|
Táchira Depression
The Táchira Depression ( es, Depresión de Táchira) is a saddle of land connecting the Lake Maracaibo basin to the Orinoco basin in the state of Táchira, Venezuela. It forms a break in the eastern Andes, separating the Tamá Massif to the west from the Cordillera de Mérida to the east. The depression has been thought to present a barrier to the movement of species between the Colombian and Venezuelan Andes, but this effect may have been relatively low during the recent ice ages. The mountains of the region have potential for coffee farming and hydroelectric power generation, while the lower levels are suitable for farming. Location The Eastern Cordillera of the Colombian Andes forks from the Pamplona Node into two long branches. The Cordillera de Periiá extends northward and the Tamá Massif and Cordillera de Mérida extends in a northeast direction. The second branch is divided by the Táchira depression, an area of low lands between the valleys of the Táchira River to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubio, Venezuela
Rubio is a town in the Venezuelan Andean state of Táchira. Founded in 1794 by Gervasio Rubio, this town is the shire town of the Junín Municipality and, according to the 2001 Venezuelan census, the municipality has a population of 68,869.http://www.tachira.gov.ve/paginaweb/tachira/estadisticas/Estadisticas_Municipios/junin.pdf Rubio is one of the largest towns in the state of Táchira. Its importance derives from its coffee production and the nearby commerce that exists with Colombia. Venezuela's former president, Carlos Andrés Pérez, was also born in Rubio. Rubio has beautiful natural tunnels called La Cueva de los Miagros. There are some rivers and waterfalls on the outskirts of town. The town has many bridges especially in Old Rubio. For this reason it is called "Ciudad Pontalida" or "City of Bridges." Rubio is located in the west of Estado Táchira and is a 40-minute drive from San Cristóbal, the capital of Táchira. History Rubio was founded by Gervasio Rubio in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
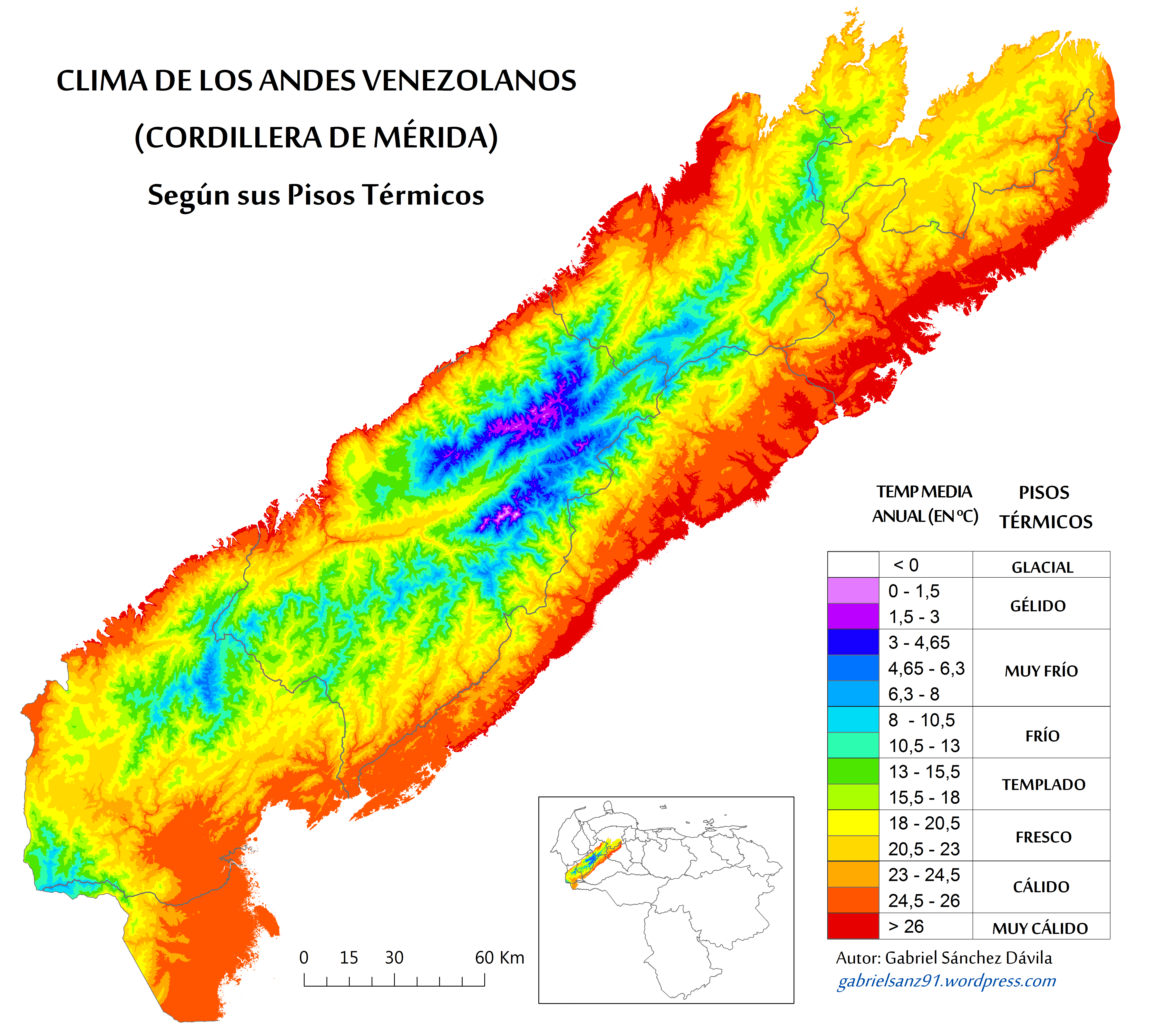
Merida Brocket
Mérida or Merida may refer to: Places *Mérida (state), one of the 23 states which make up Venezuela *Mérida, Mérida, the capital city of the state of Mérida, Venezuela *Merida, Leyte, Philippines, a municipality in the province of Leyte *Mérida, Spain, the capital city of the autonomous community of Extremadura *Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, the capital city of the state of Yucatán * or , an ancient name for Mardin, Turkey Football clubs *CP Mérida, a defunct club in Mérida, Spain *Estudiantes de Mérida, Venezuela *Imperio de Mérida CP, Mérida, Spain *Mérida AD, a club in Mérida, Spain * Mérida F.C., Mexico *Mérida UD, a defunct club in Mérida, Spain Other uses *Merida (Disney), the main character of the 2012 animated film ''Brave'' *Merida (Dragon Prince), a fictional people created by fantasy author Melanie Rawn for her ''Dragon Prince'' series * ''Merida'' (moth), a genus of moth in the family Geometridae *Merida Bikes, one of the world's largest bicycle mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesic Habitat
In ecology, a mesic habitat is a type of habitat with a moderate or well-balanced supply of moisture, e.g., a mesic forest, a temperate hardwood forest, or dry-mesic prairie. Mesic habitats transition to xeric shrublands in a non-linear fashion, which is evidence of a threshold. Mesic is one of a triad of terms used to describe the amount of water in a habitat. The others are xeric and hydric. Further examples of mesic habitats include streamsides, wet meadows, springs, seeps, irrigated fields, and high elevation habitats. These habitats effectively provide drought insurance as land at higher elevations warms due to seasonal or other change. Healthy mesic habitats act like sponges in that they store water in such a way that it can be deposited to neighboring habitats as needed. They are common in dryer regions of the western United States, and can be a good water source to neighboring desert habitats. Healthy mesic habitats also provide forb and insects for organisms belonging t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apure–Villavicencio Dry Forests
The Apure–Villavicencio dry forests (NT0201) is an ecoregion in Venezuela and Colombia to the east of the eastern cordillera of the Andes. The ecoregion covers the transition zone between montane forests in the Andes and the llanos, or lowland grasslands. It has been severely degraded by deforestation, farming and ranching. The remnants are poorly protected. Geography Location The Apure–Villavicencio dry forests ecoregion runs along the eastern edge of the Andes of Colombia and Venezuela from the southwest to the northeast. It has an area of . It forms a broad band between the mountains and grasslands in the north that becomes narrower further south. In Venezuela it covers parts of the states of Portuguesa (Venezuela), Portuguesa, Barinas (state), Barinas, and Apure, and in Colombia it lies in the departments of Arauca Department, Arauca, Casanare Department, Casanare, and Meta Department, Meta. Along the southeast and northern margin the dry forests ecoregion gives way to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catatumbo Moist Forests
The Catatumbo moist forests (NT0108) is an ecoregion in Venezuela and Colombia to the west and east of Lake Maracaibo. It includes four regions of moist forest on slightly higher ground than the dry forest and mangroves that surround the lake. The forest has unique flora related to the flora of the Amazon basin. It is badly degraded due to farming, livestock grazing and oil exploration. Geography Location The Catatumbo moist forests ecoregion is in western Venezuela and northeastern Colombia found on both sides of Lake Maracaibo. To the west it extends to the foothills of the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes, and in the south reaches the foothills of the Venezuelan Andes. It has an area of . In Venezuela the forest is in the states of Zulia and Lara. In Colombia it is in the Norte de Santander Department. The moist forests are mainly found to the southwest of Lake Maracaibo, but include two patches to the east of the lake surrounded by Maracaibo dry forests. A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuelan Andes Montane Forests
The Venezuelan Andes montane forests (NT0175) is an ecoregion in the northern arm of the Andes in Venezuela. It contains montane and cloud forests, reaching up to the high-level Cordillera de Merida páramo high moor ecoregion. The forests are home to many endemic species of flora and fauna. Their lower levels are threatened by migrant farmers, who clear patches of forest to grow crops, then move on. Geography Location The Venezuelan Andes montane forests ecoregion covers most of the Venezuelan states of Mérida and Trujillo, much the state of Táchira and the highlands of the states of Lara and Barinas. It includes a small area in Colombia. It covers the lower part of the Venezuelan extension of the Cordillera Occidental of the northern Andes. It has an area of . To the southeast it adjoins the Llanos and the Apure–Villavicencio dry forests, and to the southwest adjoins the Cordillera Oriental montane forests. To the northwest it adjoins the Catatumbo moist forests and the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Oriental Montane Forests
The Cordillera Oriental montane forests (NT0118) is an ecoregion in Venezuela and Colombia along the east slopes of the eastern cordillera of the Andes. The extensive region of submontane and montane forests includes distinctive flora and fauna in the north, center and southern sections. The ecoregion is home to numerous endemic species of fauna. Despite extensive changes due to logging, farming and ranching, large areas of the original habitat remain intact, and the ecoregion has rich biodiversity. Geography Location The Cordillera Oriental montane forests ecoregion extends along eastern slopes of the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes, mostly in Colombia but in the northwest of Venezuela to the west of Lake Maracaibo. It has an area of . At the northern end of the cordillera the ecoregion gives way to Guajira–Barranquilla xeric scrub. To the east, from north it south it adjoins the Maracaibo dry forests, Catatumbo moist forests, Venezuelan Andes montane forests, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureña, Táchira
Ureña is a city and the shire town of Pedro María Ureña Municipality, Táchira in Venezuela Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th .... It is located on the border with Colombia. The city was founded by Pedro María Ureña,Gobierno Bolívariano - Pedro María Ureña Consultado el 23 de julio de 2013. having been elevated to the category of parish by means of the provincial law of December 4, 1851. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Antonio Del Táchira
San Antonio del Táchira is a city in the Venezuelan Andean state of Táchira. The busy highway across the Simón Bolívar International Bridge linking the cities of Cúcuta, Colombia, and San Cristóbal, Venezuela, passes through San Antonio del Táchira, making it an important gateway between the two nations. This city is the shire town of the Municipio Bolívar de Táchira and, according to the 2001 Venezuelan census, the municipality has a population of 48,171. History General passed through this city during his |