|
Tashigang, Ngari Prefecture
Tashigang (, transl. "auspicious hillock"), with a Chinese spelling Zhaxigang (), is a village in the Gar County of the Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. The village forms the central district of the Zhaxigang Township. It houses an ancient monastery dating to the 11th century. Geography Tashigang is in the Indus Valley, close to the border with Ladakh (Indian union territory), near the confluence of the Sengge Zangbo and Gartang rivers (the two headwaters of the Indus River). Sven Hedin described the Tashigang monastery as follows: Tashigang was described by European travellers in the 18th and 19th centuries as the first Tibetan village, as they travelled from Ladakh towards Kailas–Manasarovar. : "The earliest of these was the account by an Italian Jesuit, Ippolito Desideri, who traveled this route in 1716 and who described "Trescy-Khang" (Tashigong) as a "town on the frontier between Second and Third Tibet .e., between Ladakh and Tibet. In 1820, J. B. Fraser published an itiner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Postal Codes In China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures or prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000–009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People's Republic of China. Mail to ROC is treated as international mail, and uses postal codes set forth by Chunghwa Post. Codes starting from 999 are the internal codes use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasarovar
Lake Manasarovar (Sanskrit: मानसरोवर), also called Mapam Yutso (;) locally, is a high altitude freshwater lake fed by the Kailash Glaciers near Mount Kailash in Burang County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. The lake along with Mount Kailash to its north are sacred sites in four religions: Bön, Buddhism, Hinduism and Jainism. Etymology The Sanskrit word "''Manasarovar''" (मानसरोवर) is a combination of two Sanskrit words; "''Mānas''" (मानस्) meaning "mind (in its widest sense as applied to all the mental powers), intellect, intelligence, understanding, perception, sense, conscience''" while "''sarovara''" (सरोवर) means "''a lake or a large pond deep enough for a lotus''". Geography It is located about 50 kilometers to the northwest of Nepal, about 100 kilometers east of Uttarakhand, and in the southwest region of Tibet. The lake lies at above mean sea level, a relatively high elevation for a large freshw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demchok Karpo
Demchok (), KNAB Place Name Databse, retrieved 27 July 2021. previously called New Demchok, and called Parigas () by the Chinese, is a village and military encampment in the Indian-administered that is disputed between India and China. It is administered as part of the in the of |
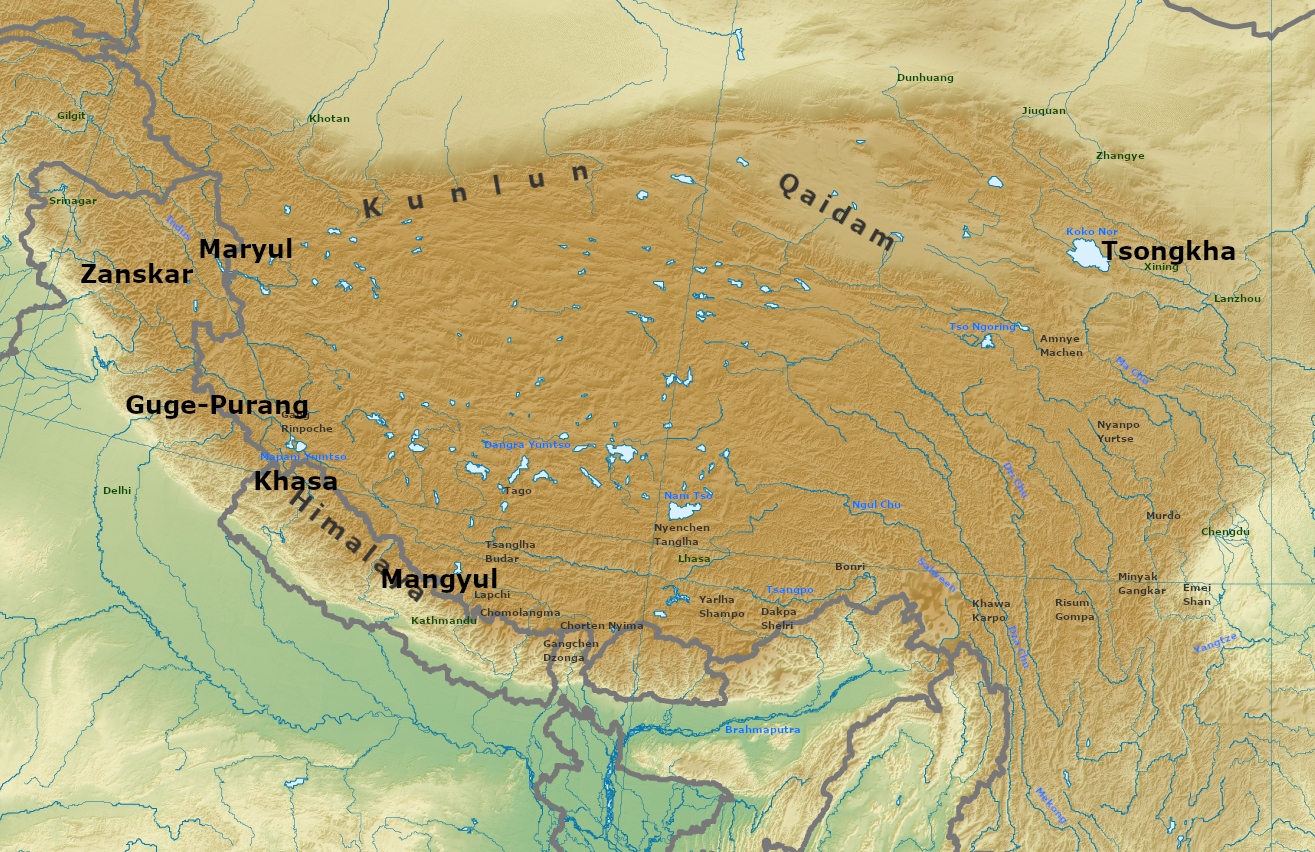
Zanskar
Zanskar, Zahar (locally) or Zangskar, is a tehsil of Kargil district, in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. The administrative centre is Padum (former Capital of Zanskar). Zanskar, together with the neighboring region of Ladakh, was briefly a part of the kingdom of Guge in Western Tibet. Zanskar lies 250 km south of Kargil town on NH301. The Zanskar Range is a mountain range in the union territory of Ladakh that separates the Zanskar valley from Indus valley at Leh. Geologically, the Zanskar Range is part of the Tethys Himalaya, an approximately 100-km-wide synclinorium formed by strongly folded and imbricated, weakly metamorphosed sedimentary series. The average height of the Zanskar Range is about 6,000 m (19,700 ft). Its eastern part is known as Rupshu. The Zanskar had a population of approximately 20,000 in 2020. There has been demands to convert Zanskar into a district. Etymology Zanskar ( ''zangs dkar'') appears as ''“Zangskar”'' mostly in aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burang Town
Purang or Burang, known as Puhreng in Tibetan (, IPA: puʂeŋ), is a town which serves as the administrative center of Purang County, Ngari Prefecture of the Tibet Autonomous Region ''(TAR)'', China. The town lies at an altitude of 3,900m (12,795 feet) in the valley of the Karnali River. As of 2010, the town had a population of 6,047. To the south are Gurla Mandhata (Mount Namonanyi) and the Abi Gamin ranges. Lake Manasarovar and Mount Kailash are to the north. This region is the mythological and actual river nexus of the Himalaya with sources of the Indus, Ganges and Yarlung Tsangpo/Brahmaputra all within of Purang. Etymology The Tibetan name of the town (''spu hreng'') is a corruption of the Zhang-zhung words ''pu hrang'', meaning 'horse head'. Nepalese and Indians call the town Taklakot from Tibetan 'Takla Khar' (). ''Takla Khar'' means ''Tiger Hill Castle'', which is the name of a historic Zhang-zhung fortress in the county. Saryu Karnali River's ''Peacock Mouth'' source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast area including south-eastern Zanskar, Upper Kinnaur district, and Spiti Valley, either by conquest or as tributaries. The ruins of the former capital of the Guge kingdom are located at Tsaparang in the Sutlej valley, not far from Mount Kailash and westwards from Lhasa. History Founding Guge was founded in the 10th century. Its capitals were located at Tholing and Tsaparang. Kyide Nyimagon, a great-grandson of Langdarma, the last monarch of the Tibetan Empire, fled from the insecure conditions in Ü-Tsang in 910 to arrive in Ngari (West Tibet). He established a kingdom around 912, annexing Purang and Guge. He established his capital in Guge. Nyimagon later divided his lands into three parts. The king's eldest son Palgyigon bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryul
Maryul (also called ''Mar-yul'' of ''mNgah-ris''), later the Kingdom of Ladakh, was a west Tibetan kingdom based in modern-day Ladakh and Tibet. The kingdom had its capital at Shey. The kingdom was founded by Lhachen Palgyigon, during the rule of his father Kyide Nyimagon, in .: "it seems that his father bequeathed him a theoretical right of sovereignty, but the actual conquest was effected by dPal-gyi-mgon himself." It stretched from the Zoji La at the border of Kashmir to Demchok in the southeast, and included Rudok and other areas presently in Tibet. The kingdom came under the control of the Namgyal dynasty in 1460, eventually acquiring the name "Ladakh", and lasted until 1842. In that year, the Dogra general Zorawar Singh, having conquered it, made it part of the would-be princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. Etymology ''Mar-yul'' has been interpreted in Tibetan sources as lowland (of Ngari),. Scholars suspect that it was a proper name that was in use earlier, even bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese National Geography
''Chinese National Geography'' () is a Chinese monthly magazine similar to the ''National Geographic Magazine''. Founded in 1949 in China, the magazine has revamped itself several times, and is now a popular magazine in mainland China. There is also an edition in traditional Chinese for readers in Hong Kong and Taiwan. History Founded by a group of teachers with a keen interest in geography in 1949, the original Chinese edition was first published in January 1950 under the name ''Dili Zhishi'' (''Knowledge of Geography''; Chinese: 《地理知识》). The magazine focused on delivering scientific and geographical concepts. At first only 600 copies were printed, but the publication quickly became popular, and soon 2,000 copies of each volume were being printed. From August–December 1960, ''Dili Zhishi'' temporarily stopped publication. It reformed itself and resumed publication in January 1961 under a new name, ''Dili'' (''Geography''; Chinese: 《地理》). However, this new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rala
Ras-related protein Ral-A (RalA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RALA'' gene on chromosome 7. This protein is one of two paralogs of the Ral protein, the other being RalB, and part of the Ras GTPase family. RalA functions as a molecular switch to activate a number of biological processes, majorly cell division and transport, via signaling pathways. Its biological role thus implicates it in many cancers. Structure The Ral isoforms share an 80% overall match in amino acid sequence and 100% match in their effector-binding region. The two isoforms mainly differ in the C-terminal hypervariable region, which contains multiple sites for post-translational modification, leading to diverging subcellular localization and biological function. For example, phosphorylation of Serine 194 on RalA by the kinase Aurora A results in the relocation of RalA to the inner mitochondrial membrane, where RalA helps carry out mitochondrial fission; whereas phosphorylation of Serine 198 on R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langdarma
Darma Udumtsen (), better known by his nickname Langdarma (, "Mature Bull" or "Dharma the Bull") was most likely the last Tibetan Emperor who most likely reigned from 838 to 841 CE. Early sources call him Tri Darma "King Dharma". His domain extended beyond Tibet to include Dunhuang and neighbouring Chinese regions.Samten Karmay ''in'' , pg. 57 By tradition Langdarma is held to have been anti-Buddhist and a follower of Bon. He is attributed with the assassination of his brother, King Ralpacan, in 838 AD and he is generally held to have persecuted Buddhists. According to traditional accounts, during the first two years of his rule, Langdarma remained a Buddhist, but under the influence of Wégyel Toré (), he became a follower of Bon. Following his persecution of Buddhism Atiśa was called from Sumatra to restore Buddhism to Tibet. The anti-Buddhist portrayal of this king has been questioned by several historians, most prominently Zuiho Yamaguchi. Yamaguchi, Zuiho. “The F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
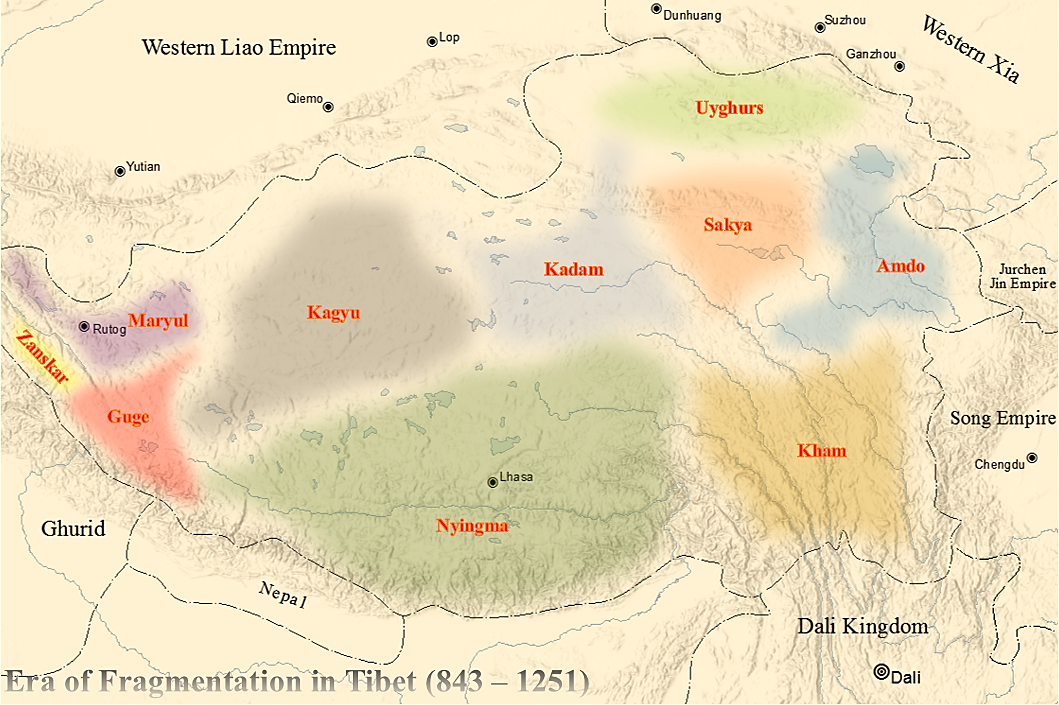
Kyide Nyimagon
Kyide Nyimagon () (), whose original name was Khri-skyid-lding, was a member of the Yarlung dynasty of Tibet and a descendant of emperor Langdarma. He migrated to Western Tibet and founded the kingdom of Ngari Khorsum ("the three divisions of Ngari") around 912 CE. After his death, his large kingdom was divided among his three sons, giving rise to the three kingdoms of Maryul (Ladakh), Guge-Purang and Zanskar-Spiti. Family After the assassination of the emperor Langdarma, the Tibetan empire entered a period of civil war over succession by Langdarma's two sons (Yum-brtan) and ('Odsrung), which divided the empire into two parts. Ösung's son Depal Khortsen (–) is believed to have controlled most or part of Central Tibet. Nyimagon was one of the sons of Depal Khortsen, the other being Trashi Tsentsän (''bKraśis-brtsegs-brtsan''). Both the sons fled Ü-Tsang (Central Tibet) in 910 when their father was murdered, at the end of the 3rd , which is taken to mark the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Era Of Fragmentation
The Era of Fragmentation (; ) was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three provinces of Tibet in 1253, under the Yuan dynasty. During this period, the political unity of the Tibetan Empire collapsed following a civil war between Yumtän (''Yum brtan'') and Ösung (''’Od-srung''), after which followed numerous rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Civil war and the decline of imperial Tibet The last emperor of the unified Tibetan Empire, Langdarma, was assassinated in 842–846, by either a Buddhist hermit or a monk named Pelgyi Dorje of Lhalung. The assassination left two possible heirs, Yumtän and Ösung, to fight for the throne, leading to a civil war. The successors of Ösung controlled the region of Ngari, while the successors of Yumtän controlled the Ü region. The son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)