Most of the knowledge about Ogmios comes from comparisons between him and powerful deities and heroes in other ancient cultures. About the deity Even though there is not much on the history of Ogmios, one can tell that he was a powerful deity worshipped by the |
Foundation For Endangered Languages
The Foundation for Endangered Languages is a non-profit organization, registered as Charity 1070616 in England and Wales, founded in 1996. Its current chairman is Nicholas Ostler. It exists to support, enable, and assist the documentation, protection, and promotion of endangered languages An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a "dead langu .... The Foundation awards small grants (of the order of US$1,000) for all kinds of projects that fall within this remit. It also publishes a newsletter, ''OGMIOS: Newsletter of Foundation for Endangered Languages'', and hosts an annual conference, with proceedings that are available as published volumes. External links Foundation for Endangered Languages web site Educational charities based in the United Kingdom Endangered languages projects L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The New York Academy Of Sciences
The ''Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences'' is an academic journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the New York Academy of Sciences. It is one of the oldest science journals still being published, having been founded in 1823. The editor-in-chief is Douglas Braaten. Each issue is of substantial length and explores a single topic with a multidisciplinary approach. A review published on ''Ulrichsweb'' states the scope is enormous and describes the journal as highly respected and the articles as penetrating. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.728, ranking it 13th out of 71 journals in the category " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)