|
TERF2
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 is a protein that is present at telomeres throughout the cell cycle. It is also known as TERF2, TRF2, and TRBF2, and is encoded in humans by the ''TERF2'' gene. It is a component of the shelterin nucleoprotein complex and a second negative regulator of telomere length, playing a key role in the protective activity of telomeres. It was first reported in 1997 in the lab of Titia de Lange, where a DNA sequence similar, but not identical, to TERF1 was discovered, with respect to the Myb-domain. De Lange isolated the new Myb-containing protein sequence and called it TERF2. Structure and domains TERF2 has a similar structure to that of TERF1. Both proteins carry a C-terminus Myb motif and large TERF1-related dimerization domains near their N-terminus. However, both proteins exist exclusively as homodimers and do not heterodimerize with each other, as proven by co-immunoprecipitation assay analysis. Also, TERF2 has a basic N-terminus, differing fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TERF1
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TERF1'' gene. Gene The human TERF1 gene is located in the chromosome 8 at 73,921,097-73,960,357 bp. Two transcripts of this gene are alternatively spliced products. The TERF1 gene is also known as TRF, PIN2 (Proteinase Inhibitor 2), TRF1, t-TRF1 and h-TRF1-AS. Protein The protein structure contains a C-terminal Myb motif, a dimerization domain (TERF homology) near its N-terminus and an acidic N-terminus. Subcellular distribution The cellular distribution of this DNA binding protein features the nucleoplasm, chromosomes, a telomeric region, a nuclear telomere cap complex, the cytoplasm, the spindle, the nucleus and a nucleolus and a nuclear chromosome. Function TERF 1 gene encodes a telomere specific protein which is a component of the telomere's shelterin nucleoprotein complex. This protein is present at telomeres throughout the cell cycle and functions as an inhibitor of telomerase, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rap1
Rap1 (Ras-proximate-1 or Ras-related protein 1) is a small GTPase, which are small cytosolic proteins that act like cellular switches and are vital for effective signal transduction. There are two isoforms of the Rap1 protein, each encoded by a separate gene, RAP1A and RAP1B. Rap1 belongs to Ras-related protein family. GTPases are inactive when in their GDP-bound form, and become active when they bind to GTP. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) and guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) regulate small GTPases, with GAPs promoting the GDP-bound (inactive) form, and GEFs promoting the GTP-bound (active) form. When bound to GTP, small GTPases regulate myriad cellular processes. These proteins are divided into families depending on their protein structure, and the most well studied is the Ras superfamily, of which Rap1 is a member. Whereas Ras is known for its role in cell proliferation and survival, Rap1 is predominantly involved in cell adhesion and cell junction formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shelterin
Shelterin (also called telosome) is a protein complex known to protect telomeres in many eukaryotes from DNA repair mechanisms, as well as to regulate telomerase activity. In mammals and other vertebrates, telomeric DNA consists of repeating double-stranded 5'-TTAGGG-3' (G-strand) sequences (2-15 kilobases in humans) along with the 3'-AATCCC-5' (C-strand) complement, ending with a 50-400 nucleotide 3' (G-strand) overhang. Much of the final double-stranded portion of the telomere forms a T-loop (Telomere-loop) that is invaded by the 3' (G-strand) overhang to form a small D-loop (Displacement-loop). The absence of shelterin causes telomere uncapping and thereby activates damage-signaling pathways that may lead to non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), homology directed repair (HDR), end-to-end fusions, genomic instability, senescence, or apoptosis. Subunits Shelterin has six subunits: TRF1, TRF2, POT1, RAP1, TIN2, and TPP1. They can operate in smaller subsets to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XRCC3
DNA repair protein XRCC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''XRCC3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the RecA/Rad51-related protein family that participates in homologous recombination to maintain chromosome stability and repair DNA damage. This gene functionally complements Chinese hamster irs1SF, a repair-deficient mutant that exhibits hypersensitivity to a number of different DNA-damaging agents and is chromosomally unstable. A rare microsatellite polymorphism in this gene is associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity. The XRCC3 protein is one of five paralogs of RAD51, including RAD51B (RAD51L1), RAD51C (RAD51L2), RAD51D (RAD51L3), XRCC2 and XRCC3. They each share about 25% amino acid sequence identity with RAD51 and each other. The RAD51 paralogs are all required for efficient DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination and depletion of any paralog results in significant decreases in homologous recombination freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian Myeloblastosis
''Alpharetrovirus'' is a genus of the family Retroviridae. It has type C morphology. Members can cause sarcomas, other tumors, and anaemia of wild and domestic birds and also affect rats. Species include the Rous sarcoma virus, avian leukosis virus, and avian myeloblastosis virus Avian may refer to: *Birds or Aves, winged animals *Avian (given name) (russian: Авиа́н, link=no), a male forename Aviation *Avro Avian, a series of light aircraft made by Avro in the 1920s and 1930s *Avian Limited, a hang glider manufacture ... (AMV). Not all animals that can infect develop cancer. The tumor caused by the virus is usually in the form of lymphoma and leukemia. It occurs after a long and latent process. The tumor cells formed consist of a single progenitor cell and are clonal. However, infection from retroviruses does not directly produce tumors, but only placement and recombination events leading to tumor cell formation. References External links * ICTVdb Alpharetrovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TINF2
TERF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TINF2'' gene. TINF2 is a component of the shelterin protein complex found at the end of telomeres. Interactions TINF2 has been shown to interact with ACD, POT1 and TERF1 Telomeric repeat-binding factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TERF1'' gene. Gene The human TERF1 gene is located in the chromosome 8 at 73,921,097-73,960,357 bp. Two transcripts of this gene are alternatively spliced produ .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Dyskeratosis CongenitaPDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human TERF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 (TINF2) Telomere-related proteins {{gene-14-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Protein
A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and do not have the means to reproduce on their own, instead depending on their host cell's resources in order to reproduce. Thus, viruses do not code for many of their own viral proteins, and instead use the host cell's machinery to produce the viral proteins they require for replication. Viral structural proteins Most viral structural proteins are components for the capsid and the envelope of the virus. Capsid The genetic material of a virus is stored within a viral protein structure called the capsid. The capsid is a "shield" that protects the viral nucleic acids from getting degraded by host enzymes or other types of pesticides or pestilences. It also functions to attach the virion to its host, and enable the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
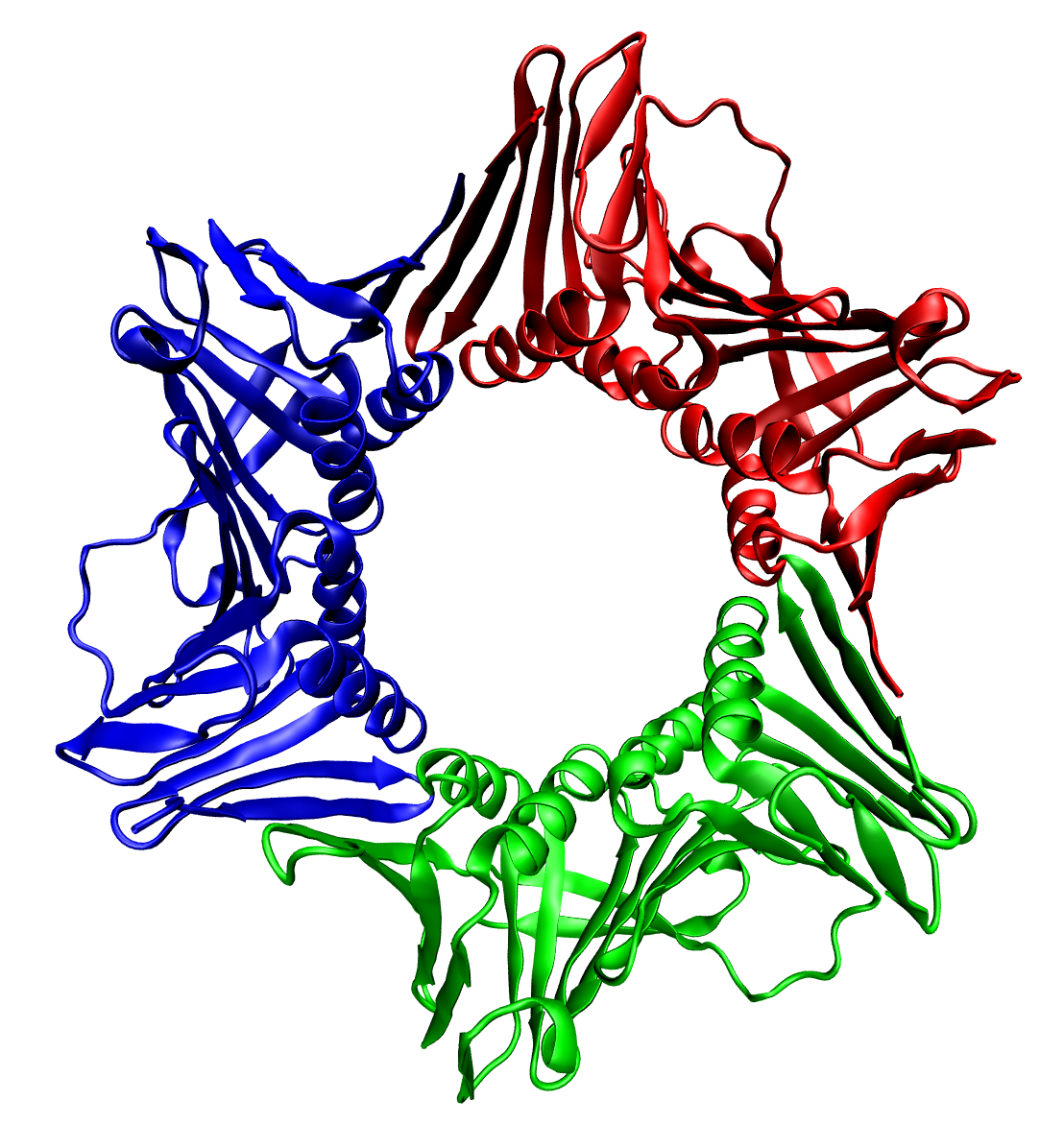
Protein Quaternary Structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also referred to as subunits). Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple protein folding, folded protein subunits in a Multiprotein complex, multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple protein dimer, dimers to large homooligomers and multiprotein complex, complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors. Description and examples Many proteins are actually assemblies of multiple polypeptide c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYB (gene)
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains. Function Viral The Myb gene family is named after the eponymous gene in Avian myeloblastosis virus. The viral Myb (v-Myb, ) recognizes the sequence 5'-YAACKG-3'. It causes myeloblastosis (myeloid leukemia) in chickens. Compared to the normal animal cellular Myb (c-myb), v-myb contains deletions in the C-terminal regulatory domain, leading to aberrant activation of other oncogenes. Animals Myb proto-oncogene protein is a member of the MYB (myeloblastosis) family of transcription factors. The protein contains three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central transcriptional activation domain and a C-terminal domain involved in transcriptional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaffold Protein
In biology, scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signalling pathways. Although scaffolds are not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signalling pathway, tethering them into complexes. In such pathways, they regulate signal transduction and help localize pathway components (organized in complexes) to specific areas of the cell such as the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi, endosomes, and the mitochondria. History The first signaling scaffold protein discovered was the Ste5 protein from the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Three distinct domains of Ste5 were shown to associate with the protein kinases Ste11, Ste7, and Fus3 to form a multikinase complex. Function Scaffold proteins act in at least four ways: tethering signaling components, localizing these components to specific areas of the cell, regulating signal transduction by coordinating positive and negative feedback s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |