|
TAS2R10
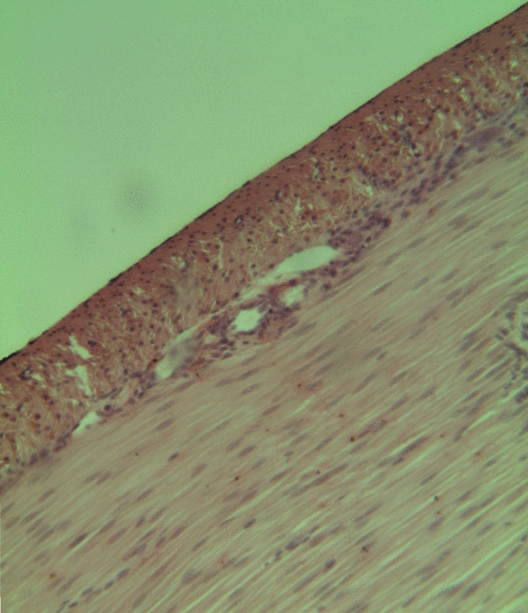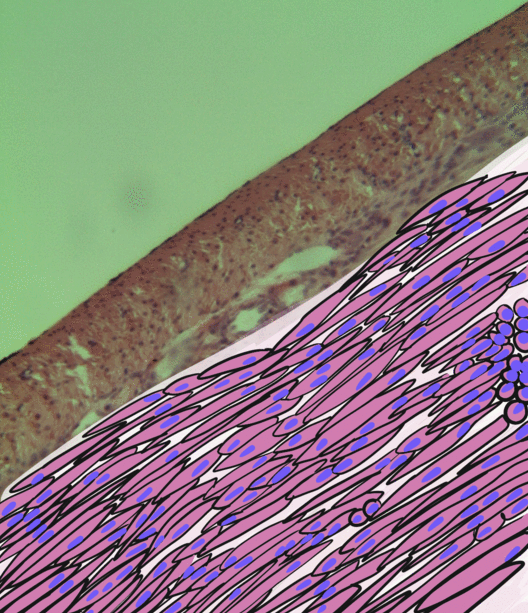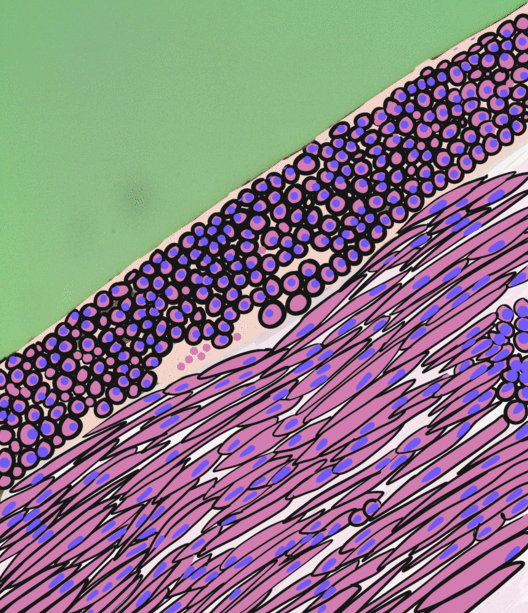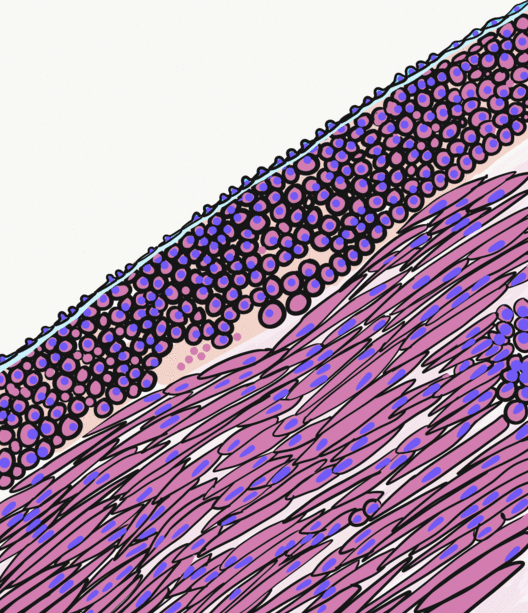
Taste receptor type 2 member 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS2R10'' gene. Function This gene product belongs to the family of candidate taste receptors that are members of the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily. These proteins are specifically expressed in the taste receptor cells of the tongue and palate epithelia. They are organized in the genome in clusters and are genetically linked to loci that influence bitter perception in mice and humans. In functional expression studies, they respond to bitter tastants. This gene maps to the taste receptor gene cluster on chromosome 12p13. TAS2R10 is also expressed in the smooth muscle of human airways, along with several other bitter taste receptors. Their activation in these cells causes an increase in intracellular calcium ion, which in turn triggers the opening of potassium channels which hyperpolarize the membrane and cause the smooth muscle to relax. Hence, activation of these receptors leads to bronch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taste Receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor which facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations. Molecules which give a sensation of taste are considered "sapid". Vertebrate taste receptors are divided into two families: * Type 1, sweet, first characterized in 2001: – * Type 2, bitter, first characterized in 2000: In humans there are 25 known different bitter receptors, in cats there are 12, in chickens there are three, and in mice there are 35 known different bitter receptors. Visual, olfactive, "sapictive" (the perception of tastes), trigeminal (hot, cool), mechanical, all contribute to the perception of ''taste''. Of these, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) vanilloid receptors are responsible for the perception of heat from some molecules such as capsaicin, and a CMR1 receptor is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taste Receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor which facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations. Molecules which give a sensation of taste are considered "sapid". Vertebrate taste receptors are divided into two families: * Type 1, sweet, first characterized in 2001: – * Type 2, bitter, first characterized in 2000: In humans there are 25 known different bitter receptors, in cats there are 12, in chickens there are three, and in mice there are 35 known different bitter receptors. Visual, olfactive, "sapictive" (the perception of tastes), trigeminal (hot, cool), mechanical, all contribute to the perception of ''taste''. Of these, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) vanilloid receptors are responsible for the perception of heat from some molecules such as capsaicin, and a CMR1 receptor is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Ion
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Channel
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regulate ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization. It inhibits action potentials by increasing the stimulus required to move the membrane potential to the action potential threshold. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ (a cation) through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– (an anion) through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g. Na+ through Na+ channels or Ca2+ through Ca2+ channels, inhibits hyperpolarization. If a cell has Na+ or Ca2+ currents at rest, then inhibition of those currents will also result in a hyperpolarization. This voltage-gated ion channel response is how the hyperpolarization state is achieved. In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. While hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchodilation
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. Although this remains somewhat controversial, they might be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases. Bronchodilators are either short-acting or long-acting. Short-acting medications provide quick or "rescue" relief from acute bronchoconstriction. Long-acting bronchodilators help to control and prevent symptoms. The three types of presc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |