|
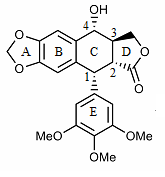
Teniposide
Teniposide (trade name Vumon) is a chemotherapeutic medication used in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), Hodgkin's lymphoma, certain brain tumours, and other types of cancer. It is in a class of drugs known as podophyllotoxin derivatives and slows the growth of cancer cells in the body.Drugs.com: Teniposide . Medical uses Teniposide is used for the treatment of a number of cancer types in children. In the US, it is approved for the second-line therapy of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) in combination with other antineoplastic drugs. In Europe, it is also approved for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma, generalized malignant lymphoma, reticulocyte sarcoma, acute leukaemia, primary brain tumours (glioblastoma, ependymoma, astrocytoma), bladder cancer, neuroblastoma and other solid tumours in children. Administration The medication is injected though a vein and burns if it leaks under the skin. It can be used in combination with other anticancer drugs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podophyllotoxin
Podophyllotoxin (PPT) is the active ingredient in Podofilox, which is a medical cream that is used to treat genital warts and molluscum contagiosum. It is not recommended in HPV infections without external warts. It can be applied either by a healthcare provider or the person themselves. It is a non-alkaloid toxin lignin extracted from the roots and rhizomes of ''Podophyllum'' species. A less refined form known as podophyllum resin is also available, but has greater side effects. Podophyllotoxin was first isolated in pure form in 1880 by Valerian Podwyssotzki (1818 – 28 January 1892), a Polish-Russian privatdozent at the University of Dorpat (now: Tartu, Estonia) and assistant at the Pharmacological Institute there. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Podophyllotoxin possesses a large number of medical applications, as it is able to stop replication of both cellular and viral DNA by binding necessary enzymes. It can addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP2C19
Cytochrome P450 2C19 (abbreviated CYP2C19) is an enzyme protein. It is a member of the CYP2C subfamily of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system. This subfamily includes enzymes that catalyze metabolism of xenobiotics, including some proton pump inhibitors and antiepileptic drugs. In humans, it is the ''CYP2C19'' gene that encodes the CYP2C19 protein. CYP2C19 is a liver enzyme that acts on at least 10% of drugs in current clinical use, most notably the antiplatelet treatment clopidogrel (Plavix), drugs that treat pain associated with ulcers, such as omeprazole, antiseizure drugs such as mephenytoin, the antimalarial proguanil, and the anxiolytic diazepam. CYP2C19 has been annotated as (R)-limonene 6-monooxygenase and (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase in UniProt. Function The gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. Enzymes in the CYP2C subfamily, including CYP2C19, account for approximately 20% of cytochrome P450 in the adult liver. These pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the neck, chest, abdomen, or spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin. Typically, neuroblastoma occurs due to a genetic mutation occurring during early development. Rarely, it may be due to a mutation inherited from a person's parents. Environmental factors have not been found to be involved. Diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Occasionally, it may be found in a baby by ultrasound during pregnancy. At diagnosis, the cancer has usually already spread. The cancer is divided into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups based on a child's age, cancer stage, and what the cancer looks like. Treatment and outcomes depends on the risk group a person is in. Treatments may include observation, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or stem cell t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all animals (including humans) is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has nipples; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only one species of mammal, the Dayak fruit bat from Southeast Asia, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is critical for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately – new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow Suppression
Bone marrow suppression also known as myelotoxicity or myelosuppression, is the decrease in production of cells responsible for providing immunity (leukocytes), carrying oxygen (erythrocytes), and/or those responsible for normal blood clotting (thrombocytes). Bone marrow suppression is a serious side effect of chemotherapy and certain drugs affecting the immune system such as azathioprine. The risk is especially high in cytotoxic chemotherapy for leukemia. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), in some rare instances, may also cause bone marrow suppression. The decrease in blood cell counts does not occur right at the start of chemotherapy because the drugs do not destroy the cells already in the bloodstream (these are not dividing rapidly). Instead, the drugs affect new blood cells that are being made by the bone marrow. When myelosuppression is severe, it is called myeloablation. Many other drugs including common antibiotics may cause bone marrow suppression. Unlike che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring is not usually present. Hair loss in some people causes psychological distress. Common types include male- or female-pattern hair loss, alopecia areata, and a thinning of hair known as telogen effluvium. The cause of male-pattern hair loss is a combination of genetics and male hormones; the cause of female pattern hair loss is unclear; the cause of alopecia areata is autoimmune; and the cause of telogen effluvium is typically a physically or psychologically stressful event. Telogen effluvium is very common following pregnancy. Less common causes of hair loss without inflammation or scarring include the pulling out of hair, certain medications including chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, hypothyroidism, and malnutrition including iron defici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging and uncomfortable. This is an immunologic term and is not to be confused with the psychiatric term of being hypersensitive which implies to an individual who may be overly sensitive to physical (i.e. sound, touch, light, etc.) and/or emotional stimuli. Although there is a relation between the two – studies have shown that those individuals that have ADHD (a psychiatric disorder) are more likely to have hypersensitivity reactions such as allergies, asthma, eczema than those who do not have ADHD. Hypersensitivity reactions can be classified into four types. Type I: IgE mediated immediate reaction Type II: Antibody-mediated reaction (IgG or IgM antibodies) Type III: Immune complex-mediated rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas are a type of brain tumor. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. Astrocytomas are the most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord. Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with: * Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images * Diffuse zones of infiltration (e.g., high-grade astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an intrins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)