|
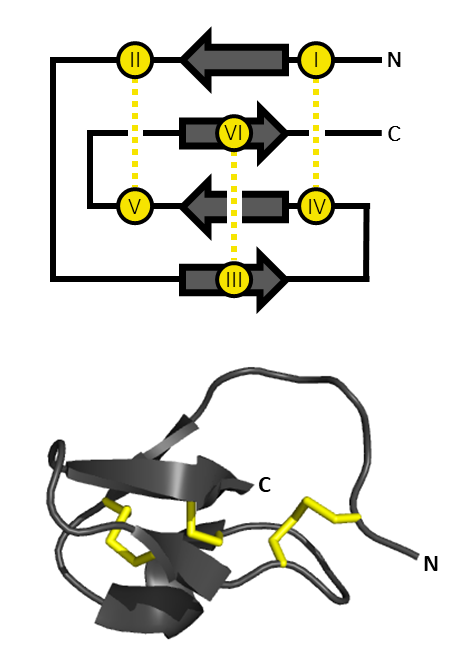
Tachystatin
Tachystatins are antimicrobial chitin-binding peptides from Tachypleus tridentatus, Japanese horseshoe crab. Amino acid residues Tyr(14) and Arg(17) in Tachystatin B are thought to be the essential Residue (chemistry), residues for chitin binding. These small proteins contain a cysteine-stabilised triple-stranded beta-sheet with an inhibitor inhibitor cystine knot, cystine knot motif and show features common to membrane-interactive peptides. Tachystatin A is thought to have an antimicrobial activity similar to defensins. References {{InterPro content, IPR022717 Protein families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibitor Cystine Knot
An inhibitor cystine knot (aka ICK or Knottin) is a protein structural motif containing three disulfide bridges. Knottins are one of three folds in the cystine knot motif; the other closely related knots are the Growth Factor Cystine Knot (GFCK) and the Cyclic Cystine Knot (CCK; cyclotide). Types include a) cyclic mobius, b) cyclic bracelet, c) acyclic inhibitor knottins. Cystine knot motifs are found frequently in nature in a plethora of plants, animals, and fungi and serve diverse functions from appetite suppression to anti-fungal activity. Along with the sections of polypeptide between them, two disulfides form a loop through which the third disulfide bond (linking the 3rd and 6th cysteine in the sequence) passes, forming a knot. The motif is common in invertebrate toxins such as those from arachnids and molluscs. The motif is also found in some inhibitor proteins found in plants, but the plant and animal motifs are thought to be a product of convergent evolution. The ICK moti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachypleus Tridentatus
''Tachypleus tridentatus'', commonly known as the Chinese horseshoe crab, Japanese horseshoe crab, or tri-spine horseshoe crab, is a species of horseshoe crab found in Southeast and East Asia, with records from China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. It is found in coastal Marine life, marine and brackish waters, and tolerates colder temperatures than the other Asian horseshoe crabs (''Tachypleus gigas'' and ''Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda''), although juveniles still need water warmer than to moult. Description Horseshoe crabs are not crabs at all, but are most closely related to spiders and scorpions, and may even be arachnids themselves. The cephalothorax is protected by this single large, horseshoe-shaped plate, and neither it nor the abdomen is visibly segmented. The tail bears a long spike, known as the telson. Like other horseshoe crabs, the carapace of ''T. tridentatus'' consists of a larger frontal one (the prosoma) and a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is whatever remains or acts as a contaminant after a given class of events. Residue may be the material remaining after a process of preparation, separation, or purification, such as distillation, evaporation, or filtration. It may also denote the undesired by-products of a chemical reaction. Food safety Toxic chemical residues, wastes or contamination from other processes, are a concern in food safety. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) have guidelines for detecting chemical residues that are possibly dangerous to consume. Characteristic units within a molecule ''Residue'' may refer to an atom or a group of atoms that forms part of a molecule, such as a methyl group. Biochemistry In biochemistry and molecular biology, a residue refers to a specific monomer within the polymeric chain of a polysaccharide, protein or nucleic acid. One might say, "This protein consists of 118 amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defensins
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate and invertebrate animals, plants, and fungi. They are host defense peptides, with members displaying either direct antimicrobial activity, immune signalling activities, or both. They are variously active against bacteria, fungi and many enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. They are typically 18-45 amino acids in length, with three or four highly conserved disulphide bonds. In animals, they are produced by cells of the innate immune system and epithelial cells, whereas in plants and fungi they are produced by a wide variety of tissues. An organism usually produces many different defensins, some of which are stored inside the cells (e.g. in neutrophil granulocytes to kill phagocytosed bacteria), and others are secreted into the extracellular medium. For those that directly kill microbes, their mechanism of action varies from disruption of the microbial cell membrane to metabolic disruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |