|
Tama Lakes
The Tama Lakes are two crater lakes in New Zealand's Tongariro National Park. They fill two (Upper and Lower Tama) of a series of explosion craters on the Tama Saddle between Mount Ruapehu and Mount Ngaruahoe (a main Mount Tongariro vent). See also *List of volcanoes in New Zealand This is a partial list of active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes in New Zealand. Kermadec Arc and Havre Trough North Island Taupō Volcanic Zone Elsewhere Mangakino Culdera South Island Other Ross Dependency New Zealand a ... External linksAerial photo of the Tama Lakes Tongariro Volcanic Centre Volcanoes of Manawatū-Whanganui Volcanic crater lakes Tongariro National Park {{ManawatuWanganui-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
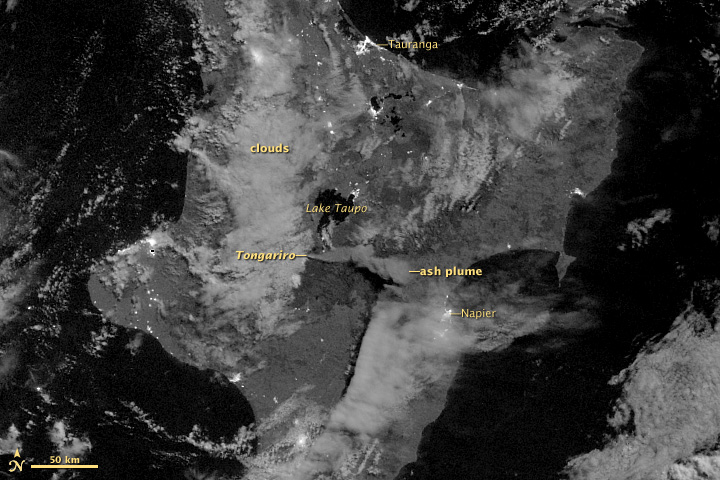
Tongariro NP Satellite
Mount Tongariro (; ) is a compound volcano in the Taupō Volcanic Zone of the North Island of New Zealand. It is located to the southwest of Lake Taupō, and is the northernmost of the three active volcanoes that dominate the landscape of the central North Island. Geology Mount Tongariro is part of the Tongariro volcanic centre, which consists of four massifs made of andesite: Tongariro, Kakaramea-Tihia Massif, Pihanga, and Ruapehu at the southern end of the North Island Volcanic Plateau. The andesitic eruptions formed Tongariro, a steep stratovolcano, reaching a height of . Tongariro is composed of layers of both lava and tephra and the eruptions that built the current stratovolcano commenced about 275,000 years ago. Tongariro consists of at least 12 cones. Ngāuruhoe, while often regarded as a separate mountain, is geologically a cone of Tongariro. It is also the most active vent, having erupted more than 70 times since 1839, the last episode in 1973 to 1975. Activity h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lake
A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a crater that was formed by explosive activity or a collapse during a volcanic eruption. Formation Lakes in calderas fill large craters formed by the collapse of a volcano during an eruption. Lakes in maars fill medium-sized craters where an eruption deposited debris around a vent. Crater lakes form as the created depression, within the crater rim, is filled by water. The water may come from precipitation, groundwater circulation (often hydrothermal fluids in the case of volcanic craters) or melted ice. Its level rises until an equilibrium is reached between the rates of incoming and outgoing water. Sources of water loss singly or together may include evaporation, subsurface seepage, and, in places, surface leakage or overflow when the lake level reaches the lowest point on its rim. At such a saddle location, the upper portion of the lake is contained only by its adjacent natural volcanic dam; continued leakage through or surface outflow ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongariro National Park
Tongariro National Park (; ) is the oldest national park in New Zealand,Department of Conservation"Tongariro National Park: Features", retrieved 21 April 2013 located in the central North Island. It has been acknowledged by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site of mixed cultural and natural values. Tongariro National Park was the sixth national park established in the world. The active volcanic mountains Ruapehu, Ngauruhoe, and Tongariro are located in the centre of the park. There are a number of Māori religious sites within the park, and many of the park's summits, including Ngauruhoe and Ruapehu, are '' tapu'', or sacred. The park includes many towns around its boundary including Ohakune, Waiouru, Horopito, Pokaka, Erua, National Park Village, Whakapapa skifield and Tūrangi. The Tongariro National Park is home to the famed Tongariro Alpine Crossing, widely regarded as one of the world's best one-day hikes. Geography Location Tongariro National Park covers 786 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Ruapehu
Mount Ruapehu (; ) is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is northeast of Ohakune and southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupō, within the Tongariro National Park. The North Island's major ski resorts and only glaciers are on its slopes. Ruapehu, the largest active volcano in New Zealand, has the highest point in the North Island and has three major peaks: Tahurangi (2,797 m), Te Heuheu (2,755 m) and Paretetaitonga (2,751 m). The deep, active volcanic crater, crater is between the peaks and fills with water between major eruptions, being known as Crater Lake ( mi, Te Wai ā-moe). The name ''Ruapehu'' means "pit of noise" or "exploding pit" in Māori language, Māori. Geography Ruapehu is located in the center of the North Island of New Zealand, northeast of Ohakune, New Zealand and southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupō, within Tongariro National Park. Rua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Ngaruahoe
Mount Ngāuruhoe (also spelled Ngauruhoe; Māori: ''Ngāuruhoe'') is a volcanic cone in New Zealand. It is the youngest vent in the Tongariro stratovolcano complex on the Central Plateau of the North Island and first erupted about 2,500 years ago. Although often regarded as a separate mountain, geologically, it is a secondary cone of Mount Tongariro. The volcano lies between the active volcanoes of Mount Tongariro to the north and Mount Ruapehu to the south, to the west of the Rangipo Desert and 25 kilometres to the south of the southern shore of Lake Taupō. Etymology The local Māori traditions state that the volcano was named by Ngātoro-i-rangi, an ancestor of the local Māori iwi, Ngāti Tūwharetoa. Ngātoro-i-rangi called volcanic fire from his homeland Hawaiki, which eventually emerged at Ngāuruhoe. The name given by Ngātoro-i-rangi (Ngāuruhoe) either commemorates his slave, who had died from the cold before the fire arrived, or refers to the insertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Tongariro
Mount Tongariro (; ) is a compound volcano in the Taupō Volcanic Zone of the North Island of New Zealand. It is located to the southwest of Lake Taupō, and is the northernmost of the three active volcanoes that dominate the landscape of the central North Island. Geology Mount Tongariro is part of the Tongariro volcanic centre, which consists of four massifs made of andesite: Tongariro, Kakaramea-Tihia Massif, Pihanga, and Ruapehu at the southern end of the North Island Volcanic Plateau. The andesitic eruptions formed Tongariro, a steep stratovolcano, reaching a height of . Tongariro is composed of layers of both lava and tephra and the eruptions that built the current stratovolcano commenced about 275,000 years ago. Tongariro consists of at least 12 cones. Ngāuruhoe, while often regarded as a separate mountain, is geologically a cone of Tongariro. It is also the most active vent, having erupted more than 70 times since 1839, the last episode in 1973 to 1975. Activity h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In New Zealand
This is a partial list of active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes in New Zealand. Kermadec Arc and Havre Trough North Island Taupō Volcanic Zone Elsewhere Mangakino Culdera South Island Other Ross Dependency New Zealand also has ''de facto'' administration over Ross Dependency in Antarctica, which contains the following volcanoes: References External links {{GeoGroupTemplateNew Zealand's Volcanoesat GNS Science New Zealand Volcanoes Volcanoes A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ... Geography of the Kermadec Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongariro Volcanic Centre
The North Island Volcanic Plateau (often called the Central Plateau and occasionally the Waimarino Plateau) is a volcanic plateau covering much of central North Island of New Zealand with volcanoes, lava plateaus, and crater lakes. It contains the Taupō caldera complex, Okataina caldera complex and Tongariro Volcanic Centre being currently the most frequently active and productive area of silicic volcanism on Earth. New Zealand is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. Location and description The plateau is approximately east–west and the north–south distance is about . Extensive ignimbrite sheets spread east and west from the Central Taupō Volcanic Zone, centred on the huge active supervolcanic caldera of Lake Taupō, now the largest lake in New Zealand. This last erupted less than 2000 years ago. The volcanic area includes the three active peaks of Mount Tongariro, Mount Ngāuruhoe, and Mount Ruapehu in the south, and extends beyond Rotorua in the north reaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Manawatū-Whanganui
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lakes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)