|
Tandridge (hundred)
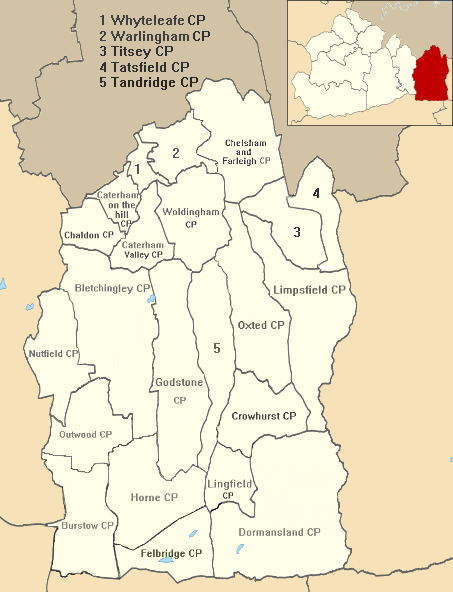
Tandridge Hundred was a hundred in Surrey, England. It comprised areas in the Tandridge District, the easternmost part of the county, bordering Kent, West Sussex and the 1965-created county of Greater London. Composition It included the parishes of Bletchingley, Caterham, Chelsham, Crowhurst, Farleigh, Godstone, Horne, Limpsfield, Lingfield, Oxted, Tandridge, Tatsfield, Titsey, Warlingham and Woldingham which at 1974 formed approximately 90% of the Tandridge District. The hundred has remained unchanged since the Domesday Book of 1086 where it was called ''Tenrige''. Approximately one sixth of all the serfs in Surrey belonged to the Tandridge hundred before the abolition of that social status across the country in the early Middle Ages. The History of Parliament Trust, University of Portsmouth and others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, Curonia, the Ukrainian state of the Cossack Hetmanate and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''hérað'' (Icelandic), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), '' satakunta'' or ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), ''kihelkond'' (Estonian), ''kiligunda'' (Livonian), '' cantref'' (Welsh) and ''sotnia'' (Slavic). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limpsfield
Limpsfield is a village and civil parish in Surrey, England, at the foot of the North Downs close to Oxted railway station and the A25.Online map distance reference tool Retrieved 27 April 2012 The composer Frederick Delius and orchestral conductor Sir Thomas Beecham are buried in the village churchyard and there are 89 s. History The village lay within the Anglo-Saxon |
List Of Hundreds Of England And Wales
Most of the counties of England were divided into hundreds or wapentakes from the late Anglo-Saxon period and these were, with a few exceptions, effectively abandoned as administrative divisions in the 19th century. In Wales a similar Celtic system of division called cantrefi (a hundred farmsteads) had existed for centuries and was of particular importance in the administration of the Welsh law. Following the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, Wales was divided into hundreds to be consistent with England. Bedfordshire *Barford *Biggleswade *Clifton *Flitt * Manshead *Redbornestoke *Stodden * Willey * Wixamtree Berkshire The County of Berkshire comprised 20 Hundreds and 193 parishes and parts of four others. From The National Gazetteer of Britain and Ireland' (1868), ''Victoria County History Berkshire'' Vol 3 (1923) & Vol 4 (1924) Buckinghamshire Until at least the time of the Domesday Survey in 1086 there were 18 hundreds in Buckinghamshire. It has been suggested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James I Of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until his death in 1625. The kingdoms of Scotland and England were individual sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, though both were ruled by James in personal union. James was the son of Mary, Queen of Scots, and a great-great-grandson of Henry VII, King of England and Lord of Ireland, and thus a potential successor to all three thrones. He succeeded to the Scottish throne at the age of thirteen months, after his mother was compelled to abdicate in his favour. Four different regents governed during his minority, which ended officially in 1578, though he did not gain full control of his government until 1583. In 1603, he succeeded Elizabeth I, the last Tudor monarch of England and Ireland, who died childless. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria County History
The Victoria History of the Counties of England, commonly known as the Victoria County History or the VCH, is an English history project which began in 1899 with the aim of creating an encyclopaedic history of each of the historic counties of England, and was dedicated to Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. In 2012 the project was rededicated to Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II in celebration of her Diamond Jubilee year. Since 1933 the project has been coordinated by the Institute of Historical Research in the University of London. History The history of the VCH falls into three main phases, defined by different funding regimes: an early phase, 1899–1914, when the project was conceived as a commercial enterprise, and progress was rapid; a second more desultory phase, 1914–1947, when relatively little progress was made; and the third phase beginning in 1947, when, under the auspices of the Institute of Historical Research, a high academic standard was set, and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed during the Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages in Europe and lasted in some countries until the mid-19th century. Unlike slaves, serfs could not be bought, sold, or traded individually though they could, depending on the area, be sold together with land. The kholops in Russia, by contrast, could be traded like regular slaves, could be abused with no rights over their own bodies, could not leave the land they were bound to, and could marry only with their lord's permission. Serfs who occupied a plot of land were required to work for the lord of the manor who owned that land. In return, they were entitled to protection, justice, and the right to cultivate certain fields within the manor to maintain their own subsistence. Serfs were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name ''Liber de Wintonia'', meaning "Book of Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him. Written in Medieval Latin, it was highly abbreviated and included some vernacular native terms without Latin equivalents. The survey's main purpose was to record the annual value of every piece of landed property to its lord, and the resources in land, manpower, and livestock from which the value derived. The name "Domesday Book" came into use in the 12th century. Richard FitzNeal wrote in the '' Dialogus de Scaccario'' ( 1179) that the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woldingham
Woldingham is a village and civil parish high on the North Downs between Oxted and Warlingham in Surrey, England, within the M25, southeast of London. The village has 2,141 inhabitants, many of whom commute to London, making Woldingham part of the London commuter belt. The village is served by the Oxted line and central London can be reached in 33 minutes by train. History Early history Two bronze fibulae, some stone arrow-heads and celts were found here about 1800. Dark and Middle Ages The place-name 'Woldingham' is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as ''Wallingeham''. It appears as ''Waldingham'' in the Close Rolls of 1232, and as ''Waldingeham'' in 1242 in the ''Book of Fees''. The name means "the village or homestead of the people of the Weald or wood". The village lay within the Anglo-Saxon administrative division of Tandridge hundred, and was held by John in 1086 from Richard Fitz Gilbert. Its Domesday assets were: 1 hide. It had 4� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warlingham
Warlingham is a villages in England, village in the Tandridge (district), Tandridge district of Surrey, England, south of the centre of London and east of the county town, Guildford. Warlingham is the centre of a civil parishes in England, civil parish that includes Hamsey Green, a wikt:contiguous, contiguous, smaller settlement to the north. Caterham is the nearest town, to the southwest. History Etymology The name means the home(stead) ''(-ham)'' of the followers ''(-(l)ing)'' of ''Waer(l)a''. The letters "ae" here are the implied earlier spelling of any Anglo-Saxon scribes to denote the sound , which when Norman scribes replaced them was replaced with "a" as in today's orthography. No trace of a local Warra or Warla has been found in Norman texts (after 1066), nor of a Waera or Waera in Anglo-Saxon texts (before 1066). It is a man's name of the period which has a comparator in Warrington. Early history, Dark Ages and Middle Ages Flint implements are not uncommon, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titsey
Titsey is a rural village and a civil parish on the North Downs almost wholly within the M25 London Orbital Motorway in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. In local government it forms the south-western part of the ward ''Tatsfield and Titsey'' and in national statistics approximates to output area E00157289. It has no railway stations however one is centred south-west, Oxted which also has the administrative centre of the district. Approximately half of it land is owned by a charity running the Titsey Place estate, with the remainder being a mixture of common and privately owned woodland and smallholdings. History The village lay within the Tandridge hundred, of greatest use in the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of England and it continues to form a parish in the church of England until its church became appropriated by that of Tatsfield. The eastern parish boundary follows the London to Lewes Way Roman road which descends the escarpment of the North Downs here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatsfield
Tatsfield is a village and civil parish in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. It is located 3.3 miles north west of Westerham and 3.9 miles north east of Oxted, and is adjacent to the Surrey border with both Greater London and Kent. Geography The village itself is on the North Downs with its centre near its highest point, at an altitude of around north of the ridge of the North Downs where the North Downs Way passes through the parish. The 'village' area is in a small salient of Surrey into the London Borough of Bromley, Greater London (to the west, north and east). Biggin Hill is immediately to the north. The boundary with Kent is less than mile to the east. Tatsfield is covered by the Westerham post town, meaning Tatsfield's postal county was Kent. Since 1996, the postal county has not been required in postal addresses. Etymology The origin of the village name is uncertain. The English Place Name Society suggests it is derived from 'a field or open land b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandridge, Surrey
Tandridge is a village and civil parish in the Tandridge District, in the county of Surrey, England. Its nucleus is on a rise of the Greensand Ridge between Oxted and Godstone. It includes, towards its middle one named sub-locality (hamlet), Crowhurst Lane End. In 2011 the parish had a population of 663 and the district had a population of 82,998. In landmarks it has one of the oldest yew trees in the country, a Grade I-listed church and the tomb of the church's main benefactor Sir George Gilbert Scott's wife, Lady Scott who lived in the parish. The village is acknowledged locally for its friendly atmosphere and sense of community. There is active use of the village hall from the annual Christmas show to many parties and social events. The Village fete and Bonfire events are well attended and add to the sense of village community. History Middle Ages The village lay within the Anglo-Saxon Tandridge hundred. Tandridge appears in Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Tenrige''. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






