|
Tyromyces Albovinaceus
''Tyromyces'' is a genus of poroid fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Petter Karsten in 1881. The type species is the widely distributed '' Tyromyces chioneus'', commonly known as the white cheese polypore. The phylogenetic position of ''Tyromyces'' within the Polyporales is uncertain, but it appears that it does not belong to the "core polyporoid clade". ''Tyromyces'' is polyphyletic as it is currently circumscribed, and has been described as "a dumping place for monomitic white-rot species with thin-walled spores." The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ("cheese") and (fungus"). Description ''Tyromyces'' fungi have fruit bodies that are pileate (i.e., with a cap) to resupinate ( crust-like). Fruit bodies are short-lived, and often mostly white, but turning a darker colour when dry. The colour of the pore surface is usually white to cream, sometime with greenish tinges. Like the cap surface, it darkens when dry. Microscopic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petter Karsten
Petter Adolf Karsten (16 February 1834 – 22 March 1917) was a Finnish mycologist, the foremost expert on the fungi of Finland in his day, and known in consequence as the "father of Finnish mycology". Karsten was born in Merimasku near Turku, studied at the University of Helsinki, and then moved to the inland of Tammela, where he spent most of his life with teaching botany and doing research at the Mustiala Agriculture Institute (now the Faculty of Agriculture of the HAMK University of Applied Sciences). He amassed a vast collection, both by his own efforts and those of his correspondents, and named about 200 new genera and 2,000 new species. In his mycological studies he extensively used the microscope and can be considered as the pioneer of fungal microscopy. ''Karstenia'', the international journal of mycology published by the Finnish Mycological Society, is dedicated to Karsten. Honours In 1885, botanist Elias Magnus Fries published ''Karstenia'' is a genus of fungi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
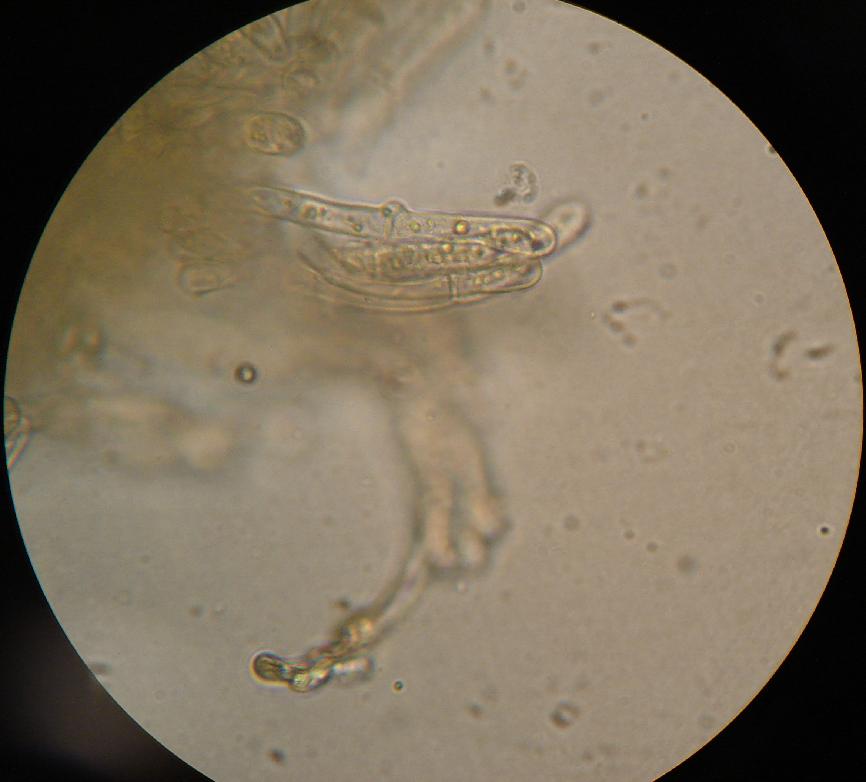
Clamp Connection
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyromyces Albus
''Tyromyces'' is a genus of poroid fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Petter Karsten in 1881. The type species is the widely distributed '' Tyromyces chioneus'', commonly known as the white cheese polypore. The phylogenetic position of ''Tyromyces'' within the Polyporales is uncertain, but it appears that it does not belong to the "core polyporoid clade". ''Tyromyces'' is polyphyletic as it is currently circumscribed, and has been described as "a dumping place for monomitic white-rot species with thin-walled spores." The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ("cheese") and (fungus"). Description ''Tyromyces'' fungi have fruit bodies that are pileate (i.e., with a cap) to resupinate ( crust-like). Fruit bodies are short-lived, and often mostly white, but turning a darker colour when dry. The colour of the pore surface is usually white to cream, sometime with greenish tinges. Like the cap surface, it darkens when dry. Microscopic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyromyces Albovinaceus
''Tyromyces'' is a genus of poroid fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Petter Karsten in 1881. The type species is the widely distributed '' Tyromyces chioneus'', commonly known as the white cheese polypore. The phylogenetic position of ''Tyromyces'' within the Polyporales is uncertain, but it appears that it does not belong to the "core polyporoid clade". ''Tyromyces'' is polyphyletic as it is currently circumscribed, and has been described as "a dumping place for monomitic white-rot species with thin-walled spores." The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ("cheese") and (fungus"). Description ''Tyromyces'' fungi have fruit bodies that are pileate (i.e., with a cap) to resupinate ( crust-like). Fruit bodies are short-lived, and often mostly white, but turning a darker colour when dry. The colour of the pore surface is usually white to cream, sometime with greenish tinges. Like the cap surface, it darkens when dry. Microscopic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyromyces Albogilvus
''Tyromyces'' is a genus of poroid fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Petter Karsten in 1881. The type species is the widely distributed '' Tyromyces chioneus'', commonly known as the white cheese polypore. The phylogenetic position of ''Tyromyces'' within the Polyporales is uncertain, but it appears that it does not belong to the "core polyporoid clade". ''Tyromyces'' is polyphyletic as it is currently circumscribed, and has been described as "a dumping place for monomitic white-rot species with thin-walled spores." The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ("cheese") and (fungus"). Description ''Tyromyces'' fungi have fruit bodies that are pileate (i.e., with a cap) to resupinate ( crust-like). Fruit bodies are short-lived, and often mostly white, but turning a darker colour when dry. The colour of the pore surface is usually white to cream, sometime with greenish tinges. Like the cap surface, it darkens when dry. Microscopic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyromyces Albiformis
''Tyromyces'' is a genus of poroid fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Petter Karsten in 1881. The type species is the widely distributed '' Tyromyces chioneus'', commonly known as the white cheese polypore. The phylogenetic position of ''Tyromyces'' within the Polyporales is uncertain, but it appears that it does not belong to the "core polyporoid clade". ''Tyromyces'' is polyphyletic as it is currently circumscribed, and has been described as "a dumping place for monomitic white-rot species with thin-walled spores." The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ("cheese") and (fungus"). Description ''Tyromyces'' fungi have fruit bodies that are pileate (i.e., with a cap) to resupinate ( crust-like). Fruit bodies are short-lived, and often mostly white, but turning a darker colour when dry. The colour of the pore surface is usually white to cream, sometime with greenish tinges. Like the cap surface, it darkens when dry. Microscopic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names ( scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is somewhat comparable to the International Plant Names Index (IPNI), in which the Royal Botanic Gardens is also involved. A difference is that where IPNI does not indicate correct names, the ''Index Fungorum'' does indicate the status of a name. In the returns from the search page a currently correct name is indicated in green, while others are in blue (a few, aberrant usages of names are indicated in red). All names are linked to pages giving the correct name, with lists of synonyms. ''Index Fungorum'' is one of three nomenclatural repositories recognized by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi; the others are ''MycoBank'' and ''Fungal Names''. Current names in ''Index Fungorum'' (''Speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
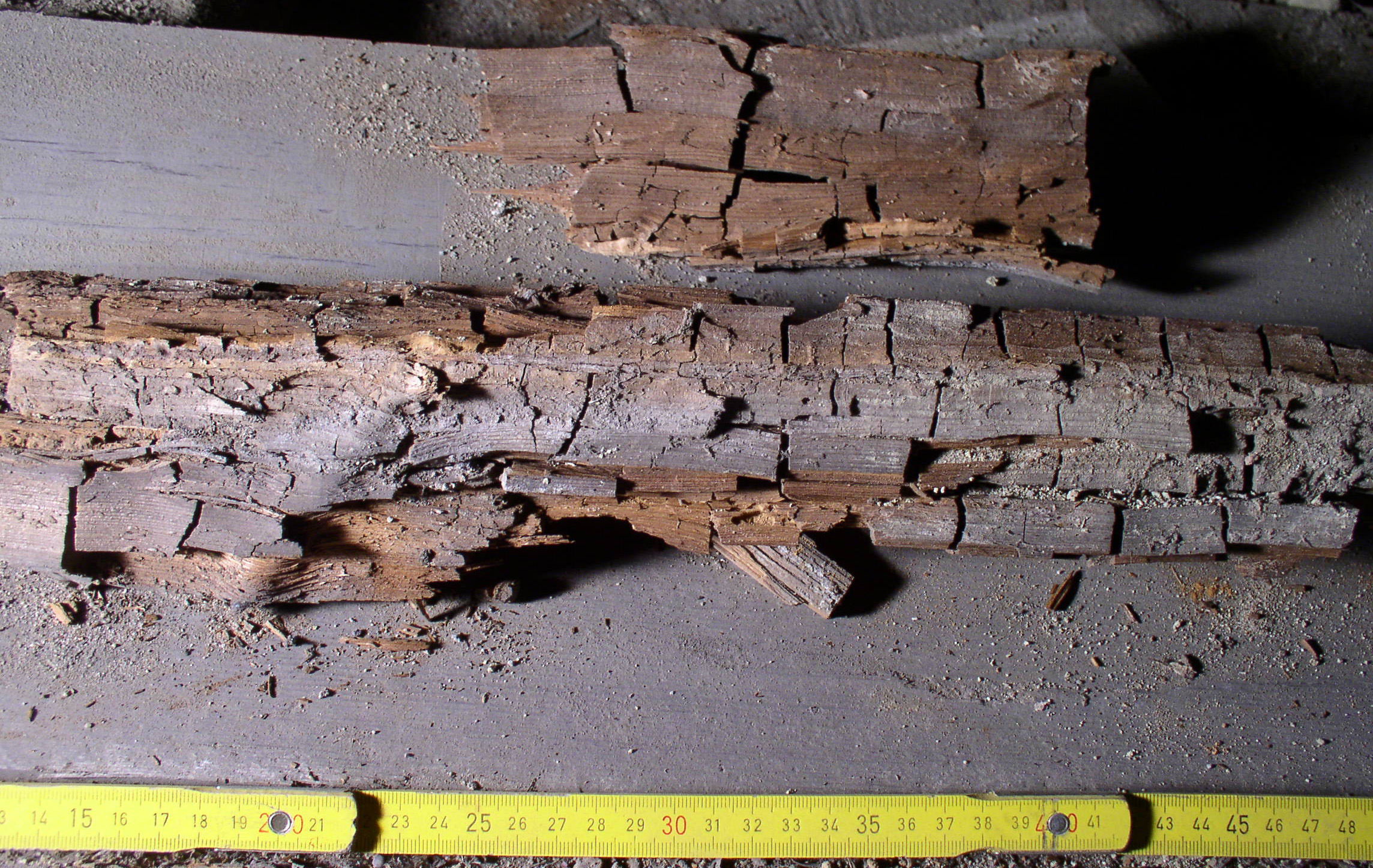
Wood-decay Fungus
A wood-decay or xylophagous fungus is any species of fungus that digests moist wood, causing it to rot. Some species of wood-decay fungi attack dead wood, such as brown rot, and some, such as ''Armillaria'' (honey fungus), are parasitic and colonize living trees. Excessive moisture above the fibre saturation point in wood is required for fungal colonization and proliferation. In nature, this process causes the breakdown of complex molecules and leads to the return of nutrients to the soil. Wood-decay fungi consume wood in various ways; for example, some attack the carbohydrates in wood and some others decay lignin. The rate of decay of wooden materials in various climates can be estimated by empirical models.Viitanen, T. et al. (2010). Towards modelling of decay risk of wooden materials. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 68:303-313. Wood-decay fungi can be classified according to the type of decay that they cause. The best-known types are brown rot, soft rot, and whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidia
A basidium () is a microscopic sporangium (a spore-producing structure) found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi which are also called tertiary mycelium, developed from secondary mycelium. Tertiary mycelium is highly-coiled secondary myceliuma dikaryon. The presence of basidia is one of the main characteristic features of the Basidiomycota. A basidium usually bears four sexual spores called basidiospores; occasionally the number may be two or even eight. In a typical basidium, each basidiospore is borne at the tip of a narrow prong or horn called a sterigma (), and is forcibly discharged upon maturity. The word ''basidium'' literally means "little pedestal", from the way in which the basidium supports the spores. However, some biologists suggest that the structure more closely resembles a club. An immature basidium is known as a basidiole. Structure Most basidiomycota have single celled basidia (holobasidia), but in some groups basidia can be multice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia (basidiomycetes) or paraphyses (ascomycetes). Cystidia are often important for microscopic identification. The subhymenium consists of the supportive hyphae from which the cells of the hymenium grow, beneath which is the hymenophoral trama, the hyphae that make up the mass of the hymenophore. The position of the hymenium is traditionally the first characteristic used in the classification and identification of mushrooms. Below are some examples of the diverse types which exist among the macroscopic Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. * In agarics, the hymenium is on the vertical faces of the gills. * In boletes and polypores, it is in a spongy mass of downward-pointing tubes. * In puffballs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystidium
A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood. Classification of cystidia By position Cystidia may occur on the edge of a lamella (or analogous hymenophoral structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe (caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)