|
Tahoe-LAFS
Tahoe-LAFS (Tahoe Least-Authority File Store) is a free and open, secure, decentralized, fault-tolerant, distributed data store and distributed file system. It can be used as an online backup system, or to serve as a file or Web host similar to Freenet, depending on the front-end used to insert and access files in the Tahoe system. Tahoe can also be used in a RAID-like fashion using multiple disks to make a single large Redundant Array of Inexpensive Nodes (RAIN) pool of reliable data storage. The system is designed and implemented around the "principle of least authority" (POLA), described by Brian Warner (one of the project's original founders) as the idea "that any component of the system should have as little power of authority as it needs to get its job done". Strict adherence to this convention is enabled by the use of cryptographic capabilities that provide the minimum set of privileges necessary to perform a given task by asking agents. A RAIN array acts as a storage v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahoe-LAFS
Tahoe-LAFS (Tahoe Least-Authority File Store) is a free and open, secure, decentralized, fault-tolerant, distributed data store and distributed file system. It can be used as an online backup system, or to serve as a file or Web host similar to Freenet, depending on the front-end used to insert and access files in the Tahoe system. Tahoe can also be used in a RAID-like fashion using multiple disks to make a single large Redundant Array of Inexpensive Nodes (RAIN) pool of reliable data storage. The system is designed and implemented around the "principle of least authority" (POLA), described by Brian Warner (one of the project's original founders) as the idea "that any component of the system should have as little power of authority as it needs to get its job done". Strict adherence to this convention is enabled by the use of cryptographic capabilities that provide the minimum set of privileges necessary to perform a given task by asking agents. A RAIN array acts as a storage v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Distributed File Systems
In computing, a distributed file system (DFS) or network file system is any file system that allows access to files from multiple hosts sharing via a computer network. This makes it possible for multiple users on multiple machines to share files and storage resources. Distributed file systems differ in their performance, mutability of content, handling of concurrent writes, handling of permanent or temporary loss of nodes or storage, and their policy of storing content. Locally managed FOSS Proprietary Remote access Comparison Some researchers have made a functional and experimental analysis of several distributed file systems including HDFS, Ceph, Gluster, Lustre and old (1.6.x) version of MooseFS, although this document is from 2013 and a lot of information are outdated (e.g. MooseFS had no HA for Metadata Server at that time). The cloud based remote distributed storage from major vendors have different APIs and different consistency models. See also *Distributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn
Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn (born Bryce Wilcox; 13 May 1974 in Phoenix, Arizona), is an American Colorado-based computer security specialist, self-proclaimed cypherpunk, and CEO of the Electric Coin Company (ECC), a for-profit company leading the development of Zcash. Biography He is known for the Tahoe Least-Authority File Store (or Tahoe-LAFS), a secure, decentralized, fault-tolerant filesystem released under GPL and the TGPPL licenses. He is the creator of the Transitive Grace Period Public Licence (TGPPL). Wilcox-O'Hearn is the designer of multiple network protocols that incorporate concepts such as self-contained economies and secure reputation systems. He is a member of the development team of ZRTP and the BLAKE2 cryptographic hash function. Zooko's triangle is named after Wilcox-O'Hearn, who described the schema that relates three desirable properties of identifiers in 2001. Wilcox-O'Hearn was founder and CEO of Least Authority Enterprises in Boulder, Colorado where he is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Data Store
A distributed data store is a computer network where information is stored on more than one node, often in a replicated fashion. It is usually specifically used to refer to either a distributed database where users store information on a ''number of nodes'', or a computer network in which users store information on a ''number of peer network nodes''. Distributed databases Distributed databases are usually non-relational databases that enable a quick access to data over a large number of nodes. Some distributed databases expose rich query abilities while others are limited to a key-value store semantics. Examples of limited distributed databases are Google's Bigtable, which is much more than a distributed file system or a peer-to-peer network, Amazon's Dynamo and Microsoft Azure Storage. As the ability of arbitrary querying is not as important as the availability, designers of distributed data stores have increased the latter at an expense of consistency. But the high-speed r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasure Code
In coding theory, an erasure code is a forward error correction (FEC) code under the assumption of bit erasures (rather than bit errors), which transforms a message of ''k'' symbols into a longer message (code word) with ''n'' symbols such that the original message can be recovered from a subset of the ''n'' symbols. The fraction ''r'' = ''k''/''n'' is called the code rate. The fraction ''k’/k'', where ''k’'' denotes the number of symbols required for recovery, is called reception efficiency. Optimal erasure codes Optimal erasure codes have the property that any ''k'' out of the ''n'' code word symbols are sufficient to recover the original message (i.e., they have optimal reception efficiency). Optimal erasure codes are maximum distance separable codes (MDS codes). Parity check Parity check is the special case where ''n'' = ''k'' + 1. From a set of ''k'' values \_, a checksum is computed and appended to the ''k'' source values: :v_= - \sum_^k v_i. The set of ''k''& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
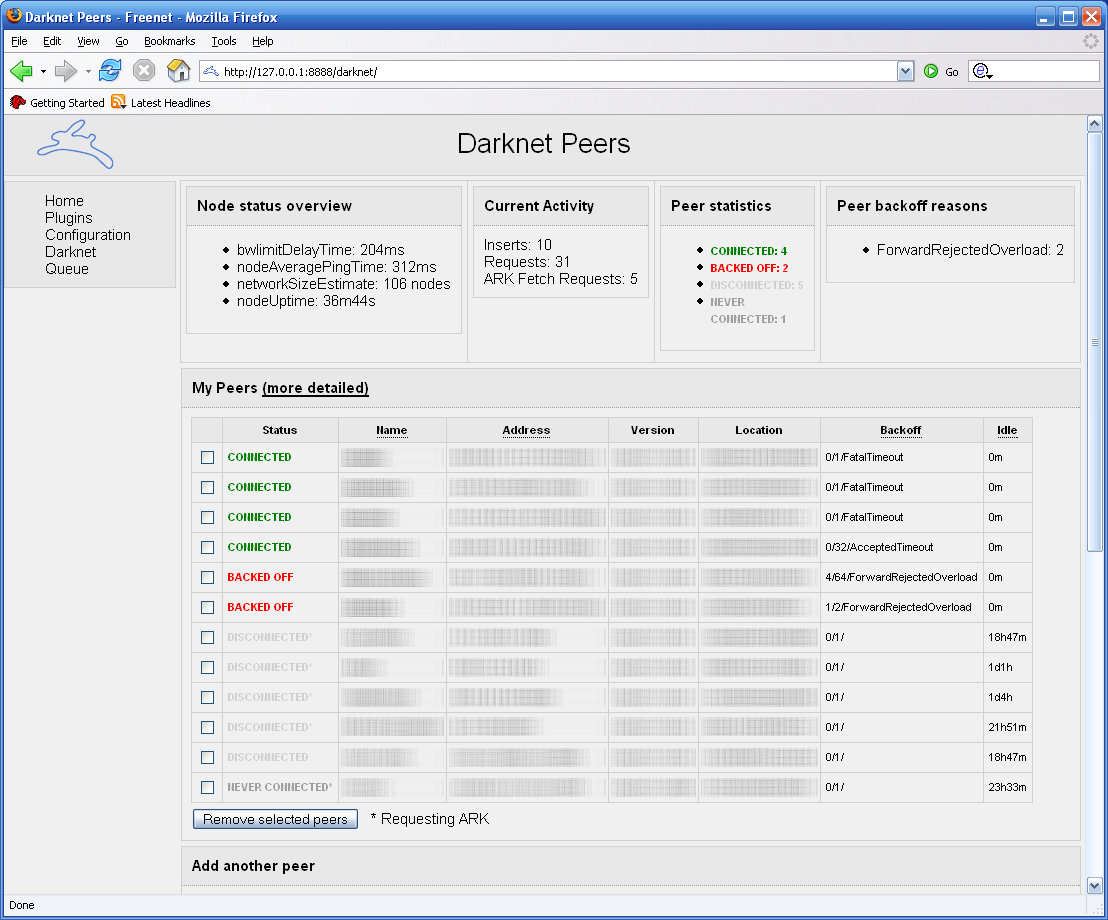
Freenet
Freenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing |
Privilege (computing)
In computing, privilege is defined as the delegation of authority to perform security-relevant functions on a computer system. A privilege allows a user to perform an action with security consequences. Examples of various privileges include the ability to create a new user, install software, or change kernel functions. Users who have been delegated extra levels of control are called privileged. Users who lack most privileges are defined as unprivileged, regular, or normal users. Theory Privileges can either be automatic, granted, or applied for. An automatic privilege exists when there is no requirement to have permission to perform an action. For example, on systems where people are required to log into a system to use it, logging out will not require a privilege. Systems that do not implement file protection - such as MS-DOS - essentially give unlimited privilege to perform any action on a file. A granted privilege exists as a result of presenting some credential to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose File System
Moose File System (MooseFS) is an open-source, POSIX-compliant distributed file system developed by Core Technology. MooseFS aims to be fault-tolerant, highly available, highly performing, scalable general-purpose network distributed file system for data centers. Initially proprietary software, it was released to the public as open source on May 30, 2008. Currently two editions of MooseFS are available: * MooseFS - released under GPLv2 license, * MooseFS Professional Edition (MooseFS Pro) - release under proprietary license in binary packages form. Design The MooseFS follows similar design principles as Fossil (file system), Google File System, Lustre or Ceph. The file system comprises three components: * Metadata server (MDS) — manages the location (layout) of files, file access and namespace hierarchy. The current version of MooseFS does support multiple metadata servers and automatic failover. Clients only talk to the MDS to retrieve/update a file's layout and attributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluster
Gluster Inc. (formerly known as Z RESEARCH) was a software company that provided an open source platform for scale-out public and private cloud storage. The company was privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster was funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index Ventures. Gluster was acquired by Red Hat on October 7, 2011. History The name ''Gluster'' comes from the combination of the terms ''GNU'' and ''cluster''. Despite the similarity in names, Gluster is not related to the Lustre file system and does not incorporate any Lustre code. Gluster based its product on ''GlusterFS'', an open-source software-based network-attached filesystem that deploys on commodity hardware. The initial version of GlusterFS was written by Anand Babu Periasamy, Gluster's founder and CTO. In May 2010 Ben Golub became the president and chief executive officer. Red Hat became the primary author and maintainer of the GlusterFS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coda (file System)
Coda is a distributed file system developed as a research project at Carnegie Mellon University since 1987 under the direction of Mahadev Satyanarayanan. It descended directly from an older version of Andrew File System (AFS-2) and offers many similar features. The InterMezzo file system was inspired by Coda. Features Coda has many features that are desirable for network file systems, and several features not found elsewhere. # Disconnected operation for mobile computing. # Is freely available under the GPL # High performance through client-side persistent caching # Server replication # Security model for authentication, encryption and access control # Continued operation during partial network failures in server network # Network bandwidth adaptation # Good scalability # Well defined semantics of sharing, even in the presence of network failure Coda uses a local cache to provide access to server data when the network connection is lost. During normal operation, a user reads an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceph (software)
Ceph (pronounced ) is an open-source software-defined storage platform that implements object storage on a single distributed computer cluster and provides 3-in-1 interfaces for object-, block- and file-level storage. Ceph aims primarily for completely distributed operation without a single point of failure, scalability to the exabyte level, and to be freely available. Since version 12, Ceph does not rely on other filesystems and can directly manage HDDs and SSDs with its own storage backend BlueStore and can completely self reliantly expose a POSIX filesystem. Ceph replicates data and makes it fault-tolerant, using commodity hardware and Ethernet IP and requiring no specific hardware support. The Ceph’s system offers disaster recovery and data redundancy through techniques such as replication, erasure coding, snapshots and storage cloning. As a result of its design, the system is both self-healing and self-managing, aiming to minimize administration time and other co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |