|
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation), a step that TKIs inhibit. TKIs are typically used as anticancer drugs. For example, they have substantially improved outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. They have also been used to treat other diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. They are also called tyrphostins, the short name for "tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor", originally coined in a 1988 publication, which was the first description of compounds inhibiting the catalytic activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The 1988 study was the first demonstration of a systematic search and discovery of small-molecular-weight inhibitors of tyrosine phosphorylation, which do not inhibit protein kinases that phospho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
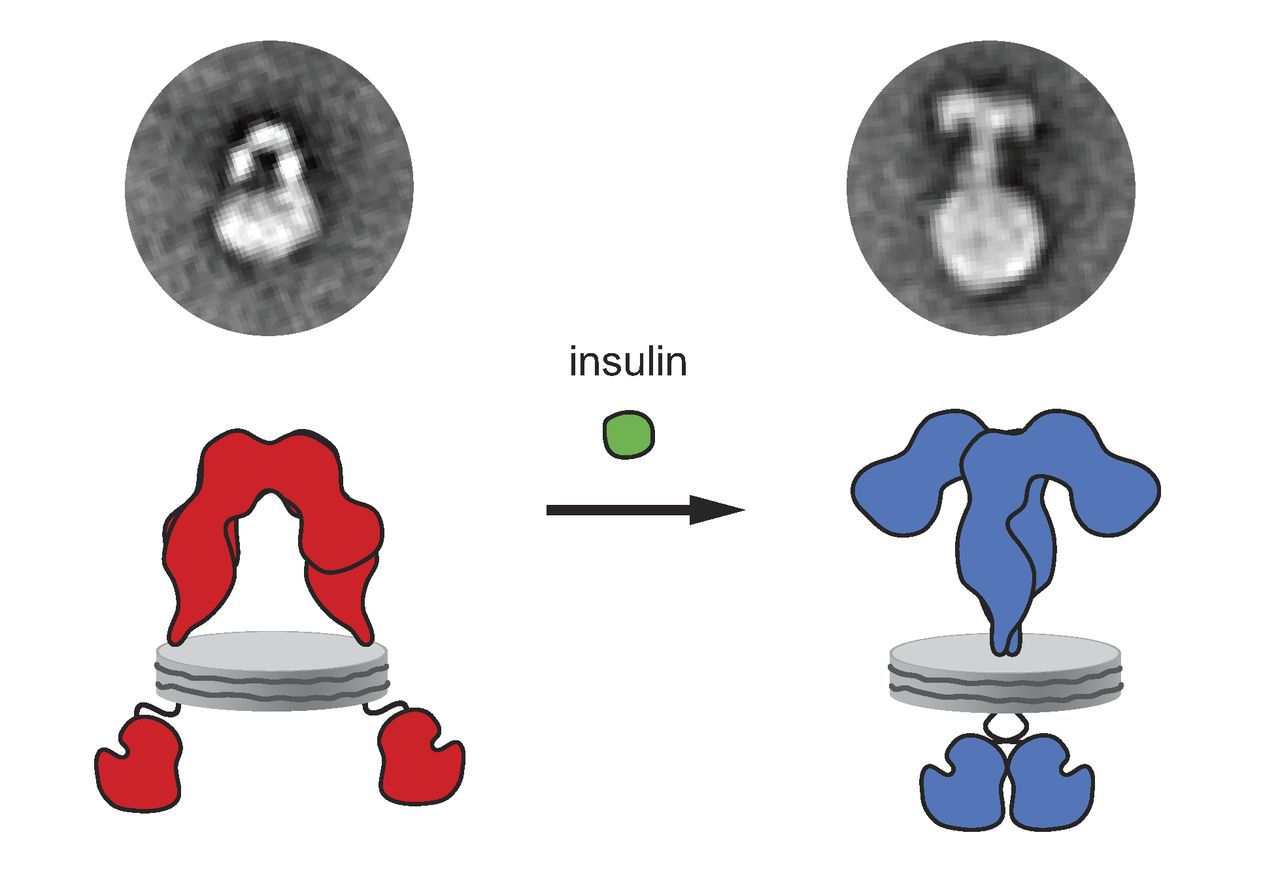
Insulin Receptor
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis, a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene , from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet-derived Growth Factor
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one among numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood vessel tissue, mitogenesis, i.e. proliferation, of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts, osteoblasts, tenocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal stem cells as well as chemotaxis, the directed migration, of mesenchymal cells. Platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein that can be composed of two A subunits (PDGF-AA), two B subunits (PDGF-BB), or one of each (PDGF-AB). PDGF is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin, including fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and glial cells. In both mouse and human, the PDGF signalling network consists of five ligands, PDGF-AA through -DD (including -AB), and two receptors, PDGFRalpha and PDGFRbeta. All PDGFs function as secreted, disulphide-linked homodimers, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans and are released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is also kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunitinib
Sunitinib, sold under the brand name Sutent, is a medication used to treat cancer. It is a small-molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that was approved by the FDA for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) on January 26, 2006. Sunitinib was the first cancer drug simultaneously approved for two different indications. As of August 2021, sunitinib is available as a generic medicine in the US. Medical uses Gastrointestinal stromal tumor Like RCC, GIST does not generally respond to standard chemotherapy or radiation. Imatinib was the first cancer agent proven effective for metastatic GIST and represented a major development in the treatment of this rare but challenging disease. However, approximately 20% of patients do not respond to imatinib (early or primary resistance), and among those who do respond initially, 50% develop secondary imatinib resistance and disease progression withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers In Pharmacology
Frontiers Media S.A. (corporation), SA is a publisher of peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journals currently active in science, technology, and medicine. It was founded in 2007 by Kamila and Henry Markram, and has since expanded to other academic fields. Frontiers is based in Lausanne, Switzerland, with other offices in London, Madrid, Seattle and Brussels. In 2022, Frontiers employed more than 1,400 people, across 14 countries. All Frontiers journals are published under a Creative Commons Attribution License. As of 2022, Frontiers publishes over 185 academic journals, including 48 journals indexed within the Science Citation Index Expanded, and 4 journals indexed within the Social Sciences Citation Index, with a total of 51 journals ranked with an impact factor. Frontiers journals are included in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Frontiers is also a member of the Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA), a participating publisher and supporter of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senolytic
A senolytic (from the words ''senescence'' and ''-lytic'', "destroying") is among a class of small molecules under basic research to determine if they can selectively induce death of senescent cells and improve health in humans. A goal of this research is to discover or develop agents to delay, prevent, alleviate, or reverse age-related diseases. A related concept is "senostatic", which means to suppress senescence. Research Possible senolytic agents are under preliminary research, including some which are in early-stage human trials. The majority of candidate senolytic compounds are repurposed anti-cancer molecules, such as the chemotherapeutic drug dasatinib and the experimental small molecule navitoclax. According to reviews, it is thought that senolytics can be administered intermittently while being as effective as continuous administration. This could be an advantage of senolytic drugs and decrease adverse effects, for instance circumventing potential off-target effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Src Inhibitor
Src inhibitor is a class of inhibitors that targets the Src kinase family of tyrosine kinase, which is transcribed by the Src proto-oncogene (short for "sarcoma gene") that potentially induce malignant transformations of certain cells. Because of the crucial position of the Src kinase in cells, Src inhibitors are potential antineoplastic agents for e.g. pancreatic cancer, breast cancer and stomach cancer Examples * KX2-391 is an oral src inhibitor and the first clinical inhibitor with GI50 of 9–60 nM in cancer cell lines. * Bosutinib has been developed for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia by Pfizer Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfize .... * Saracatinib, the first Src inhibitor to show inhibition of the Src pathway in human tumor tissue, has anti-tumor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasatinib
Dasatinib, sold under the brand name Sprycel among others, is a targeted therapy medication used to treat certain cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Specifically it is used to treat cases that are Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+). It is taken by mouth. Common adverse effects include low white blood cells, low blood platelets, anemia, swelling, rash, and diarrhea. Severe adverse effects may include bleeding, pulmonary edema, heart failure, and prolonged QT syndrome. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. It is a tyrosine-kinase inhibitor and works by blocking a number of tyrosine kinases such as Bcr-Abl and the Src kinase family. Dasatinib was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in 2006. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Dasatinib is used to treat people with chronic myeloid leukemia and people with acute lymphobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlotinib
Erlotinib, sold under the brand name Tarceva among others, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and pancreatic cancer. Specifically it is used for NSCLC with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) — either an exon 19 deletion (del19) or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutation — which has spread to other parts of the body. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include rash, diarrhea, muscle pain, joint pain, and cough. Serious side effects may include lung problems, kidney problems, liver failure, gastrointestinal perforation, stroke, and corneal ulceration. Use in pregnancy may harm the baby. It is a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which acts on the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Erlotinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2004. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Lung cancer Erlotinib in unresectable non-small cell lung cancer when added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gefitinib
Gefitinib, sold under the brand name Iressa, is a medication used for certain breast, lung and other cancers. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in target cells. Therefore, it is only effective in cancers with mutated and overactive EGFR, but resistances to gefitinib can arise through other mutations. It is marketed by AstraZeneca and Teva. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Mechanism of action Gefitinib is the first selective inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor's (EGFR) tyrosine kinase domain. Thus gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor. The target protein (EGFR) is a member of a family of receptors ( ErbB) which includes Her1(EGFR), Her2(erb-B2), Her3(erb-B3) and Her4 (Erb-B4). EGFR is overexpressed in the cells of certain types of human carcinomas - for example in lung and breast cancers. This leads to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple receptor tyrosine kinases such as CSF1R, ABL, c-KIT, FLT3, and PDGFR-β. Specifically, it is used for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) that are Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+), certain types of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES), chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL), systemic mastocytosis, and myelodysplastic syndrome. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, headache, and rash. Severe side effects may include fluid retention, gastrointestinal bleeding, bone marrow suppression, liver problems, and heart failure. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Imatinib works by stopping the Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase. This can slow grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |