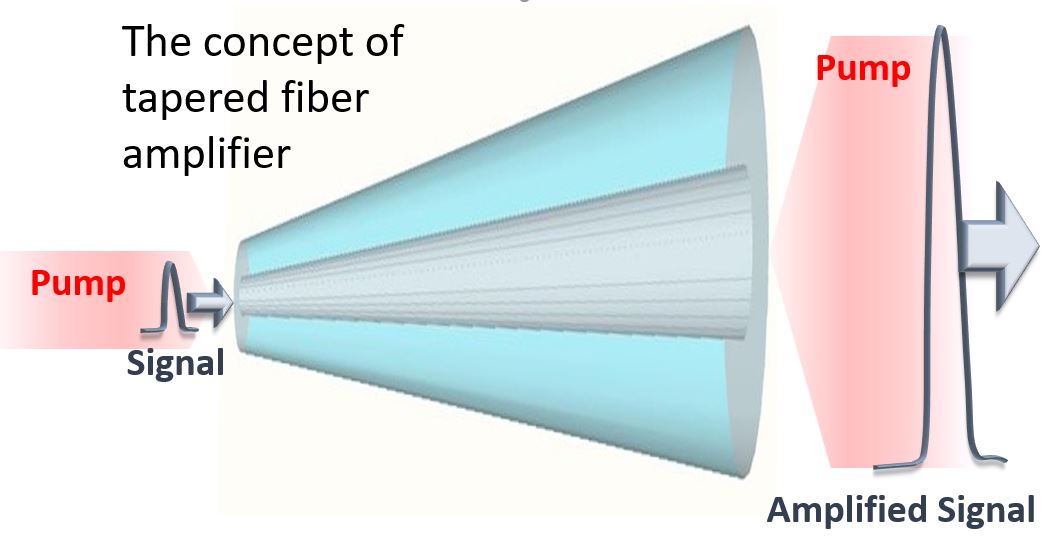
|
Tapered Double-clad Fiber
A tapered double-clad fiber (T-DCF) is a double-clad optical fiber which is formed using a specialised fiber drawing process, in which temperature and pulling forces are controlled to form a taper along the length of the fiber. By using pre-clad fiber preforms both the fiber core and the inner and outer cladding layers vary in diameter and thickness along the full length of the fiber. This tapering of the fiber enables the combination of the characteristics of conventional 8–10 µm diameter double-clad single-mode fibers to propagate light in fundamental mode with those of larger diameter (50–100 µm) double-clad multi-mode fibers used for optical amplification and lasing. The result is improved maintenance of pulse fidelity compared to conventional consistent diameter fiber amplifiers. By virtue of the large cladding diameter T-DCF can be pumped by optical sources with very poor brightness factor such as laser diode bars or even VECSELs matrices, significantly redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-clad Fiber
Double-clad fiber (DCF) is a class of optical fiber with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the ''core''. It is surrounded by the ''inner cladding'', which is surrounded by the ''outer cladding''. The three layers are made of materials with different refractive indices. There are two different kinds of double-clad fibers. The first was developed early in optical fiber history with the purpose of engineering the dispersion of optical fibers. In these fibers, the core carries the majority of the light, and the inner and outer cladding alter the waveguide dispersion of the core-guided signal. The second kind of fiber was developed in the late 1980s for use with high power fiber amplifiers and fiber lasers. In these fibers, the core is doped with active dopant material; it both guides and amplifies the signal light. The inner cladding and core together guide the pump light, which provides the energy ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-mode Optical Fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber (SMF), also known as fundamental- or mono-mode, is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single mode of light - the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions. These modes define the way the wave travels through space, i.e. how the wave is distributed in space. Waves can have the same mode but have different frequencies. This is the case in single-mode fibers, where we can have waves with different frequencies, but of the same mode, which means that they are distributed in space in the same way, and that gives us a single ray of light. Although the ray travels parallel to the length of the fiber, it is often called transverse mode since its electromagnetic oscillations occur perpendicular (transverse) to the length of the fiber. The 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Charles K. Kao for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-mode Optical Fiber
Multi-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Multi-mode links can be used for data rates up to 100 Gbit/s. Multi-mode fiber has a fairly large core diameter that enables multiple light modes to be propagated and limits the maximum length of a transmission link because of modal dispersion. The standard G.651.1 defines the most widely used forms of multi-mode optical fiber. Applications The equipment used for communications over multi-mode optical fiber is less expensive than that for single-mode optical fiber. Typical transmission speed and distance limits are 100 Mbit/s for distances up to 2 km (100BASE-FX), 1 Gbit/s up to 1000 m, and 10 Gbit/s up to 550 m. Because of its high capacity and reliability, multi-mode optical fiber generally is used for backbone applications in buildings. An increasing number of users are taking the benefits of fiber closer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiberoptic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links. There are several different physical mechanisms that can be used to amplify a light signal, which correspond to the major types of optical amplifiers. In doped fiber amplifiers and bulk lasers, stimulated emission in the amplifier's gain medium causes amplification of incoming light. In semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), electron-hole recombination occurs. In Raman amplifiers, Raman scattering of incoming light with phonons in the lattice of the gain medium produces photons coherent with the inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tampere University
, image_name = , motto = ''Human Potential Unlimited'' , established = 1925; , type = Public , rector = Mari Walls , academic_staff = 4,200 (2021) , students = 21,500 (2021) , city = Tampere , country = Finland , campus = Urban , colours = Violet , affiliations = , website = Tampere University (, shortened TAU) is a Finnish university that was established on 1 January, 2019 as a merger between the University of Tampere and Tampere University of Technology. The new university is also the major shareholder of Tampere University of Applied Sciences. History University of Tampere was founded in 1925 as the Civic College in Helsinki teaching public administration, organisation management and journalism. In 1930, a total of 195 students were enrolled at the College and its name was amended to the School of Social Sciences. As the institution grew, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear-optical Susceptibility
The Kuzyk quantum gap is a discrepancy between the maximum value of the nonlinear-optical susceptibility allowed by quantum mechanics and the highest values actually observed in real molecules. The highest possible value (in theory) is known as the Kuzyk limit, after its discoverer Professor Mark G. Kuzyk of Washington State University. Background In 2000, Professor Mark G. Kuzyk of Washington State University calculated the fundamental limit of the nonlinear-optical susceptibility of molecules. The nonlinear susceptibility is a measure of how strongly light interacts with matter. As such, these results can be used to predict the maximum attainable efficiency of various types of optical devices. For example, Kuzyk's theory can be used to estimate how efficiently optical information can be manipulated in an optical fiber (based on the Kerr effect), which in turn is related to the amount of information that a fiber-optic system can handle. In effect, the speed limit of the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Laser
A fiber laser (or fibre laser in British English) is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing. Fiber nonlinearities, such as stimulated Raman scattering or four-wave mixing can also provide gain and thus serve as gain media for a fiber laser. Advantages and applications An advantage of fiber lasers over other types of lasers is that the laser light is both generated and delivered by an inherently flexible medium, which allows easier delivery to the focusing location and target. This can be important for laser cutting, welding, and folding of metals and polymers. Another advantage is high output power compared to other types of laser. Fiber lasers can have active regions several kilometers long, and so can provide very high optical gain. They can support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Amplifier
An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiberoptic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links. There are several different physical mechanisms that can be used to amplify a light signal, which correspond to the major types of optical amplifiers. In doped fiber amplifiers and bulk lasers, stimulated emission in the amplifier's gain medium causes amplification of incoming light. In semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), electron-hole recombination occurs. In Raman amplifiers, Raman scattering of incoming light with phonons in the lattice of the gain medium produces photons coherent with the inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brillouin Scattering
Brillouin scattering (also known as Brillouin light scattering or BLS), named after Léon Brillouin, refers to the interaction of light with the material waves in a medium (e.g. electrostriction and magnetostriction). It is mediated by the refractive index dependence on the material properties of the medium; as described in optics, the ''index of refraction'' of a transparent material changes under deformation (compression-distension or shear-skewing). The result of the interaction between the light-wave and the carrier-deformation wave is that a fraction of the transmitted light-wave changes its momentum (thus its frequency and energy) in preferential directions, as if by diffraction caused by an oscillating 3-dimensional diffraction grating. If the medium is a solid crystal, a macromolecular chain condensate or a viscous liquid or gas, then the low frequency atomic-chain-deformation waves within the transmitting medium (not the transmitted electro-magnetic wave) in the carrier (re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Scattering
Raman scattering or the Raman effect () is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrational energy being gained by a molecule as incident photons from a visible laser are shifted to lower energy. This is called normal Stokes Raman scattering. The effect is exploited by chemists and physicists to gain information about materials for a variety of purposes by performing various forms of Raman spectroscopy. Many other variants of Raman spectroscopy allow rotational energy to be examined (if gas samples are used) and electronic energy levels may be examined if an X-ray source is used in addition to other possibilities. More complex techniques involving pulsed lasers, multiple laser beams and so on are known. Light has a certain probability of being scattered by a material. When photons are scattered, most of them are elastically scattered (Rayleigh scatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface. The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an objective (and hence its light-gathering ability and resolution), and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it. General optics In most areas of optics, and especially in microscopy, the numerical aperture of an optical system such as an objective lens is defined by :\mathrm = n \sin \theta, where is the index of refraction of the medium i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |