|
TORCH Syndrome
TORCH syndrome is a cluster of symptoms caused by congenital infection with toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and other organisms including syphilis, parvovirus, and Varicella zoster. Zika virus is considered the most recent member of TORCH infections. ''TORCH'' is an acronym for , Agents, , , and Simplex. Signs and symptoms Though caused by different infections, the signs and symptoms of TORCH syndrome are consistent. They include hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen), fever, lethargy, difficulty feeding, anemia, petechiae, purpurae, jaundice, and chorioretinitis. The specific infection may cause additional symptoms. TORCH syndrome may develop before birth, causing stillbirth, in the neonatal period, or later in life. Pathophysiology TORCH syndrome is caused by in-utero infection with one of the TORCH agents, disrupting fetal development Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertically Transmitted Infection
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or Pathogenic virus, viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, Transmission (medicine), transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It can occur when the mother has a pre-existing disease in pregnancy, pre-existing disease or becomes infected during pregnancy. Nutritional deficiencies may exacerbate the risks of perinatal infections. Types of infections Bacteria, viruses, and other organisms are able to be passed from mother to child. Several vertically transmitted infections are included in the TORCH complex: # T – toxoplasmosis from ''Toxoplasma gondii'' # O – other infections (see below) # R – rubella # C – cytomegalovirus # H – herpes simplex virus-2 or neonatal herpes simplex Other infections include: * Parvovirus B19 * Coxsackievirus * Chickenpox (caused by varicella zoster virus) * ''Chlamydia infection, Chlamydi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Development
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth. In human pregnancy, prenatal development is also called antenatal development. The development of the human embryo follows fertilization, and continues as fetal development. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age the embryo has acquired its basic form and is referred to as a fetus. The next period is that of fetal development where many organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age. The very early stages of embryonic development are the same in all mammals, but later stages of development, and the length of gestation varies. Terminology In the human: Different terms are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorioretinitis
Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid (thin pigmented vascular coat of the eye) and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient. Symptoms Symptoms may include the presence of floating black spots, blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, or excessive tearing. Causes Chorioretinitis is often caused by toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections (mostly seen in immunodeficient subjects such as people with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressant drugs). Congenital toxoplasmosis via transplacental transmission can also lead to sequelae such as chorioretinitis along with hydrocephalus and cerebral calcifications. Other possible causes of chorioretinitis are syphilis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types – unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, genetic conditions s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, or other causes. They measure 3–10 mm, whereas petechiae measure less than 3 mm, and ecchymoses greater than 1 cm. Purpura is common with typhus and can be present with meningitis caused by meningococci or septicaemia. In particular, meningococcus (''Neisseria meningitidis''), a Gram-negative diplococcus organism, releases endotoxin when it lyses. Endotoxin activates the Hageman factor (clotting factor XII), which causes disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). The DIC is what appears as a rash on the affected individual. Classification Purpura are a common and nonspecific medical sign; however, the underlying mechanism commonly involves one of: * Platelet disorders (thrombocytopenic purpura) ** Primary thromboc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petechia
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and Mucous membrane, mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' of obscure origin. It refers to one of the three descriptive types of hematoma differentiated by size, the other two being ecchymosis (>1cm in diameter) and purpura (4-10mm in diameter). The term is always used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant. Causes Physical trauma The most common cause of petechiae is through physical trauma such as a hard bout of coughing, holding breath, vomiting, or crying, which can result in facial petechiae, especially around the eyes. Such instances are harmless and usually disappear within a few days. * Constriction, asphyxiation – petechiae, especially in the eyes, may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .σπλήν Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Digital Library The spleen plays very important roles in regard to s (erythrocytes) and the . It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of |
Hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly (commonly abbreviated HSM) is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver (hepatomegaly) and the spleen (splenomegaly). Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and histoplasmosis or it can be the sign of a serious and life-threatening lysosomal storage disease. Systemic venous hypertension can also increase the risk for developing hepatosplenomegaly, which may be seen in those patients with right-sided heart failure. Common causes Rare disorders * Lipoproteinlipase deficiency * Multiple sulfatase deficiency * Osteopetrosis Osteopetrosis, literally "stone bone", also known as marble bone disease or Albers-Schönberg disease, is an extremely rare inherited disorder whereby the bones harden, becoming denser, in contrast to more prevalent conditions like osteoporosis ... * Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) References External links Symptoms and signs: Digestive system and abdomen Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
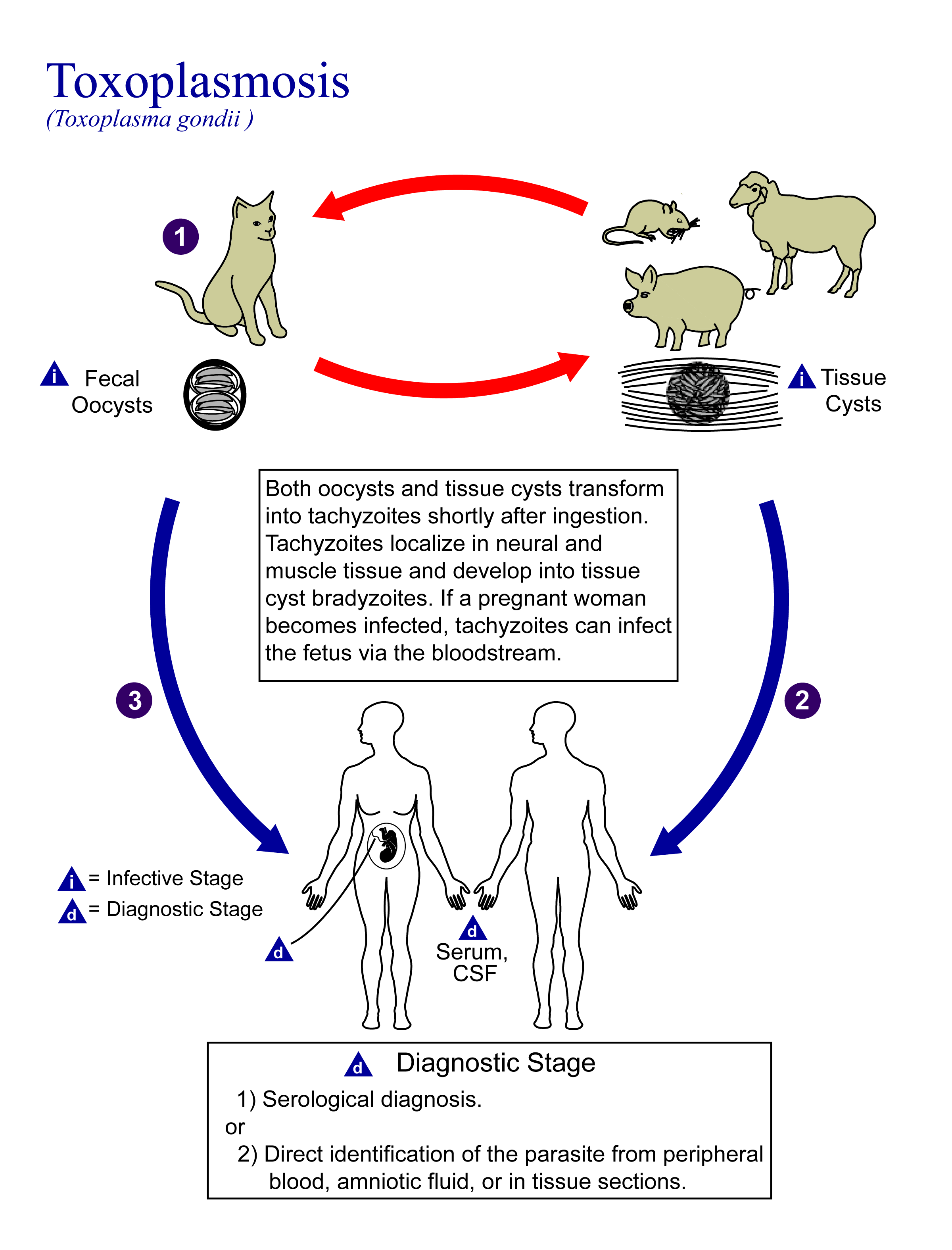
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zika Virus
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where the virus was first isolated in 1947. ''Zika virus'' shares a genus with the dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and West Nile viruses. Since the 1950s, it has been known to occur within a narrow equatorial belt from Africa to Asia. From 2007 to , the virus spread eastward, across the Pacific Ocean to the Americas, leading to the 2015–2016 Zika virus epidemic. The infection, known as Zika fever or ''Zika virus'' disease, often causes no or only mild symptoms, similar to a very mild form of dengue fever. While there is no specific treatment, paracetamol (acetaminophen) and rest may help with the symptoms. Zika can spread from a pregnant woman to her baby. This can result in microcephaly, severe brain malformations, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)