|
Taplejung
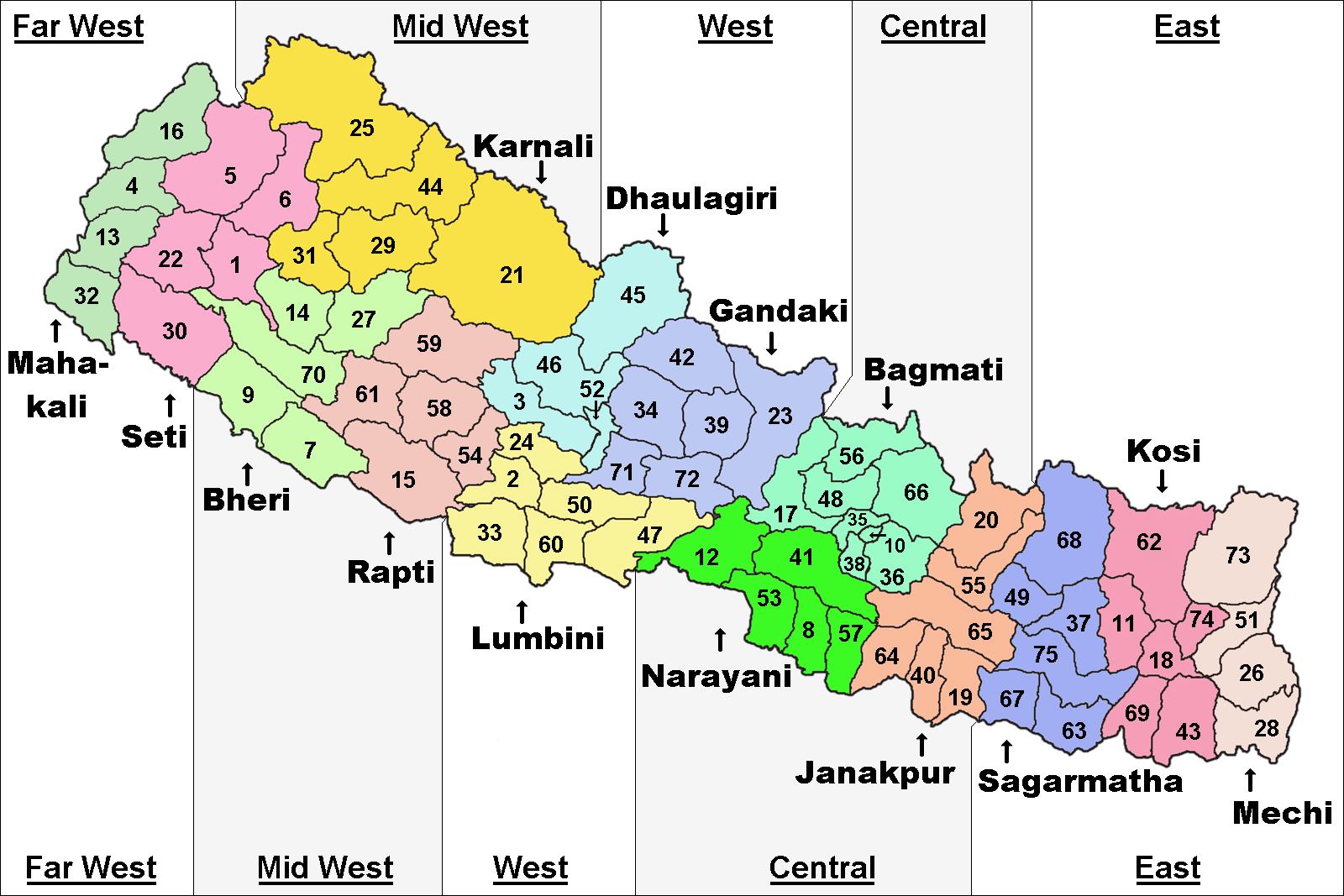
Taplejung District ( ne, ताप्लेजुङ जिल्ला ) is one of 77 districts of Nepal and one of the 14 districts of Province No. 1. It is remotely located in the Himalayas in Eastern Nepal with Tibet to the north across the Himalayas. Taplejung is the third largest district (by area) of Nepal. The district covers an area of and has a total population (2011 Nepal census) of 127,461. The district is surrounded by Tibet in the north, Sankhuwasabha District in the west, Tehrathum District and Panchthar District in the south and Sikkim (India) in the east. Geographically, the district is located at a latitude of 27º 06’ to 27º 55’N and a longitude of 87º57’ to 87º40’ E. Etymology Literally meaning of Taplejung is "a fort of King Taple" in Limbu language. There was a fort situated at that area in medieval times which was built by King Taple. History Before the unification of Nepal, the area of Taplejung and its surrounds were called ''Pallo Kirat'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phungling Municipality
Phungling Municipality (previously also ''Taplejung Municipality'') is a municipality located in Taplejung District in the Province No. 1 of Nepal. The municipality was formed merging the then two Village Development Committees of Phungling and Dokhu in May 2014. At the time of the 2011 Nepal census it had a population of 19,085 people and 4,480 individual households. Background Phungling was a Village Development Committee along with other 49 VDCs in Taplejung District before 2014. At the time of 2011 Nepal census, it had total population of 14,974 individuals and 3571 households. On 8 May 2014, Government of Nepal announced 72 new municipalities. The government merged 283 VDCs to create 72 new municipalities. Dokhu VDC was merged with Phungling VDC to form new Taplejung Municipality. On 10 March 2017, Nepal restructured the old administrative system into 753 new local level body thus Hangdeva, Phurumbu and Phawakhola VDCs merged with the then Taplejung municipality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanchenjunga
Kangchenjunga, also spelled Kanchenjunga, Kanchanjanghā (), and Khangchendzonga, is the third List of highest mountains on Earth, highest mountain in the world. Its summit lies at in a section of the Himalayas, the ''Kangchenjunga Himal'', which is bounded in the west by the Tamur River, in the north by the Lhonak River and Jongsong Peak, Jongsang La, and in the east by the Teesta River. It lies in the border region between Nepal and Sikkim state of India, with three of the five peaks, namely Main, Central and South, directly on the border, and the peaks West and Kangbachen in Nepal's Taplejung District. Until 1852, Kangchenjunga was assumed to be the List of past presumed highest mountains, highest mountain in the world, but calculations and measurements by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India in 1849 showed that Mount Everest, known as Peak XV at the time, is actually higher. After allowing for further verification of all calculations, it was officially announced in 185 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankhuwasabha District
Sankhuwasabha District ( ne, सङ्खुवासभा जिल्ला ) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. The district's area is 3,480 km2 with a population of 159,203 in 2001 and 158,742 in 2011. The administrative center is Khandbari. Bordering districts are Bhojpur, Terhathum and Dhankuta in Koshi Zone; Solukhumbu in Sagarmatha Zone; and Taplejung in Province No. 1. Tingri County of Shigatse Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China borders to the north. Geography and climate The Arun River enters from Tibet at an elevation of about 3,500 meters (11,500 feet) and flows south across the district, forming one of the world's deepest valleys relative to 8,481 meter Makalu to the west and 8,586 meter Kangchenjunga to the east. Demographics Religion Languages See also * Arun Valley *Tumlingtar Airport * khadbari *Panchkhapan Panchkhapan ( ne, पाँचखप्पन) is an urban municipality out of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roads In Nepal
The Economic Survey 2014–15 released by the Ministry of Finance (Nepal), shows that the country has total road network of 80,078 km that includes 26,935 km roads constructed and being maintained by the Department of Roads (DoR) and 53,143 km roads constructed by the government local bodies. This includes the national highway system, feeder roads, district roads and urban roads. National Highways This is the list of national highways in Nepal. Feeder Roads This is the list of feeder or regional roads in Nepal. District Roads Road that improve the commutes and connectivity within a district are considered District Roads. Below is data from Department of Roads, Nepal.https://dor.gov.np/home/publication/statistics-of-strategic-road-network-2-17-18/force/part-2-ssrn-2-17-18 See also * National Highway System (Nepal) *Churia Tunnel External links * * * {{cite web , url = https://dor.gov.np/home/publication/general-documents/nepal-road-standard-2-7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Nepal
The Eastern Development Region ( Nepali: पुर्वाञ्चल विकास क्षेत्र, ''Purwānchal Bikās Kshetra'') was one of Nepal's five development regions. It is also known as Kirata region. It was located at the eastern end of the country with its headquarters at Dhankuta. The town of Dhankuta was the headquarter of the Eastern Region, as well as the headquarter of the Dhankuta District. History On April 13, 1961 Mahendra, the king of Nepal, divided the existing 35 districts into 75 districts and grouped them into 14 administrative zones. In 1972, the King of Nepal grouped 14 zones into total 4 development regions, thus Eastern Development Region came into existence. On 20 September 2015, Eastern Development Region including all other development regions of Nepal were abolished, when the new Constitution of Nepal-2015 was proclaimed. The total area of the region was 28,456 km². Administrative divisions The region administratively was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbu Language
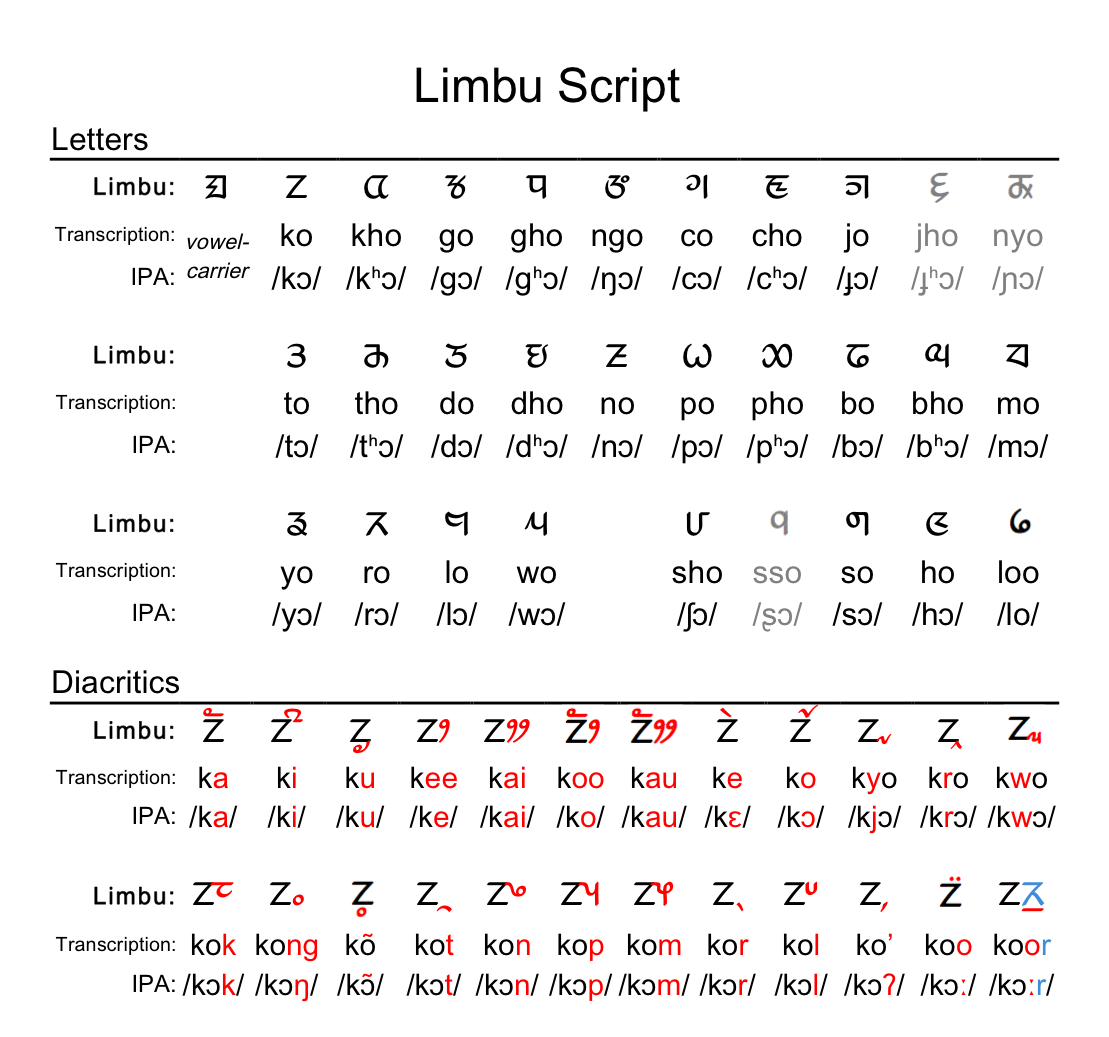
Limbu (Limbu: , ''yakthuṅ pan'') is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Limbu people of Nepal and Northeastern India (particularly Darjeeling, Kalimpong, Sikkim, Assam and Nagaland) as well as expatriate communities in Bhutan. The Limbu refer to themselves as ''Yakthung'' and their language as ''Yakthungpan.'' Yakthungpan has four main dialects: Phedape, Chhathare, Tambarkhole and Panthare dialects. Among four dialects and/or many dialects, the Phedape dialect is widely spoken and well understood by most Yakthungpan speakers. However, as there are some dominant Panthare scholars who have role to create knowledge and control knowledge in the Limbu communities, Panthare dialect is being popularised as a "standard" Limbu language. As Panthare Yakthungs are much more engaged in central political position and administrative positions, they are trying to introduce Panthare dialect as a Standard Yakthungpan. Yakthungpan (Limbu language) is one of the major languages spoken and wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Nepal
Districts in Nepal are second level of administrative divisions after provinces. Districts are subdivided in municipalities and rural municipalities. There are seven provinces and 77 districts in Nepal. After the state's reconstruction of administrative divisions, Nawalparasi District and Rukum District were divided into Parasi District (officially Nawalparasi (West of Bardaghat Susta) District) and Nawalpur District (officially Nawalparasi (East of Bardaghat Susta) District), and Eastern Rukum District and Western Rukum District respectively. District official include: * Chief District Officer, an official under Ministry of Home Affairs is appointed by the government as the highest administrative officer in a district. The C.D.O is responsible for proper inspection of all the departments in a district such as health, education, security and all other government offices. * District Coordination Committee acts as an executive to the District Assembly. The DCC coordinates with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Coordination Committee
District administration makes up the third level of government division in Nepal. The provision for a District Assembly, which acts as the legislature at the district-level, is mentioned in Part 17 of the Constitution of Nepal. The 77 districts of Nepal each have their own district assemblies which in turn elect their own District Coordination Committees, which serves as the executive at the district-level. In addition to this each district also has a District Administration Office which oversees the general administration of each district. District Administration Office The District Administration Office ( ne, जिल्ला प्रशासन कार्यालय) is a general administration of government in each district of Nepal. The government of Nepal appoints a Chief District Officer in each district to function as a Chief Administration Officer. The Local Administration Act, 2028 (1971) was implemented to conduct local administration in accordance with the dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Nepal
Nepal measures about along its Himalayan axis by across. It has an area of . Nepal is landlocked by China's Tibet Autonomous Region to the north and India on other three sides. West Bengal's narrow ''Siliguri Corridor'' separate Nepal and Bangladesh. To the east are Bhutan and India. Landform regions For a country of its size, Nepal has tremendous geographic diversity. It rises from as low as elevation in the tropical Terai—the northern rim of the Gangetic Plain, through beyond the perpetual snow line to 90 peaks over including Earth's highest ( Mount Everest or ''Sagarmatha''). In addition to the continuum from tropical warmth to cold comparable to polar regions, average annual precipitation varies from as little as in its narrow proportion of the rainshadow north of the Himalayas to as much as on windward slopes, the maximum mainly resting on the magnitude of the South Asian monsoon. Forming south-to-north transects, Nepal can be divided into three belts: Terai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanchenjunga Conservation Area
Kanchenjunga Conservation Area is a protected area in the Himalayas of eastern Nepal that was established in 1997. It covers in the Taplejung District and comprises two peaks of Kanchenjunga. In the north it adjoins the Qomolangma National Nature Preserve in Tibet, and in the east the Khangchendzonga National Park in Sikkim. To the west it borders the Sankhuwasabha District. It ranges in elevation from . It is part of the Sacred Himalayan Landscape, which is being developed by WWF Nepal in partnership with the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development. History When the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area was designated in March 1997, it was Nepal's third Conservation Area. In April 2003, a ''Kanchenjunga Conservation Area Management Council'' was formed with the support of WWF Nepal, comprising seven ''Conservation Area User Committees'', 44 ''User Groups'', and 32 ''Mother Groups''. These community based institutions support effective implementation of all planned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhankuta District
Dhankuta District ( ne, धनकुटा जिल्ला) () is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. The district covers an area of and has a population (2011) of 163,412. Dhankuta is the district headquarters of Dhankuta District. History Dhankuta was a part of Kirat Region before unification of those parts into Kingdom of Nepal. After 1816 there were 10 districts in Nepal and Dhankuta-chainpur district was one of them. All land from east of Dudhkosi river to the Mechi river was one district Dhankuta-chainpur. From 1885 to 1962 Nepal remained divided into 32 districts and there were six districts in eastern-hill region: East No. 1, East No. 2, East No. 3, East No. 4, Ilam and Dhankuta. Dhankuta was center of these districts. That time also dhankuta was a large (by area) district. Current Sankhuwasabha, Tehrathum, Taplejung, Panchthar and Dhankuta districts were Incorporated under one district. The total area of the former Dhankuta district was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbu People
The Limbu (exonym) or Yakthung (endonym) are a Sino-Tibetan indigenous tribe (Bhot-Burmeli) of the Himalayan region of eastern Nepal, Sikkim, and western Bhutan. The original name of the Limbu is ''Yakthung'' () or ''Yakthum''. Limbu males are called ''Yakthungba'' or ''Yakthumba'' and Limbu females are called "Yakthumma" or "Yakthungma". Ancient texts state that "Yakthung" or "Yakthum" is a derivative of Yaksha and some interpret its meaning as the "Yaksha winner". In the Limbu language it means "heroes of the hills" (Yak - hills, thung or thum - heroes or mighty warriors), which connotates with the ancient Kiratis. Subba is a title given by the Shah Kings only to Limbu village chiefs. Subba was not an indigenous Yakthung terminology, but now the two terms are almost interchangeable. People often debate about the use of term "Subba" as their surname in Limbu tribe. It is important to note that only the village chiefs were allowed to use the term Subba in their name. It was ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |