|
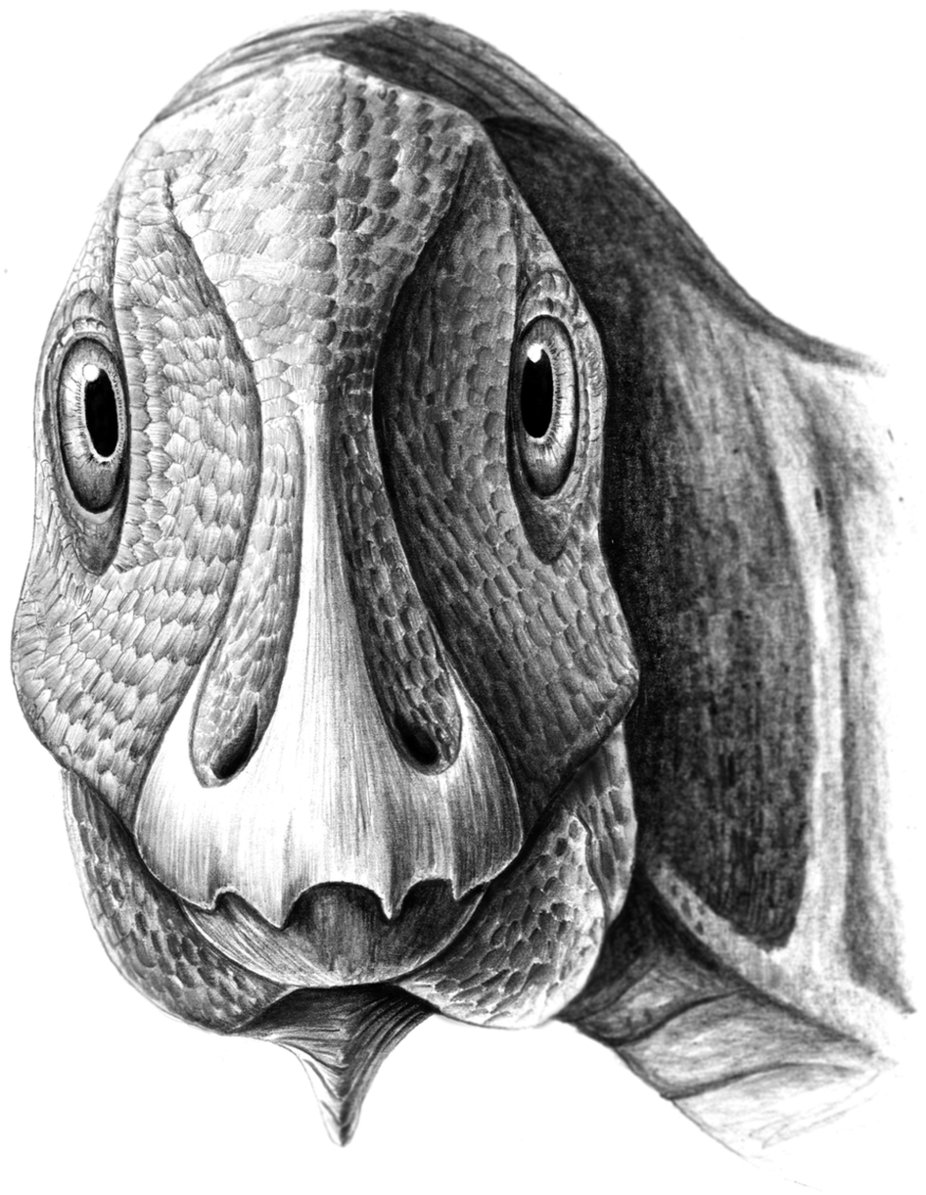
Telmatosaurus Transylvanicus
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as an instance of insular dwarfism. Discovery In 1895 some peasants presented Ilona Nopcsa, the daughter of their lord, with a dinosaur skull they had found at the estate Săcele in the district Hunedoara (then named Hunyad) in Transylvania. Ilona had an elder brother, Ferenc or Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás who was inspired by the find to become a paleontology student at the University of Vienna. In 1899 Nopcsa named the skull ''Limnosaurus transsylvanicus''. The generic name was derived from Greek λιμνή, ''limné'', "swamp", a reference to the presumed swamp-dwelling habits of hadrosaurs. The specific name referred to Transylvania. Later Nopcsa discovered that the name ''Limnosaurus'' had already been used by Othniel Charles Marsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the Chalk Group c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Vienna
The University of Vienna (german: Universität Wien) is a public research university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world. With its long and rich history, the university has developed into one of the largest universities in Europe, and also one of the most renowned, especially in the Humanities. It is associated with 21 Nobel prize winners and has been the academic home to many scholars of historical as well as of academic importance. History From the Middle Ages to the Enlightenment The university was founded on March 12, 1365, by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, hence the name "Alma Mater Rudolphina". After the Charles University in Prague and Jagiellonian University in Kraków, the University of Vienna is the third oldest university in Central Europe and the oldest university in the contemporary German-speaking world; it remains a question of definition as the Charles University in Prague ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium (ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack. This type of odontogenic neoplasm was designated as an ''adamantinoma'' in 1885 by the French physician Louis-Charles Malassez. It was finally renamed to the modern name ''ameloblastoma'' in 1930 by Ivey and Churchill. While these tumors are rarely malignant or metastatic (that is, they rarely spread to other parts of the body), and progress slowly, the resulting lesions can cause severe abnormalities of the face and jaw leading to severe disfiguration. Additionally, as abnormal cell growth easily infiltrates and destroys surrounding bony tissues, wide surgical excision is required to treat this disorder. If an aggressive tumor is left untreated, it can obstruct the nasal and oral airways making it impossible to breathe without oropharyng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
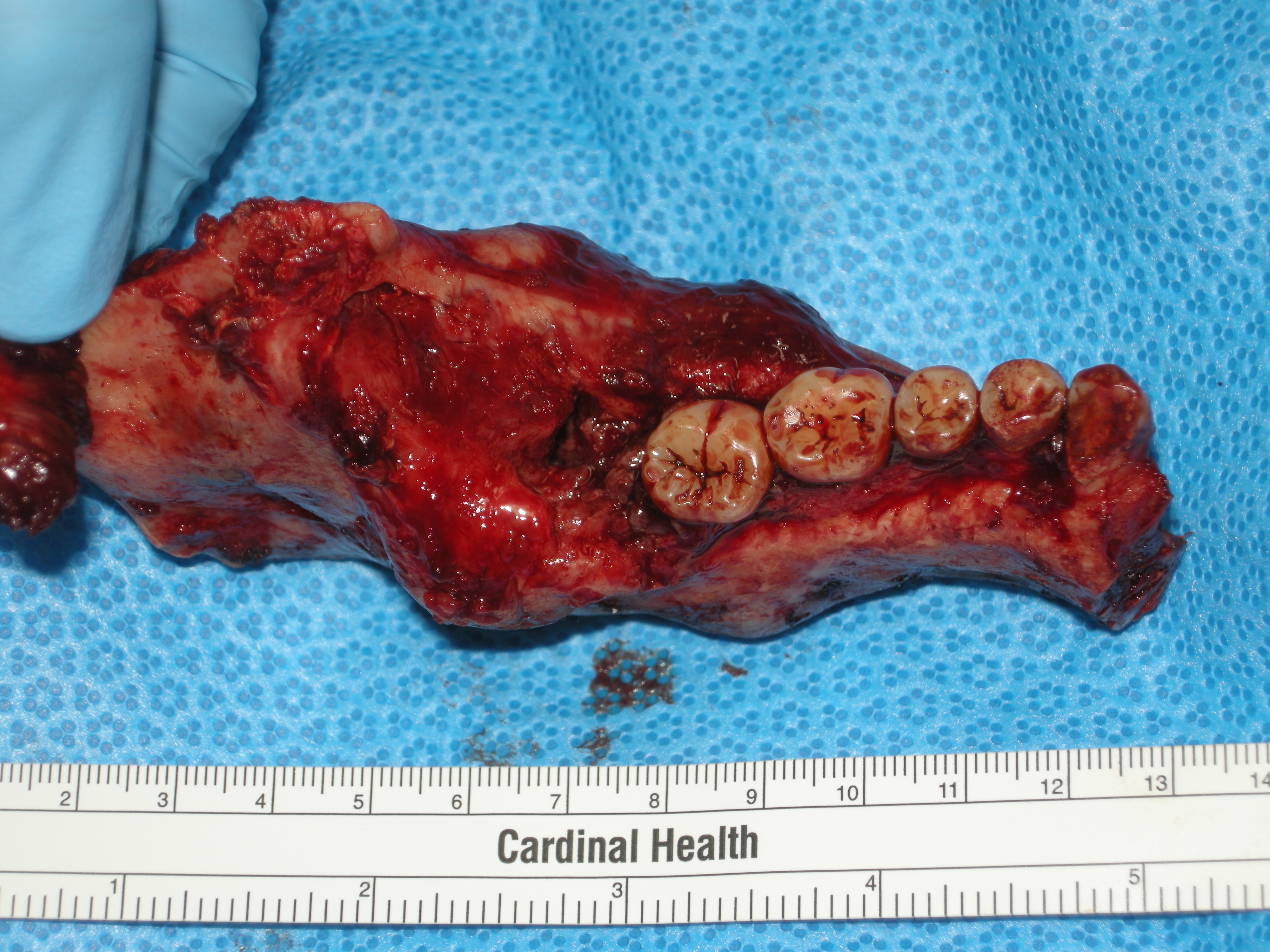
Telmatosaurus With Pathology
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as an instance of insular dwarfism. Discovery In 1895 some peasants presented Ilona Nopcsa, the daughter of their lord, with a dinosaur skull they had found at the estate Săcele in the district Hunedoara (then named Hunyad) in Transylvania. Ilona had an elder brother, Ferenc or Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás who was inspired by the find to become a paleontology student at the University of Vienna. In 1899 Nopcsa named the skull ''Limnosaurus transsylvanicus''. The generic name was derived from Greek λιμνή, ''limné'', "swamp", a reference to the presumed swamp-dwelling habits of hadrosaurs. The specific name referred to Transylvania. Later Nopcsa discovered that the name ''Limnosaurus'' had already been used by Othniel Charles Marsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application. Zoology In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a specimen belongs to that group or not. This may happen if the original type series (i. e. holotype, isotype, syntype or paratype) is lost or destroyed. The zoological and botanical codes allow for a new type specimen, or neotype, to be chosen in this case. A name may also be considered a ''nomen dubium'' if its name-bearing type is fragmentary or lacking important diagnostic features (this is often the case for species known only as fossils). To preserve stability of names, the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' allows a new type specimen, or neotype, to be chosen for a ''nomen dubium'' in this case. 75.5. Replacement of unidentifiable name-bearing type by a neotype. When an author considers that the taxonomic identity of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthomerus
''Orthomerus'' (meaning "straight femur") is a genus of dubious hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of the Netherlands. It is today an obscure genus, but in the past was conflated with the much better known ''Telmatosaurus''. Discovery and history The type species ''Orthomerus dolloi'' was in 1883 named by the well-known British paleontologist Harry Govier Seeley. The genus name is derived from the Greek ὀρθός (''orthos''), "straight", and μηρός (''meros''), "thigh". The specific name honours the French/Belgian paleontologist Louis Dollo, who had identified the bones in August 1882, during a visit to London. The type specimen, formed by the syntypes BMNH 42954-57, was probably found in the chalkstone quarries of the Sint-Pietersberg near the city of Maastricht, The Netherlands. It mainly consists of partial juvenile skeletal elements. These remains are from the Maastricht Formation of the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 million y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Archipelago
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** Citizenship of the European Union ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sânpetru Formation
The Sânpetru Formation is an early Maastrichtian geologic formation. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. It is located in Romania, near Sânpetru village, part of Sântămăria-Orlea commune. It forms a component of the Hațeg Island fauna. Description The Sânpetru Formation crops out in the central to southern Hațeg Basin along the Bărbat River and comprises sandstones and mudstones deposited in a wet floodplain environment characterized by braided fluvial channels. The formation is correlated with the Densuș-Ciula Formation of the northern section of the same basin, both dating to the Maastrichtian of the Late Cretaceous.Solomon & Codrea, 2015, p.26 Fossil content Amphibians Turtles Squamates Crocodyliformes Ornithischians Sauropods Theropods Pterosaurs Mammals See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Objective Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia leva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |