|
Teleprocessing Monitor
{{refimprove, date=July 2009 A teleprocessing monitor (also, Transaction Processing Monitor or TP Monitor) is a control program that monitors the transfer of data between multiple local and remote terminals to ensure that the transaction processes completely or, if an error occurs, to take appropriate actions. The term is frequently used in mainframe-based wide area networks, where TP monitors manage the transfer of data between several clients making requests to a server. TP monitors will control and manage the data smoothly to available servers by detecting hardware failures and switching to another node. Teleprocessing monitors were originally developed to allow several clients to connect to one server. However, they developed to what are now known as transaction processing monitors (TPMs). A TPM breaks down applications or code into transactions and ensures that all databases are updated in a single transaction. This is useful for airline reservations, car rentals, hotel accommo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components. A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using the language's compiler. ( Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within the language's interpreter. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. If the source code is requested for execution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenVMS
OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide. It was first announced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as VAX/VMS (''Virtual Address eXtension/Virtual Memory System'') alongside the VAX-11/780 minicomputer in 1977. OpenVMS has subsequently been ported to run on DEC Alpha systems, the Itanium-based HPE Integrity Servers, and select x86-64 hardware and hypervisors. Since 2014, OpenVMS is developed and supported by VMS Software Inc. (VSI). OpenVMS offers high availability through clustering — the ability to distribute the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
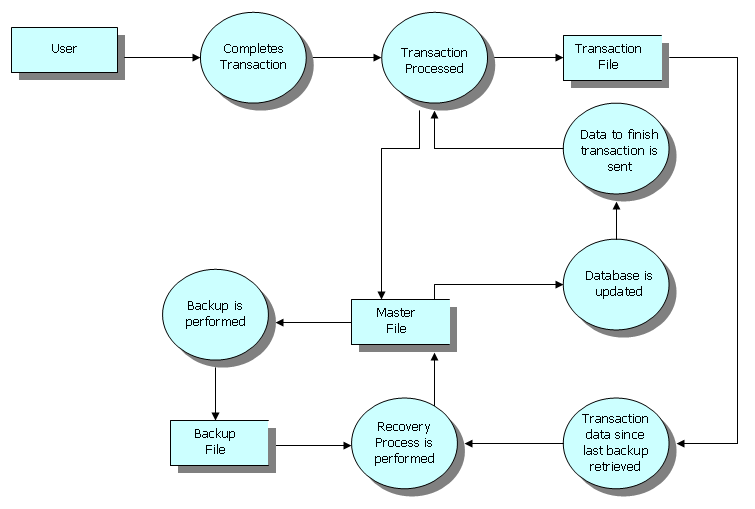
Transaction Processing System
Transaction processing is a way of computing that divides work into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. A transaction processing system (TPS) is a software system, or software/ hardware combination, that supports transaction processing. History The first transaction processing system was SABRE, made by IBM for American Airlines, which became operational in 1964. Designed to process up to 83,000 transactions a day, the system ran on two IBM 7090 computers. SABRE was migrated to IBM System/360 computers in 1972, and became an IBM product first as '' Airline control Program (ACP)'' and later as '' Transaction Processing Facility (TPF)''. In addition to airlines TPF is used by large banks, credit card companies, and hotel chains. The Hewlett-Packard NonStop system (formerly Tandem NonStop) was a hardware and software system designed for ''Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)'' introduced in 1976. The systems were designed for transaction processing and provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley (Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/Solaris (operating system), Solaris), Hewlett-Packard, HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise, HPE (HP-UX), and IBM (IBM AIX, AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuxedo (software)
Tuxedo (Transactions for Unix, Extended for Distributed Operations) is a middleware platform used to manage distributed transaction processing in distributed computing environments. Tuxedo is a transaction processing system or transaction-oriented middleware, or enterprise application server for a variety of systems and programming languages. Developed by AT&T in the 1980s, it became a software product of Oracle Corporation in 2008 when they acquired BEA Systems. Tuxedo is now part of the Oracle Fusion Middleware. History From the beginning in 1983, AT&T designed Tuxedo for high availability and to provide extremely scalable applications to support applications requiring thousands of transactions per second on commonly available distributed systems. The original development targeted the creation and administration of operations support systems for the US telephone company that required online transaction processing (OLTP) capabilities. The Tuxedo concepts derived from the Loop M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation headquartered in Austin, Texas. In 2020, Oracle was the third-largest software company in the world by revenue and market capitalization. The company sells database software and technology (particularly its own brands), cloud engineered systems, and enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software (also known as customer experience), enterprise performance management (EPM) software, and supply chain management (SCM) software. History Larry Ellison co-founded Oracle Corporation in 1977 with Bob Miner and Ed Oates under the name Software Development Laboratories (SDL). Ellison took inspiration from the 1970 paper written by Edgar F. Codd on relational database management systems ( RDBMS) named "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks." He heard about the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encina (software)
Encina was a Distributed Computing Environment, DCE-based transaction processing system developed by Transarc, who were later acquired by IBM. It was used as the basis of IBM TXSeries, which is a variant of CICS for non-mainframe platforms (however, in newer versions of TXSeries, the Encina component has been removed.) References Transaction processing IBM software {{software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transarc
Transarc Corporation was a private Pittsburgh-based software company founded in 1989 by Jeffrey Eppinger, Michael L. Kazar, Alfred Spector, and Dean Thompson of Carnegie Mellon University. Transarc commercialized the Andrew File System (AFS), now OpenAFS, which was originally developed at Carnegie Mellon. As a member of the Open Software Foundation (later The Open Group), Transarc developed the DFS distributed filesystem component of the Distributed Computing Environment (DCE) that was sold by Open Group members. Other products included the distributed transaction processing system Encina (a basis for IBM's UNIX-based CICS products; included in IBM's TXSeries and later WebSphere), and the Solaris Solaris may refer to: Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film * ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by Stanisław Lem ** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg ** ''Solaris'' (1972 film), directed by ... binary distribution of the DCE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Interface Processor
Transaction or transactional may refer to: Commerce *Financial transaction, an agreement, communication, or movement carried out between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment *Debits and credits in a Double-entry bookkeeping system *Electronic funds transfer, the electronic exchange or transfer of money from one account to another *Real estate transaction, the process whereby rights in a unit of property is transferred between two or more parties *Transaction cost, a cost incurred in making an economic exchange *Transactional law, the practice of law concerning business and commerce Computing *Transaction processing, information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations *Database transaction, a unit of work performed within a database management system *Atomic transaction, a series of database operations such that either all occur, or nothing occurs Other uses *Transactions, the published proceedings of a learned society: ** *Transaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company and successor organizations. The BINAC, built by the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation, was the first general-purpose computer for commercial use, but it was not a success. The last UNIVAC-badged computer was produced in 1986. History and structure J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly built the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) at the University of Pennsylvania's Moore School of Electrical Engineering between 1943 and 1946. A 1946 patent rights dispute with the university led Eckert and Mauchly to depart the Moore School to form the Electronic Control Company, later renamed Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation (EMCC), based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. That company first built a computer called BINAC (BINar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Control Management System
Application Control Management System (Application Control and Management System) (ACMS) is a transaction processing monitor software system for computers running the OpenVMS operating system. ACMS was developed by Digital Equipment Corporation in the early 1980s as part of an effort to gain market share in commercial applications. (Digital's initial strength was in scientific computing.) ACMS was originally released in 1984 as part of the integrated VAX Information Architecture product set along with Rdb (relational database system), DBMS (CODASYL database system), TDMS (original forms system), DECforms (a newer forms system), CDD (Common Data Dictionary), and DATATRIEVE DATATRIEVE is a database query and report writer tool originally from Digital Equipment Corporation. It runs on the OpenVMS operating system, as well as several PDP-11 operating systems. DATATRIEVE's command structure is nearly plain English, and ... (query and report writer for record-oriented files and datab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Terminal
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. Early terminals were inexpensive devices but very slow compared to punched cards or paper tape for input, yet as the technology improved and video displays were introduced, terminals pushed these older forms of interaction from the industry. A related development was time-sharing systems, which evolved in parallel and made up for any inefficiencies in the user's typing ability with the ability to support multiple users on the same machine, each at their own terminal or terminals. The function of a terminal is typically confined to transcription and input of data; a device with significant local, programmable data-processing capability may be called a "smart terminal" or fat client. A term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |