|
TAOCP
''The Art of Computer Programming'' (''TAOCP'') is a comprehensive monograph written by the computer scientist Donald Knuth presenting programming algorithms and their analysis. Volumes 1–5 are intended to represent the central core of computer programming for sequential machines. When Knuth began the project in 1962, he originally conceived of it as a single book with twelve chapters. The first three volumes of what was then expected to be a seven-volume set were published in 1968, 1969, and 1973. Work began in earnest on Volume 4 in 1973, but was suspended in 1977 for work on typesetting prompted by the second edition of Volume 2. Writing of the final copy of Volume 4A began in longhand in 2001, and the first online pre-fascicle, 2A, appeared later in 2001. The first published installment of Volume 4 appeared in paperback as Fascicle 2 in 2005. The hardback Volume 4A, combining Volume 4, Fascicles 0–4, was published in 2011. Volume 4, Fascicle 6 ("Satisfiability") was rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Knuth
Donald Ervin Knuth ( ; born January 10, 1938) is an American computer scientist, mathematician, and professor emeritus at Stanford University. He is the 1974 recipient of the ACM Turing Award, informally considered the Nobel Prize of computer science. Knuth has been called the "father of the analysis of algorithms". He is the author of the multi-volume work ''The Art of Computer Programming'' and contributed to the development of the rigorous analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms and systematized formal mathematical techniques for it. In the process, he also popularized the asymptotic notation. In addition to fundamental contributions in several branches of theoretical computer science, Knuth is the creator of the TeX computer typesetting system, the related METAFONT font definition language and rendering system, and the Computer Modern family of typefaces. As a writer and scholar, Knuth created the WEB and CWEB computer programming systems designed to encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard S
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 650
The IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Data-Processing Machine is an early digital computer produced by IBM in the mid-1950s. It was the first mass produced computer in the world. Almost 2,000 systems were produced, the last in 1962, and it was the first computer to make a meaningful profit. The first one was installed in late 1954 and it was the most-popular computer of the 1950s. The 650 was marketed to business, scientific and engineering users as a general-purpose version of the IBM 701 and IBM 702 computers which were for scientific and business purposes respectively. It was also marketed to users of unit record equipment, punched card machines who were upgrading from Unit record equipment#Calculating, calculating punches, such as the IBM 604, to computers. Because of its relatively low cost and ease of Computer programming, programming, the 650 was used to pioneer a wide variety of applications, from modeling submarine crew performance to teaching high school and college students c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A ''decimal numeral'' (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , where is an integer, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computing, the hexadecimal (also base-16 or simply hex) numeral system is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of 16. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using 10 symbols, hexadecimal uses 16 distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9, and "A"–"F" (or alternatively "a"–"f") to represent values from 10 to 15. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a human-friendly representation of binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte can have values ranging from 00000000 to 11111111 in binary form, which can be conveniently represented as 00 to FF in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computing, the hexadecimal (also base-16 or simply hex) numeral system is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of 16. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using 10 symbols, hexadecimal uses 16 distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9, and "A"–"F" (or alternatively "a"–"f") to represent values from 10 to 15. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a human-friendly representation of binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte can have values ranging from 00000000 to 11111111 in binary form, which can be conveniently represented as 00 to FF in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
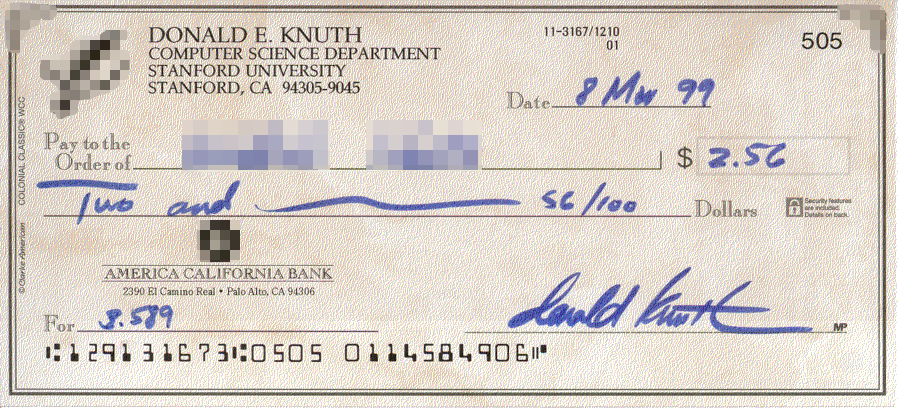
Knuth Reward Check
Knuth reward checks are checks or check-like certificates awarded by computer scientist Donald Knuth for finding technical, typographical, or historical errors, or making substantial suggestions for his publications. The ''MIT Technology Review'' describes the checks as "among computerdom's most prized trophies". History Initially, Knuth sent real, negotiable checks to recipients. He stopped doing so in October 2008 because of problems with check fraud. As a replacement, he started his own "Bank of San Serriffe", in the fictional nation of San Serriffe, which keeps an account for everyone who found an error since 2006. Knuth now sends out "hexadecimal certificates" instead of negotiable checks. , Knuth reported having written more than 2,000 checks, with an average value exceeding $8 per check.Donald Knuth (2002),All questions answered", ''Notices of the AMS'' 49(3): 318-324. , the total value of the checks signed by Knuth was over $20,000. Very few of these checks were actually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Metal Typesetting
In printing and typography, hot metal typesetting (also called mechanical typesetting, hot lead typesetting, hot metal, and hot type) is a technology for typesetting text in letterpress printing. This method injects molten type metal into a mold that has the shape of one or more glyphs. The resulting sorts or slugs are later used to press ink onto paper. Normally the typecasting machine would be controlled by a keyboard or by a paper tape. It was the standard technology used for mass-market printing from the late nineteenth century until the arrival of phototypesetting and then electronic processes in the 1950s to 1980s. History Hot metal typesetting was developed in the late nineteenth century as a development of conventional cast metal type. The technology had several advantages: it reduced labour since type sorts did not need to be slotted into position manually, and each casting created crisp new type for each printing job. In the case of Linotype machines, each line was ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typesetting
Typesetting is the composition of text by means of arranging physical ''type'' (or ''sort'') in mechanical systems or ''glyphs'' in digital systems representing ''characters'' (letters and other symbols).Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House, Inc. 23 December 2009Dictionary.reference.com/ref> Stored types are retrieved and ordered according to a language's orthography for visual display. Typesetting requires one or more fonts (which are widely but erroneously confused with and substituted for typefaces). One significant effect of typesetting was that authorship of works could be spotted more easily, making it difficult for copiers who have not gained permission. Pre-digital era Manual typesetting During much of the letterpress era, movable type was composed by hand for each page by workers called compositors. A tray with many dividers, called a case, contained cast metal '' sorts'', each with a single letter or symbol, but backwards (so they would print correctly). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasionally referred to as "CIT", most notably in its alma mater, but this is uncommon. is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California. Caltech is ranked among the best and most selective academic institutions in the world, and with an enrollment of approximately 2400 students (acceptance rate of only 5.7%), it is one of the world's most selective universities. The university is known for its strength in science and engineering, and is among a small group of Institute of Technology (United States), institutes of technology in the United States which is primarily devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Todd (computer Scientist)
John Todd (May 16, 1911 – June 21, 2007) was a Northern Irish mathematician most of whose career was spent in England and the USA; he was a pioneer in the field of numerical analysis. He was born in Carnacally, County Down, Ireland, and grew up near Belfast. He attended Methodist College Belfast after winning a scholarship. In his final year at the College he only studied maths as a result of his desire to become an engineer. He received his BSc degree from Queen's University in 1931, and went to St. John's College at Cambridge University, studying for 2 years with J. E. Littlewood, who advised him against getting a doctorate and just to do research. He taught at Queen's University Belfast 1933-1937, and was an invited speaker at the 1936 ICM in Oslo on "Transfinite Superpositions of Absolutely Continuous Functions" He worked at King's College in London for the years 1937–1939 (and again 1945–1947), where he met Olga Taussky, a matrix and number theorist (she had al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olga Taussky-Todd
Olga Taussky-Todd (August 30, 1906, Olomouc, Austria-Hungary (present-day Olomouc, Czech Republic) – October 7, 1995, Pasadena, California) was an Austrian and later Czech-American mathematician. She published more than 300 research papers on algebraic number theory, integral matrices, and matrices in algebra and analysis. Early life Olga Taussky was born into a Jewish family in what is now Olomouc, Czech Republic, on August 30, 1906. Her father, Julius David Taussky, was an industrial chemist and her mother, Ida Pollach, was a housewife. She was the second of three children. Her father preferred that, if his daughters had careers, they be in the arts, but they all went into the sciences. Ilona, three years older than Olga, became a consulting chemist in the glyceride industry, and Hertha, three years younger than Olga, became a pharmacist and later a clinical chemist at Cornell University Medical College in New York City. At the age of three, her family moved to Vienna and li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
