|
Tasmanoplectron
''Tasmanoplectron isolatum'' is a rare nocturnal species of cave cricket, and is the only species represented in the genus ''Tasmanoplectron'', belonging to the family Rhaphidophoridae. In 1971, Aola M. Richards was first to describe this species in Tasmania, Australia, where its geographical distribution is restricted to.Bryant, S. L. and Shaw, J. (Editors) (2006). "Tasman Island: 2005 flora and fauna survey". ''Hamish Saunders Memorial Trust, New Zealand and Biodiversity Conservation Branch, DPIW, Hobart, Nature Conservation Report Series 06/01.'' The genus is thought to have affinities with New Zealand fauna due to its marked differences from the other Australian Rhaphidophoridae. Distribution & Habitat ''Tasmanoplectron isolatum'' is endemic to Tasman Island off the southeast coast of Tasmania, Australia. This small long-legged insect seeks refuge among rocks, forming small artificial cavities, or in bird burrows. On Tasman Island, the species has been collected f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Island
The Tasman Island, part of the Tasman Island Group, is an oval island with an area of , lying close to the south-eastern coast of Tasmania, Australia. The island is located in the Tasman Sea, situated off the Tasman Peninsula and is contained within the Tasman National Park. The island is a plateau surrounded by steep dolerite cliffs, with its highest point above sea level (asl) and an average plateau height of asl. It is the site of the Tasman Island Lighthouse and weather station, which has been automated since 1976 and unstaffed since 1977. Flora and fauna Plants The island was once thickly forested. The forest has largely disappeared as a result of cutting the trees for firewood and of intense fires. When the lighthouse was staffed the keepers kept livestock, including cattle, sheep and draught horses, and maintained grassland for their grazing. Areas of grassland remain along with other vegetation communities of heathy scrub, regenerating scrub, sheoak woodland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaphidophoridae
The orthopteran family Rhaphidophoridae of the suborder Ensifera has a worldwide distribution. Common names for these insects include cave wētā, cave crickets, camelback crickets, camel crickets, Hogan bugs, spider crickets (sometimes shortened to "criders", or "land shrimp" or "sprickets",) and sand treaders. Those occurring in New Zealand, Australia, and Tasmania are typically referred to as jumping or cave wētā. Most are found in forest environments or within caves, animal burrows, cellars, under stones, or in wood or similar environments. All species are flightless and nocturnal, usually with long antenna (biology), antennae and legs. More than 500 species of Rhaphidophoridae are described. The well-known Gryllidae, field crickets are from a different superfamily (Grylloidea) and only look vaguely similar, while members of the family Tettigoniidae may look superficially similar in body form. Description Most cave crickets have very large hind legs with "drumstick-shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macropathinae
The orthopteran family Rhaphidophoridae of the suborder Ensifera has a worldwide distribution. Common names for these insects include cave wētā, cave crickets, camelback crickets, camel crickets, Hogan bugs, spider crickets (sometimes shortened to "criders", or "land shrimp" or "sprickets",) and sand treaders. Those occurring in New Zealand, Australia, and Tasmania are typically referred to as jumping or cave wētā. Most are found in forest environments or within caves, animal burrows, cellars, under stones, or in wood or similar environments. All species are flightless and nocturnal, usually with long antennae and legs. More than 500 species of Rhaphidophoridae are described. The well-known field crickets are from a different superfamily (Grylloidea) and only look vaguely similar, while members of the family Tettigoniidae may look superficially similar in body form. Description Most cave crickets have very large hind legs with "drumstick-shaped" femora and equally l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Cricket
The orthopteran family Rhaphidophoridae of the suborder Ensifera has a worldwide distribution. Common names for these insects include cave wētā, cave crickets, camelback crickets, camel crickets, Hogan bugs, spider crickets (sometimes shortened to "criders", or "land shrimp" or "sprickets",) and sand treaders. Those occurring in New Zealand, Australia, and Tasmania are typically referred to as jumping or cave wētā. Most are found in forest environments or within caves, animal burrows, cellars, under stones, or in wood or similar environments. All species are flightless and nocturnal, usually with long antennae and legs. More than 500 species of Rhaphidophoridae are described. The well-known field crickets are from a different superfamily (Grylloidea) and only look vaguely similar, while members of the family Tettigoniidae may look superficially similar in body form. Description Most cave crickets have very large hind legs with "drumstick-shaped" femora and equally long, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leg Spination
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element capable of changing length and rotating about an omnidirectional "hip" joint. As an anatomical animal structure it is used for locomotion. The distal end is often modified to distribute force (such as a foot). Most animals have an even number of legs. As a component of furniture, it is used for the economy of materials needed to provide the support for the useful surface such as the table top or chair seat. Terminology *Uniped: 1 leg, such as clams * Biped: 2 legs, such as humans and birds *Triped: 3 legs, which typically does not occur naturally in healthy animals * Quadruped: 4 legs, such as dogs and horses Many taxa are characterized by the number of legs: * Tetrapods have four legs. Squamates of genus '' Bipes'' have only two. Cae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulanoplectron
''Insulanoplectron'' is a genus of cave wētā in the family '' Rhaphidophoridae'', with just one species: the Snares Island Wētā. ''Insulanoplectron spinosum'' is endemic to the subantartic Snares Island of New Zealand, where it is considered to be naturally uncommon. Wētā are nocturnal crickets found all around the world. During the day on the Snares, wētā can be found hiding in seabird burrows.Butts, C. A. (1984). ''The biologies of two species of weta endemic to the snares island Zealandrosandrus subantarcticus Salmon (Orthoptera: Stenopelmatidae) and Insulanoplectron spinosum Richards (Orthoptera: Rhaphidophoridae)'' hesis https://ir.canterbury.ac.nz/server/api/core/bitstreams/5b27b533-c676-438b-bd89-36d73da30cc5/content Taxonomy Cave wētā were found on Snares Island in 1947 by R. A. Falla and C. A. Fleming. Detailed inferences could not be made about the species, as not many individuals had been found. In 1970, sufficient evidence had been collected, leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
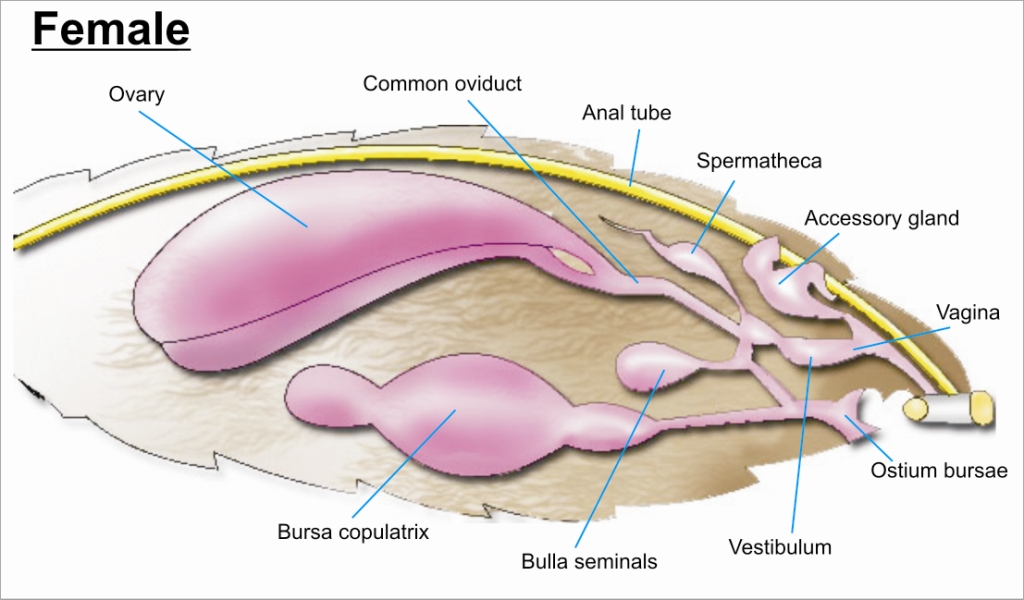
Insect Reproductive System
Most insects reproduce oviparously, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries. Sperm, produced by the male in one testis or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermathecae. At the time of fertilization, the eggs travel along oviducts to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor. Internal Female Female insects are able to make eggs, receive and store sperm, manipulate sperm from different males, and lay eggs. Their reproductive systems are made up of a pair of ovaries, accessory glands, one or more spermathecae, and ducts connecting these parts. The ovaries make eggs and accessory glands produce the substances to help package and lay the eggs. Spermathecae store sperm for varying periods of time and, along with portions of the oviducts, can control sperm use. The ducts and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman 1
Tasman most often refers to Abel Tasman (1603–1659), Dutch explorer. Tasman may also refer to: Animals and plants * Tasman booby * Tasman flax-lily * Tasman parakeet (other) * Tasman starling * Tasman whale People * Tasman (name), a name of Dutch origin, including a list of people with the name Places New Zealand * Mount Tasman, in the Southern Alps of South Island * Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere, at the northern end of South Island * Tasman Glacier, in the Southern Alps of South Island * Tasman Lake, formed by recent melting and retreat of the Tasman Glacier * Tasman Region, a region and a district of New Zealand in the north of South Island * Tasman River, flowing from Tasman Lake and contributed to by other glacial rivers Tasmania, Australia * Tasman Fracture, an ocean trench southwest of Tasmania * Tasman Island, an island off the southeast coast of the Tasman Peninsula * Tasman National Park, at the south end of the Tasman Peninsula * Tasman Outflow, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon")." Taxonomy is different from me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hindlimb With reference to quadrupeds, the term hindleg or back leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term lower limb is often used. Location It is located on the limb of an animal. Hindlimbs are present in a large number of quadrupeds. Though it is a posterior limb, it can cause lameness in some animals. The way of walking through hindlimbs are called bipedalism. Benefits of hindlimbs Hindlimbs are helpful in many ways, some examples are: Frogs Frogs can easily adapt at the surroundings using hindlimbs. The main reason is it can jump high to easily escape to its predator and also to catch prey. It can perform some tricks using the hindlimbs such as the somersault and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |