|
T2SS
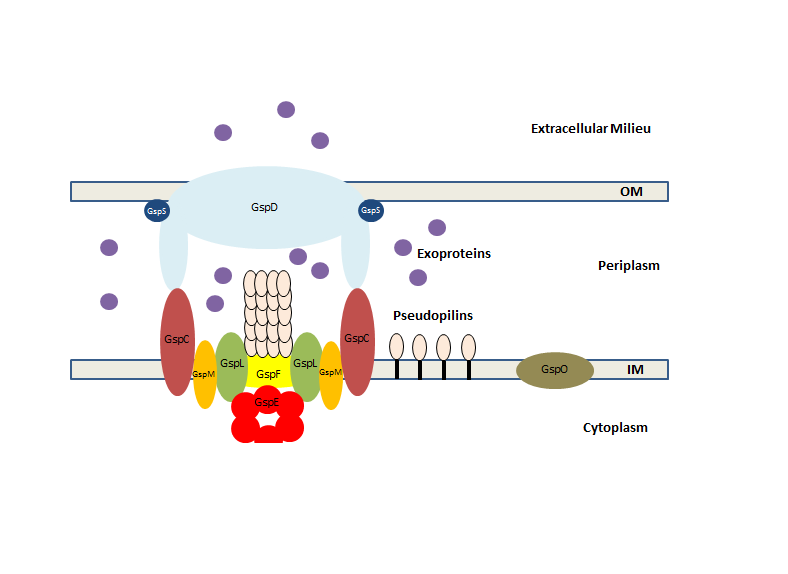
The type 2 secretion system (often referred to as the type II secretion system or by the initials T2SS) is a type of protein secretion machinery found in various species of Gram-negative bacteria, including many human pathogens such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Vibrio cholerae''. The type II secretion system is one of six protein secretory systems commonly found in Gram-negative bacteria, along with the type I, type III, and type IV secretion systems, as well as the chaperone/usher pathway, the autotransporter pathway/type V secretion system, and the type VI secretion system (some bacteria also utilize the type VII secretion system). Like these other systems, the type II secretion system enables the transport of cytoplasmic proteins across the lipid bilayers that make up the cell membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Secretion of proteins and effector molecules out of the cell plays a critical role in signaling other cells and in the invasion and parasitism of host cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretion
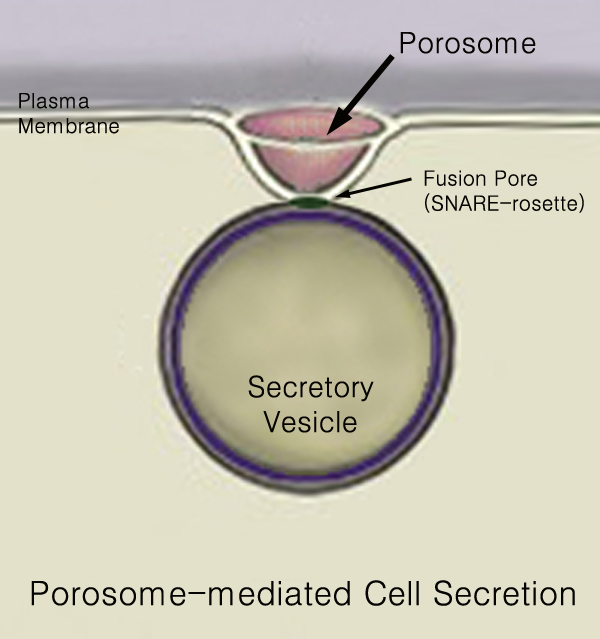
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T2SS
The type 2 secretion system (often referred to as the type II secretion system or by the initials T2SS) is a type of protein secretion machinery found in various species of Gram-negative bacteria, including many human pathogens such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Vibrio cholerae''. The type II secretion system is one of six protein secretory systems commonly found in Gram-negative bacteria, along with the type I, type III, and type IV secretion systems, as well as the chaperone/usher pathway, the autotransporter pathway/type V secretion system, and the type VI secretion system (some bacteria also utilize the type VII secretion system). Like these other systems, the type II secretion system enables the transport of cytoplasmic proteins across the lipid bilayers that make up the cell membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Secretion of proteins and effector molecules out of the cell plays a critical role in signaling other cells and in the invasion and parasitism of host cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Toxins
Microbial toxins are toxins produced by micro-organisms, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, dinoflagellates, and viruses. Many microbial toxins promote infection and disease by directly damaging host tissues and by disabling the immune system. Endotoxins most commonly refer to the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipooligosaccharide (LOS) that are in the outer plasma membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The botulinum toxin, which is primarily produced by ''Clostridium botulinum'' and less frequently by other ''Clostridium'' species, is the most toxic substance known in the world. However, microbial toxins also have important uses in medical science and research. Currently, new methods of detecting bacterial toxins are being developed to better isolate and understand these toxin. Potential applications of toxin research include combating microbial virulence, the development of novel anticancer drugs and other medicines, and the use of toxins as tools in neurobiology and cellular biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research
''Biochimica et Biophysica Acta'' (''BBA'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of biochemistry and biophysics that was established in 1947. The journal is published by Elsevier with a total of 100 annual issues in ten specialised sections. History Early years ''Biochimica et Biophysica Acta'' was first published in 1947 and was the first international journal to be devoted to the joint fields of biochemistry and biophysics.A short history of Elsevier (Elsevier; 2005) (accessed 12 December 2008) Published by in cooperation with |
Protein Subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit is a polypeptide chain or single protein molecule that assembles (or "''coassembles''") with others to form a protein complex. Large assemblies of proteins such as viruses often use a small number of types of protein subunits as building blocks. A subunit is often named with a Greek or Roman letter, and the numbers of this type of subunit in a protein is indicated by a subscript. For example, ATP synthase has a type of subunit called α. Three of these are present in the ATP synthase molecule, leading to the designation α3. Larger groups of subunits can also be specified, like α3β3-hexamer and c-ring. Naturally-occurring proteins that have a relatively small number of subunits are referred to as oligomeric.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
''Biochimica et Biophysica Acta'' (''BBA'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of biochemistry and biophysics that was established in 1947. The journal is published by Elsevier with a total of 100 annual issues in ten specialised sections. History Early years ''Biochimica et Biophysica Acta'' was first published in 1947 and was the first international journal to be devoted to the joint fields of biochemistry and biophysics.A short history of Elsevier (Elsevier; 2005) (accessed 12 December 2008) Published by in cooperation with |
Periplasm
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that a much smaller periplasmic space is also present in gram-positive bacteria., Matias, V. R., and T. J. Beveridge. 2005. Cryo-electron microscopy reveals native polymeric cell wall structure in Bacillus subtilis 168 and the existence of a periplasmic space. Mol. Microbiol. 56:240-251. ., Zuber B, Haenni M, Ribeiro T, Minnig K, Lopes F, Moreillon P, Dubochet J. 2006. Granular layer in the periplasmic space of Gram-positive bacteria and fine structures of Enterococcus gallinarum and Streptococcus gordonii septa revealed by cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections. J Bacteriol. 188:6652-6660. The periplasm may constitute up to 40% of the total cell volume of gram-negative bacteria, but is a much smaller percentage in gram-positive bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-arginine Translocation Pathway
The twin-arginine translocation pathway (Tat pathway) is a protein export, or secretion pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea. In contrast to the Sec pathway which transports proteins in an unfolded manner, the Tat pathway serves to actively translocate folded proteins across a lipid membrane bilayer. In plants, the Tat translocase is located in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast, where it acts to export proteins into the thylakoid lumen. In bacteria, the Tat translocase is found in the cytoplasmic membrane and serves to export proteins to the cell envelope, or to the extracellular space. The existence of a Tat translocase in plant mitochondria is also proposed. In the plant thylakoid membrane and in Gram-negative bacteria the Tat translocase is composed of three essential membrane proteins; TatA, TatB, and TatC. In the most widely studied Tat pathway, that of the Gram-negative bacterium ''Escherichia coli'', these three proteins are expressed from an operon with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SecYEG
Sec61, termed SecYEG in prokaryotes, is a membrane protein complex found in all domains of life. As the core component of the translocon, it transports proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes and out of the cell in prokaryotes. It is a doughnut-shaped pore through the membrane with 3 different subunits (heterotrimeric), SecY (α), SecE (γ), and SecG (β). It has a region called the plug that blocks transport into or out of the ER. This plug is displaced when the hydrophobic region of a nascent polypeptide interacts with another region of Sec61 called the seam, allowing translocation of the polypeptide into the ER lumen. Structure Much of the knowledge on the structure of the SecY/Sec61α pore comes from an X-ray crystallography structure of its archaeal version. The large SecY subunit consists of two halves, trans-membrane segments 1-5 and trans-membrane segments 6-10. They are linked at the extracellular side by a loop between trans-membrane segments 5 and 6. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Outer Membrane
The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as ''E. coli'' it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein. Porins can be found in this layer. Clinical significance If lipid A, part of the lipopolysaccharide, enters the circulatory system it causes a toxic reaction by activating toll like receptor TLR 4. Lipid A is very pathogenic and not immunogenic. However, the polysaccharide component is very immunogenic, but not pathogenic, causing an aggressive response by the immune system. The sufferer will have a high temperature and respiration rate and a low blood pressure. This may lead to endotoxic shock, which may be fatal. The bacterial outer membrane is physiologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Inner Membrane
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |