|
TROSY
Transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy (TROSY) is an experiment in protein NMR spectroscopy that allows studies of large molecules or complexes. The application of NMR to large molecules is normally limited by the fact that the line widths generally increase with molecular mass. Larger molecules have longer rotational correlation times and consequently shorter transverse relaxation times (T2). In other words, the NMR signal from larger molecules decays more rapidly, leading to line broadening in the NMR spectrum and poor resolution. In an HSQC spectrum in which decoupling has not been applied, peaks appear as multiplets due to J-coupling. Crucially the different multiplet components have different widths. This is due to constructive or destructive interaction between different relaxation mechanisms. Typically for large proteins at high magnetic field strengths, the transverse (T2) relaxation is dominated by the dipole-dipole (DD) mechanism and the chemical shift In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the National Institutes of Health, NIH, and Gerhard Wagner (physicist), Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("Atomic nucleus, nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quantity relative molecular mass is the unitless ratio of the mass of a molecule to the atomic mass constant (which is equal to one dalton). The molecular mass and relative molecular mass are distinct from but related to the ''molar mass''. The molar mass is defined as the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of the substance, and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). That makes the molar mass an ''average'' of many particles or molecules (weighted by abundance of the isotopes), and the molecular mass the mass of one specific particle or molecule. The molar mass is usually the more appropriate quantity when dealing with macroscopic (weigh-able) quantities of a substance. The definition of molecular weight is most authoritat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Induction Decay
In Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, free induction decay (FID) is the observable nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal generated by non-equilibrium nuclear spin magnetization precessing about the magnetic field (conventionally along z). This non-equilibrium magnetization can be created generally by applying a pulse of radio-frequency close to the Larmor frequency of the nuclear spins. If the magnetization vector has a non-zero component in the XY plane, then the precessing magnetisation will induce a corresponding oscillating voltage in a detection coil surrounding the sample. This time-domain signal (a sinusoid) is typically digitised and then Fourier transformed in order to obtain a frequency spectrum of the NMR signal i.e. the NMR spectrum. The duration of the NMR signal is ultimately limited by T2 relaxation, but mutual interference Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to: Communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged. An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. Each of these contributes (given suitable design, and adequate alignment) to the optical resolution of the system; the environment in which the imaging is done often is a further important factor. Lateral resolution Resolution depends on the distance between two distinguishable radiating points. The sections below describe the theoretical estimates of resolution, but the real values may differ. The results below are based on mathematical models of Airy discs, which assumes an adequate level of contrast. In low-contrast systems, the resolution may be much lower than predicted by the theory outlined below. Real optical systems are complex, and practical difficulties often increase the distance between distinguishable point sources. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
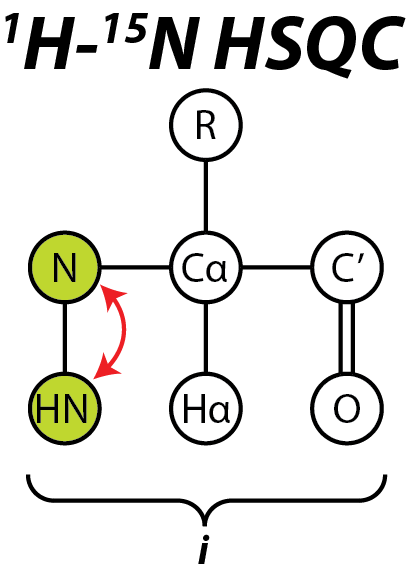
HSQC
The heteronuclear single quantum coherence or heteronuclear single quantum correlation experiment, normally abbreviated as HSQC, is used frequently in NMR spectroscopy of organic molecules and is of particular significance in the field of protein NMR. The experiment was first described by Geoffrey Bodenhausen and D. J. Ruben in 1980. The resulting spectrum is two-dimensional (2D) with one axis for proton (1H) and the other for a heteronucleus (an atomic nucleus other than a proton), which is usually 13C or 15N. The spectrum contains a peak for each unique proton attached to the heteronucleus being considered. The 2D HSQC can also be combined with other experiments in higher-dimensional NMR experiments, such as NOESY-HSQC or TOCSY-HSQC. General scheme The HSQC experiment is a highly sensitive 2D-NMR experiment and was first described in a 1H—15N system, but is also applicable to other nuclei such as 1H—13C and 1H—31P. The basic scheme of this experiment involves the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Decoupling
Nuclear magnetic resonance decoupling (NMR decoupling for short) is a special method used in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy where a sample to be analyzed is irradiated at a certain frequency or frequency range to eliminate or partially the effect of coupling between certain nuclei. NMR coupling refers to the effect of nuclei on each other in atoms within a couple of bonds distance of each other in molecules. This effect causes NMR signals in a spectrum to be split into multiple peaks. Decoupling fully or partially eliminates splitting of the signal between the nuclei irradiated and other nuclei such as the nuclei being analyzed in a certain spectrum. NMR spectroscopy and sometimes decoupling can help determine structures of chemical compounds. Explanation NMR spectroscopy of a sample produces an NMR spectrum, which is essentially a graph of signal intensity on the vertical axis vs. chemical shift for a certain isotope on the horizontal axis. The signal intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-coupling
In nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, ''J''-couplings (also called spin-spin coupling or indirect dipole–dipole coupling) are mediated through chemical bonds connecting two spins. It is an indirect interaction between two nuclear spins that arises from hyperfine interactions between the nuclei and local electrons. In NMR spectroscopy, ''J''-coupling contains information about relative bond distances and angles. Most importantly, ''J''-coupling provides information on the connectivity of chemical bonds. It is responsible for the often complex splitting of resonance lines in the NMR spectra of fairly simple molecules. ''J''-coupling is a frequency ''difference'' that is not affected by the strength of the magnetic field, so is always stated in Hz. Vector model and manifestations for chemical structure assignments The origin of ''J''-coupling can be visualized by a vector model for a simple molecule such as hydrogen fluoride (HF). In HF, the two nuclei have spin . Four st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation (NMR)
In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), an observable nuclear spin polarization (magnetization) is created by a homogeneous magnetic field. This field makes the magnetic dipole moments of the sample precess at the resonance ( Larmor) frequency of the nuclei. At thermal equilibrium, nuclear spins precess randomly about the direction of the applied field. They become abruptly phase coherent when they are hit by radiofrequency (RF) pulses at the resonant frequency, created orthogonal to the field. The RF pulses cause the population of spin-states to be perturbed from their thermal equilibrium value. The generated transverse magnetization can then induce a signal in an RF coil that can be detected and amplified by an RF receiver. The return of the longitudinal component of the magnetization to its equilibrium value is termed ''spin-lattice'' relaxation while the loss of phase-coherence of the spins is termed ''spin-spin'' relaxation, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule. Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy. Some atomic nuclei possess a magnetic moment (nuclear spin), which gives rise to different energy levels and resonance frequencies in a magnetic field. The total magnetic field experienced by a nucleus includes local magnetic fields induced by currents of electrons in the molecular orbitals (electrons have a magnetic moment themselves). The electron distribution of the same type of nucleus (e.g. ) usually varies according to the local geometry (binding partners, bond lengths, angles between bonds, and so on), and with it the local magnetic field at each nucleus. This is reflected in the spin energy levels (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipolar Coupling
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: * An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) * A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |