|
TT8
Theban Tomb 8, abbreviated TT8, is the funerary chapel and tomb of Kha, the overseer of works from Deir el-Medina in the mid- 18th Dynasty and his wife, Merit. Kha was a foreman at Deir El-Medina, where he was responsible for royal tombs constructed during the reigns of pharaohs Amenhotep II, Thutmose IV and Amenhotep III. Their chapel was discovered by Bernardino Drovetti in the early 19th century. Scenes from the chapel were copied in the 19th century by several Egyptologists, including John Gardiner Wilkinson and Karl Lepsius. Their funerary stela made its way to the Museo Egizio in Turin in 1824 and the pyramidion of the chapel, reused for a later structure, is now in the Louvre Museum. Unconventionally for non-royal Theban tombs, their tomb was cut into the base of the cliffs opposite the chapel and not in the immediate proximity of the chapel itself. Their tomb, initially given the number 269, was discovered in 1906 by Ernesto Schiaparelli on behalf of the Italian Archaeologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT8 Chapel Exterior C02053
Theban Tomb 8, abbreviated TT8, is the funerary chapel and tomb of Kha, the overseer of works from Deir el-Medina in the mid-18th Dynasty and his wife, Merit. Kha was a foreman at Deir El-Medina, where he was responsible for royal tombs constructed during the reigns of pharaohs Amenhotep II, Thutmose IV and Amenhotep III. Their chapel was discovered by Bernardino Drovetti in the early 19th century. Scenes from the chapel were copied in the 19th century by several Egyptologists, including John Gardiner Wilkinson and Karl Richard Lepsius, Karl Lepsius. Their funerary stela made its way to the Museo Egizio in Turin in 1824 and the pyramidion of the chapel, reused for a later structure, is now in the Louvre Museum. Unconventionally for non-royal Theban tombs, their tomb was cut into the base of the cliffs opposite the chapel and not in the immediate proximity of the chapel itself. Their tomb, initially given the number 269, was discovered in 1906 by Ernesto Schiaparelli on behalf of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT8 Chapel Interior
Theban Tomb 8, abbreviated TT8, is the funerary chapel and tomb of Kha, the overseer of works from Deir el-Medina in the mid- 18th Dynasty and his wife, Merit. Kha was a foreman at Deir El-Medina, where he was responsible for royal tombs constructed during the reigns of pharaohs Amenhotep II, Thutmose IV and Amenhotep III. Their chapel was discovered by Bernardino Drovetti in the early 19th century. Scenes from the chapel were copied in the 19th century by several Egyptologists, including John Gardiner Wilkinson and Karl Lepsius. Their funerary stela made its way to the Museo Egizio in Turin in 1824 and the pyramidion of the chapel, reused for a later structure, is now in the Louvre Museum. Unconventionally for non-royal Theban tombs, their tomb was cut into the base of the cliffs opposite the chapel and not in the immediate proximity of the chapel itself. Their tomb, initially given the number 269, was discovered in 1906 by Ernesto Schiaparelli on behalf of the Italian Archaeologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Egizio
The Museo Egizio (Italian language, Italian for Egyptian Museum) is an archaeological museum in Turin, Piedmont, Italy, specializing in Art of Ancient Egypt, Egyptian archaeology and anthropology. It houses List of museums of Egyptian antiquities, one of the largest collections of Art of Ancient Egypt, Egyptian antiquities, with more than 30,000 artifacts, and is considered the second most important Egyptology collection in the world, after the Egyptian Museum, Egyptian Museum of Cairo. In 2019, it received 853,320 visitors, making it one of the most visited museums in Italy. History The first object having an association with Egypt to arrive in Turin was the Bembine Tablet, Mensa Isiaca in 1630, an altar table in imitation of Egyptian style, which Dulu Jones suggests had been created for a temple to Isis in Rome. This exotic piece spurred King Charles Emmanuel III of Sardinia, Charles Emmanuel III to commission botanist Vitaliano Donati to travel to Egypt in 1753 and acquire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir El-Medina
Deir el-Medina ( arz, دير المدينة), or Dayr al-Madīnah, is an ancient Egyptian workmen's village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th Dynasties of the New Kingdom of Egypt (ca. 1550–1080 BCE)Oakes, p. 110 The settlement's ancient name was ''wikt:st#Etymology 2 2, Set wikt:mꜣꜥt#Egyptian, maat'' ("Place of Truth"), and the workmen who lived there were called "Servants in the Place of Truth". During the Christian era, the temple of Hathor was converted into a church from which the Egyptian Arabic name ''Deir el-Medina'' ("Monastery of the City") is derived. At the time when the world's press was concentrating on Howard Carter's discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamun in 1922, a team led by Bernard Bruyère began to excavate the site."Pharaoh’s Workers: How the Israelites Lived in Egypt", Leonard and Barbara Lesko, Biblical Archaeological Review, Jan/Feb 1999 This work has resulted in one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernesto Schiaparelli
Ernesto Schiaparelli (; July 12, 1856 – February 14, 1928) was an Italian Egyptologist. Biography He was born in Occhieppo Inferiore (Biella). He found Queen Nefertari's tomb in Deir el-Medina in the Valley of the Queens (1904) and excavated the TT8 tomb of the royal architect Kha (1906), found intact and displayed ''in toto'' in Turin. He was appointed director of the Egyptian Museum in Florence, where he professionally reorganized the collection in new quarters in 1880, then at the peak of his career was made director of the Museo Egizio di Torino, which became with him and his many seasons of excavating, the second biggest Egyptian museum in the world. He was the author of famous scholarly works and a Senator of the Kingdom of Italy. At the same time, he was deeply involved, from his first stay with Franciscan missionaries at Luxor in 1884, with relieving the poverty he saw among the missionaries of Upper Egypt, for whom he founded the Association to Succour Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT9 (Tomb)
The Thebes, Egypt, Theban Tomb TT9 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of an ancient Egyptian artisan (his exact title was Servant in the Place of Truth) named Amenmose, who lived during the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, 20th Dynasty, during the reign of Ramesses III. Amenmose was a Servant in the Place of Truth and a Charmer of Scorpions. His wife was named Tent-hom.Porter and Moss, Topographical Bibliography: The Theban Necropolis, pg 18-19 See also * List of Theban tombs References Buildings and structures completed in the 13th century BC Theban tombs {{AncientEgypt-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashedu
Pashedu was an ancient Egyptian artisan. Pashedu lived in Deir el-Medina on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reign of Seti I. Pashedu was a son of Menna and Huy. His wife was named Nedjmet-behdet. Pashedu was the owner of tomb TT3 and likely TT326. Benedict G. Davies, Who's Who at Deir el-Medina: A Prosopographic Study of the Royal Workmen’s Community, Nederlands Instituut Voor het nabije Oosten, Leiden, 1999, pp 2, 166 His titles included Servant in the Place of Truth, meaning that he worked on the excavation and decoration of the nearby royal tombs. Pashedu seems to have succeeded Baki as foreman for the left side during the reign of Ramesses II Ramesses II ( egy, wikt:rꜥ-ms-sw, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is oft .... A son named Menna is mentioned in TT3. He was named aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Wall And Ceiling Motif MET 30
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
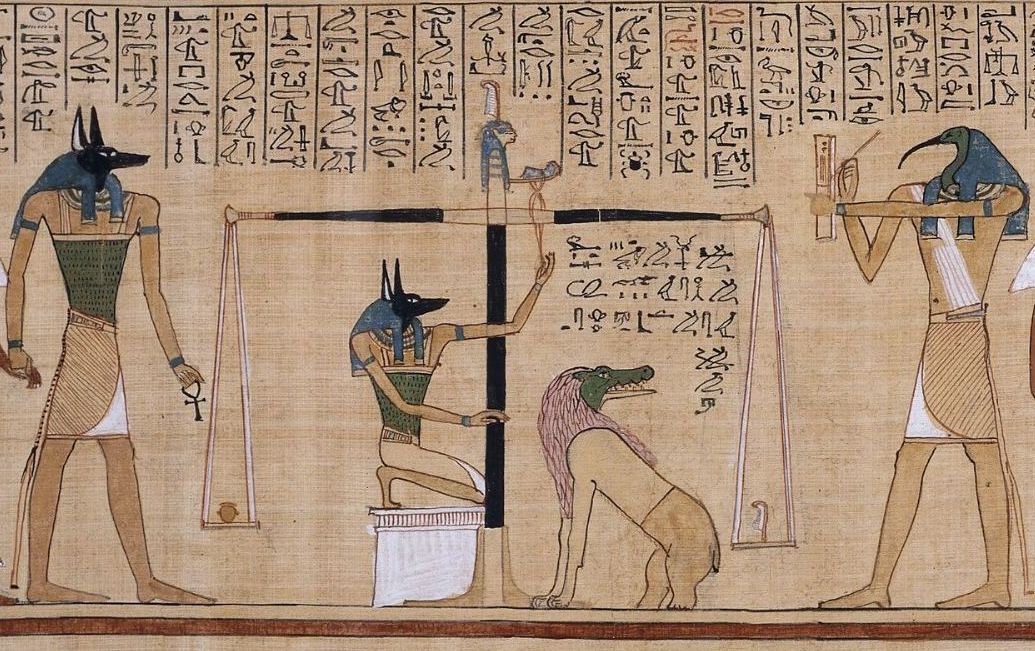
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)