|
Telespazio VEGA Deutschland
Telespazio Germany GmbH is a European aerospace company, founded in 1978. The company provides consulting, technology and engineering services in aerospace missions for ESOC (European Space Operations Centre, Darmstadt), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites, Darmstadt) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Telespazio Germany is a subsidiary of Telespazio SpA. The Telespazio group is part of the Space Business Unit within Leonardo S.p.A., Leonardo. Office sites Darmstadt (Hessen) Headquarters is near the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT). Gilching (Bavaria) Office site in Gilching, near the German Space Operations Centre(GSOC) in Oberpfaffenhofen/Weßling (Bavaria). History Telespazio Germany was established in 2012 when Telespazio Deutschland and VEGA Space GmbH were merged. The roots of Telespazio Deutschland may be traced bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privately Held Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in the respective listed markets, but rather the company's stock is offered, owned, traded, exchanged privately, or Over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter. In the case of a closed corporation, there are a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. Related terms are closely-held corporation, unquoted company, and unlisted company. Though less visible than their public company, publicly traded counterparts, private companies have major importance in the world's economy. In 2008, the 441 list of largest private non-governmental companies by revenue, largest private companies in the United States accounted for ($1.8 trillion) in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In 2005, using a substantially smaller pool size (22.7%) for comparison, the 339 companies on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BepiColombo
BepiColombo is a joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to the planet Mercury. The mission comprises two satellites launched together: the Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and ''Mio'' (Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter, MMO). The mission will perform a comprehensive study of Mercury, including characterization of its magnetic field, magnetosphere, and both interior and surface structure. It was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket on 20 October 2018 at 01:45 UTC, with an arrival at Mercury planned for on 5 December 2025, after a flyby of Earth, two flybys of Venus, and six flybys of Mercury. The mission was approved in November 2009, after years in proposal and planning as part of the European Space Agency's Horizon 2000+ programme; it is the last mission of the programme to be launched. Names ''BepiColombo'' is named after Giuseppe "Bepi" Colombo (1920–1984), a scientist, mathematician and engineer at the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philae (spacecraft)
''Philae'' ( or ) was a robotic European Space Agency lander that accompanied the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft until it separated to land on comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, ten years and eight months after departing Earth. On 12 November 2014, ''Philae'' touched down on the comet, but it bounced when its anchoring harpoons failed to deploy and a thruster designed to hold the probe to the surface did not fire. After bouncing off the surface twice, ''Philae'' achieved the first-ever "soft" (nondestructive) landing on a comet nucleus, although the lander's final, uncontrolled touchdown left it in a non-optimal location and orientation. Despite the landing problems, the probe's instruments obtained the first images from a comet's surface. Several of the instruments on ''Philae'' made the first direct analysis of a comet, sending back data that would be analysed to determine the composition of the surface. In October 2020, scientific journal ''Nature'' published an article which re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUSC
The Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) is a public medical school in South Carolina. It opened in 1824 in Charleston as a small private college aimed at training physicians and has since established hospitals and medical facilities across the state. It is one of the oldest continually operating schools of medicine in the United States and the oldest in the Deep South. The school's main building was designed by Charleston architect Albert W. Todd. The school has expanded into a state university with a medical center and six colleges for the education of health professionals, biomedical scientists, and other health care personnel. It also operates as a center for research and has a public hospital. Colleges College of Medicine History The College of Medicine began in 1823 with the incorporation of the Medical College of South Carolina, a private institution of the Medical Society of South Carolina. Seven Charleston physicians formed the initial faculty with 30 student ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout
is an asteroid sample-return mission operated by the Japanese state space agency JAXA. It is a successor to the '' Hayabusa'' mission, which returned asteroid samples for the first time in June 2010. ''Hayabusa2'' was launched on 3 December 2014 and rendezvoused in space with near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu on 27 June 2018. It surveyed the asteroid for a year and a half and took samples. It left the asteroid in November 2019 and returned the samples to Earth on 5 December 2020 UTC. Its mission has now been extended through at least 2031, when it will rendezvous with the small, rapidly-rotating asteroid . ''Hayabusa2'' carries multiple science payloads for remote sensing and sampling, and four small rovers to investigate the asteroid surface and analyze the environmental and geological context of the samples collected. Mission overview Asteroid 162173 Ryugu (formerly designated ) is a primitive carbonaceous near-Earth asteroid. Carbonaceous asteroids are thought to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
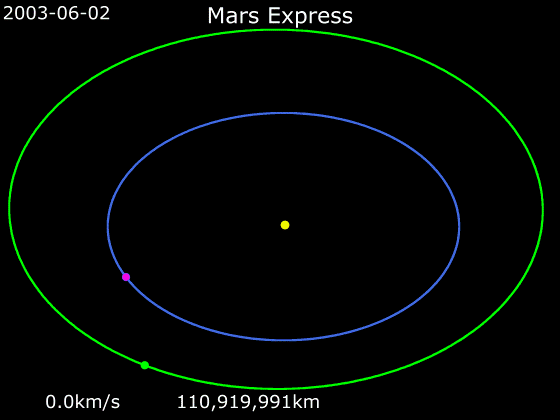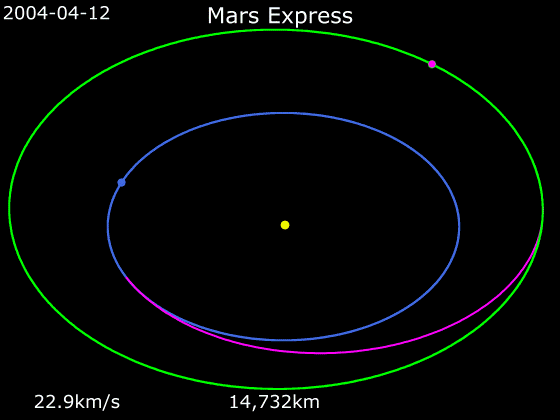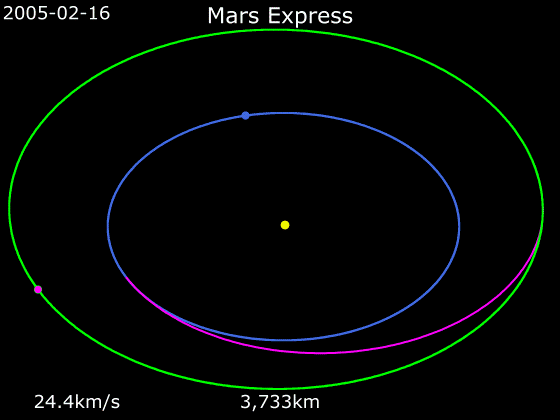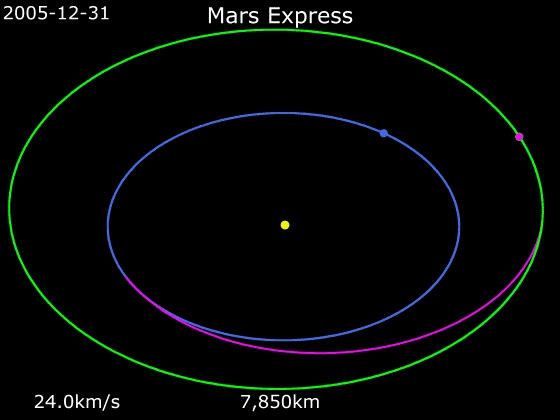
Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally referred to the speed and efficiency with which the spacecraft was designed and built. However, "Express" also describes the spacecraft's relatively short interplanetary voyage, a result of being launched when the orbits of Earth and Mars brought them closer than they had been in about 60,000 years. ''Mars Express'' consists of two parts, the ''Mars Express Orbiter'' and ''Beagle 2'', a lander designed to perform exobiology and geochemistry research. Although the lander failed to fully deploy after it landed on the Martian surface, the orbiter has been successfully performing scientific measurements since early 2004, namely, high-resolution imaging and mineralogical mapping of the surface, radar sounding of the subsurface structure down to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LISA Pathfinder
LISA Pathfinder, formerly Small Missions for Advanced Research in Technology-2 (SMART-2), was an ESA spacecraft that was launched on 3 December 2015 on board Vega flight VV06. The mission tested technologies needed for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA), an ESA gravitational wave observatory planned to be launched in 2037. The scientific phase started on 8 March 2016 and lasted almost sixteen months. In April 2016 ESA announced that LISA Pathfinder demonstrated that the LISA mission is feasible. The estimated mission cost was €400 million. Mission LISA Pathfinder placed two test masses in a nearly perfect gravitational free-fall, and controlled and measured their relative motion with unprecedented accuracy. The laser interferometer measured the relative position and orientation of the masses to an accuracy of less than 0.01 nanometres, a technology estimated to be sensitive enough to detect gravitational waves by the follow-on mission, the Laser Interferometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (satellite Navigation)
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA), operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, with two ground operations centres in Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open to everyone. A fully encrypted higher-precision service is available for free to government-authorized users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1 m precision. Galileo is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaia (spacecraft)
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented precision. The mission aims to construct by far the largest and most precise 3D space catalog ever made, totalling approximately 1 billion astronomical objects, mainly stars, but also planets, comets, asteroids and quasars, among others. To study the precise position and motion of its target objects, the spacecraft monitored each of them about 70 times over the five years of the nominal mission (2014–2019), and continues to do so during its extension. The spacecraft has enough micro-propulsion fuel to operate until about November 2024. As its detectors are not degrading as fast as initially expected, the mission could therefore be extended. ''Gaia'' targets objects brighter than magnitude 20 in a broad photometric band that covers the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter
The ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO or ExoMars Orbiter) is a collaborative project between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Russian Roscosmos agency that sent an atmospheric research orbiter and the ''Schiaparelli'' demonstration lander to Mars in 2016 as part of the European-led ExoMars programme. The Trace Gas Orbiter delivered the ''Schiaparelli'' lander on 16 October 2016, which crashed on the surface due to a premature release of the parachute. The orbiter began aerobraking in March 2017 to lower its initial orbit of . Aerobraking concluded on 20 February 2018 when a final thruster firing resulted in an orbit of . Additional thruster firings every few days raised the orbiter to a circular "science" orbit of , which was achieved on 9 April 2018. A key goal is to gain a better understanding of methane () and other trace gases present in the Martian atmosphere that could be evidence for possible biological activity. The programme will follow with the ''Kazachok'' la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsches Zentrum Für Luft- Und Raumfahrt
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. DLR also acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.261 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |