|
T Interface
A T-interface or T reference point is used for basic rate access in an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) environment. It is a User–network interface reference point that is characterized by a four-wire, 144 kbit/s (2B+D) user rate. Other characteristics of a T-interface are: * it accommodates the link access and transport layer function in the ISDN architecture * it is located at the user premises * it is distance sensitive to the servicing Network termination 1 * it functions in a manner similar to that of the Channel service units (CSUs) and the Data service units (DSUs). The T interface is electrically equivalent to the S interface, and the two are jointly referred to as the S/T interface. See also * R interface * S interface * U interface U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Rate Access
Basic Rate Interface (BRI, 2B+D, 2B1D) or Basic Rate Access is an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) configuration intended primarily for use in subscriber lines similar to those that have long been used for Plain old telephone service, voice-grade telephone service. As such, an ISDN BRI connection can use the Plain old telephone service, existing telephone infrastructure at a business. The BRI configuration provides 2 data (bearer) channels (B channels) at 64 kbit/s each and 1 control (delta) channel (D channel) at 16 kbit/s. The B channels are used for Human voice, voice or user data, and the D channel is used for any combination of data, Signaling (telecommunication), control/signaling, and X.25 packet networking. The 2 B channels can be aggregated by channel bonding providing a total data rate of 128 kbit/s. The BRI ISDN service is commonly installed for residential or small business service (ISDN PABX) in many countries. In contrast to the BRI, the Primary Rate Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Services Digital Network
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking systems with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance. Prior to ISDN, the telephone system consisted of digital links like T1/ E1 on the long-distance lines between telephone company offices and analog signals on copper telephone wires to the customers, the " last mile". At the time, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User–network Interface
In telecommunications, a user–network interface (UNI) is a demarcation point between the responsibility of the service provider and the responsibility of the subscriber. This is distinct from a network-to-network interface (NNI) that defines a similar interface between provider networks. Specifications defining a UNI Metro Ethernet Forum The Metro Ethernet Forum's Metro Ethernet Network UNI specification defines a bidirectional Ethernet reference point for Ethernet service delivery. Optical Internetworking Forum The Optical Internetworking Forum defines a UNI software interface for user systems to request a network connection from an ASON was a prestigious hereditary noble title in Japan, used mainly between Asuka and Heian periods. At first, it was the second highest, below '' Mahito'', which was given to members of the Imperial family, but after Heian period it became the h .../ GMPLS control plane. See also * Network termination External linksMetro Ethernet Forum { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Services Digital Network
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking systems with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance. Prior to ISDN, the telephone system consisted of digital links like T1/ E1 on the long-distance lines between telephone company offices and analog signals on copper telephone wires to the customers, the " last mile". At the time, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobit
The kilobit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix ''kilo-'' (symbol k) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 103 (1 thousand), and therefore, :1 kilobit = = 1000 bits. The kilobit has the unit symbol kbit or kb. Using the common byte size of 8 bits, 1 kbit is equal to 125 bytes. The kilobit is commonly used in the expression of data rates of digital communication circuits as kilobits per second (kbit/s or kb/s), or abbreviated as ''kbps'', as in, for example, ''a 56 kbps PSTN circuit'', or ''a 512 kbit/s broadband Internet connection''. The unit symbol kb (lowercase 'b') is typographically similar to the international standard unit symbol for the kilobyte, i.e. kB (upper case 'B'). The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) recommends the symbol bit instead of b. The prefix ''kilo-'' is often used in fields of computer science and information technology wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
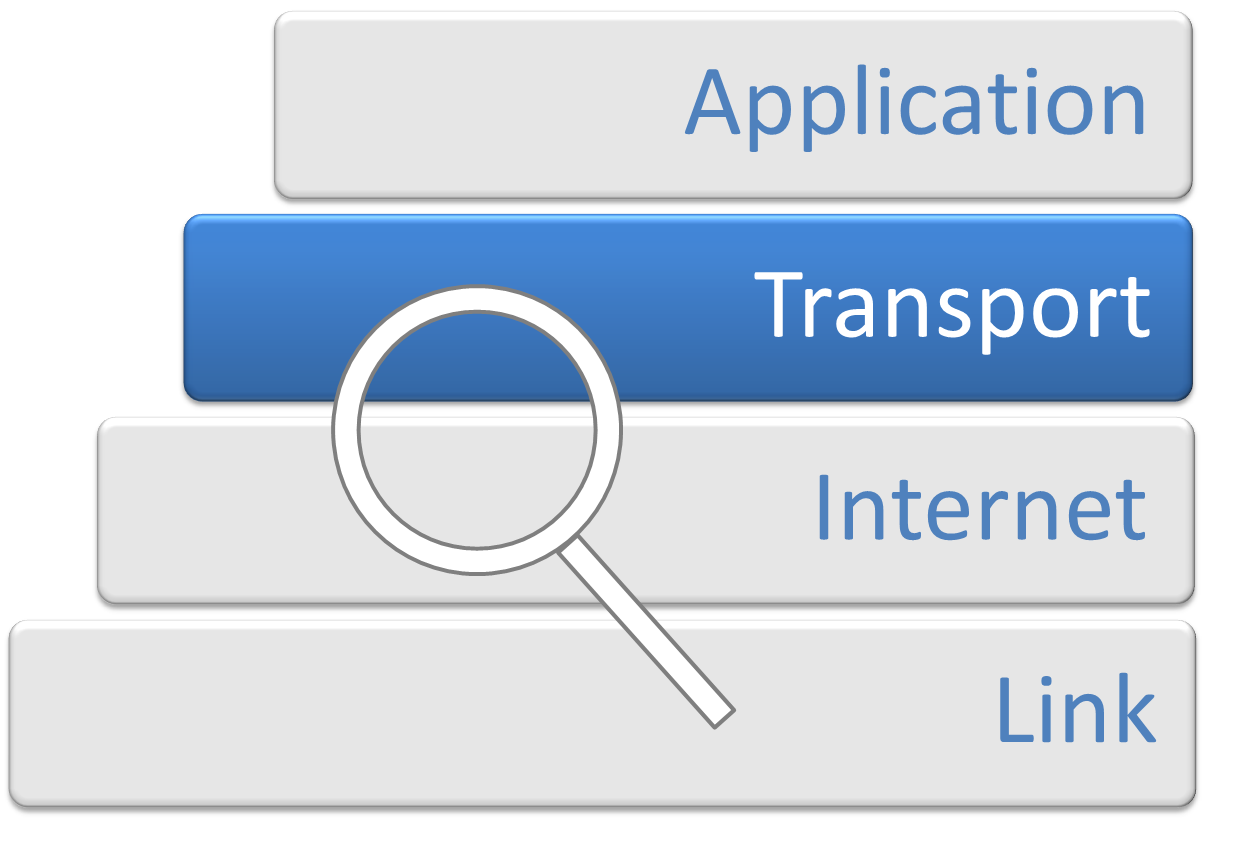
Transport Layer
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing. The details of implementation and semantics of the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite, which is the foundation of the Internet, and the OSI model of general networking are different. The protocols in use today in this layer for the Internet all originated in the development of TCP/IP. In the OSI model the transport layer is often referred to as Layer 4, or L4, while numbered layers are not used in TCP/IP. The best-known transport protocol of the Internet protocol suite is the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It is used for connection-oriented transmissions, whereas the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Termination 1
Network Termination 1 (NT1) or Network Termination type 1 refers to equipment in an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) that physically and electrically terminates the network at the customer's premises. The NT1 network termination provides signal conversion and timing functions which correspond to layer 1 of the OSI model. In a Basic Rate Interface, the NT1 connects to line termination (LT) equipment in the provider's telephone exchange via the local loop two wire U interface and to customer equipment via the four wire S interface or T interface. The S and T interfaces are electrically equivalent, and the customer equipment port of a NT1 is often labelled as S/T interface. There are many types of NT1 available. In the United States, the NT1 is considered customer-premises equipment In telecommunications, a customer-premises equipment or customer-provided equipment (CPE) is any terminal and associated equipment located at a subscriber's premises and connected with a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Service Unit
In telecommunications, a channel service unit (CSU) is a line bridging device for use with T-carrier, which *is used to perform loopback testing; *may perform bit stuffing; *may also provide a framing and formatting pattern compatible with the network; *provides a barrier for electrical interference from either side of the unit; and *is the last signal regeneration point, on the loop side, coming from the central office, before the regenerated signal reaches a multiplexer or data terminal equipment (DTE). Common varieties CSUs can be categorized by the class of service they support ( DS1, DS3, DDS, etc.) and by the capabilities within that class. For example, basic DS1 (T1) CSUs support loopback of each interface and will produce alarm indication signal to the provider's network interface device (NID) in the event of loss of signal from the customer-premises equipment (CPE). More advanced units will include internal monitors of the performance of the carrier in both direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Service Unit
A data service unit, sometimes called a digital service unit, is a piece of telecommunications circuit terminating equipment that transforms digital data between telephone company lines and local equipment. The device converts bipolar digital signals coming ultimately from a digital circuit and directly from a Channel service unit (CSU), into a format (e.g. RS- 530) compatible with the piece of data terminal equipment (DTE) (e.g. a router) to which the data is sent. The DSU also performs a similar process in reverse for data heading from the DTE toward the circuit. The telecommunications service a DSU supports can be a point-to-point or multipoint operation in a digital data network. Form and purpose A DSU is a two or more port device; one port is called the WAN (wide area network) port and the other is called a DTE port. The purpose of the DSU is to transfer serial data synchronously between the WAN port and the DTE ports. If more than one DTE port is used, the DSU assigns the DTE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Interface
The S interface or S reference point, also known as S0, is a user–network interface reference point in an ISDN BRI environment, characterized by a four-wire circuit using 144kbit/s (2 bearer and 1 signaling channel; 2B+D) user rate. The S interface is the connection between ISDN terminal equipment (TE) or terminal adapters (TAs) and an NT1 (network terminator, type 1.) Not all TE or TAs connect externally to an S interface, but instead integrate an NT1 so they can connect directly to a U interface (local loop from central office.) Contrast to the T interface, which connects between an NT2 (PBX or other local switching device) and NT1. However, the S interface is electrically equivalent to the T interface, and the two are jointly referred to as the S/T interface. The S interface operates at 4000 48-bit frames per second; i.e., 192kbit/s, with a user portion of 36bits per frame; i.e., 144kbit/s.Entry "S interface"/ref> See also * R interface * T interface * U interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Interface
R interface or R reference point defines the point between a non-ISDN device and a terminal adapter (TA) which provides translation to and from such a device. See also * S interface * T interface * U interface U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pr ... References * ITU-T recommendations Integrated Services Digital Network {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |