|
Tusratta
Tushratta (Akkadian: and ) was a king of Mitanni, c. 1358–1335 BCE, at the end of the reign of Amenhotep III and throughout the reign of Akhenaten. He was the son of Shuttarna II. Tushratta stated that he was the grandson of Artatama I. His sister Gilukhipa (Gilu-ḫepa in Hurrian) and his daughter Tadukhipa (Tadu-ḫepa in Hurrian) were married to the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III; Tadukhipa later married Akhenaten who took over his father's royal harem. He had been placed on the throne after the murder of his brother Artashumara. He was probably quite young at the time and was destined to serve as a figurehead only but he managed to dispose of the murderer. A tablet was found in a Mitanni building at Tell Brak which stated it was witnessed "in the presence of Tushratta, the king" and had a seal of an earlier king Shaushtatar on the reverse which was a common practice. Name Recorded in three distinct spellings—, , —Tushratta's name is an Akkadianised rendition of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanigalbat
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and southeast Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Since no histories or royal annals/chronicles have yet been found in its excavated sites, knowledge about Mitanni is sparse compared to the other powers in the area, and dependent on what its neighbours commented in their texts. The Hurrians were in the region as of the late 3rd millennium BC. A king of Urkesh with a Hurrian name, Tupkish, was found on a clay sealing dated c. 2300 BC at Tell Mozan.Salvini, Mirjo. "The earliest evidences of the Hurrians before the formation of the reign of Mittanni." Urkesh and the Hurrians Studies in Honor of Lloyd Cotsen. Urkesh/Mozan Studies Bibliotheca Mesopotamica. Malibu: Undena Publications (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and southeast Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Since no histories or royal annals/chronicles have yet been found in its excavated sites, knowledge about Mitanni is sparse compared to the other powers in the area, and dependent on what its neighbours commented in their texts. The Hurrians were in the region as of the late 3rd millennium BC. A king of Urkesh with a Hurrian name, Tupkish, was found on a clay sealing dated c. 2300 BC at Tell Mozan.Salvini, Mirjo. "The earliest evidences of the Hurrians before the formation of the reign of Mittanni." Urkesh and the Hurrians Studies in Honor of Lloyd Cotsen. Urkesh/Mozan Studies Bibliotheca Mesopotamica. Malibu: Undena Publications ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Of The Amarna Letters
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorites
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian language, Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied large parts of southern Mesopotamia from the 21st century BC to the end of the 17th century BC, where they established several prominent city-states in existing locations, such as Isin, Larsa and later notably Babylon, which was raised from a small town to an independent state and a major city. The term in Akkadian and Sumerian texts refers to the Amorites, Amurru (god), their principal deity and Amurru kingdom, an Amorite kingdom. The Amorites are also mentioned in the Bible as inhabitants of Canaan both before and after the conquest of the land under Joshua. Origin In the earliest Sumerian sources concerning the Amorites, beginning about 2400 BC, the land of the Amorites ("the ''Mar.tu'' land") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
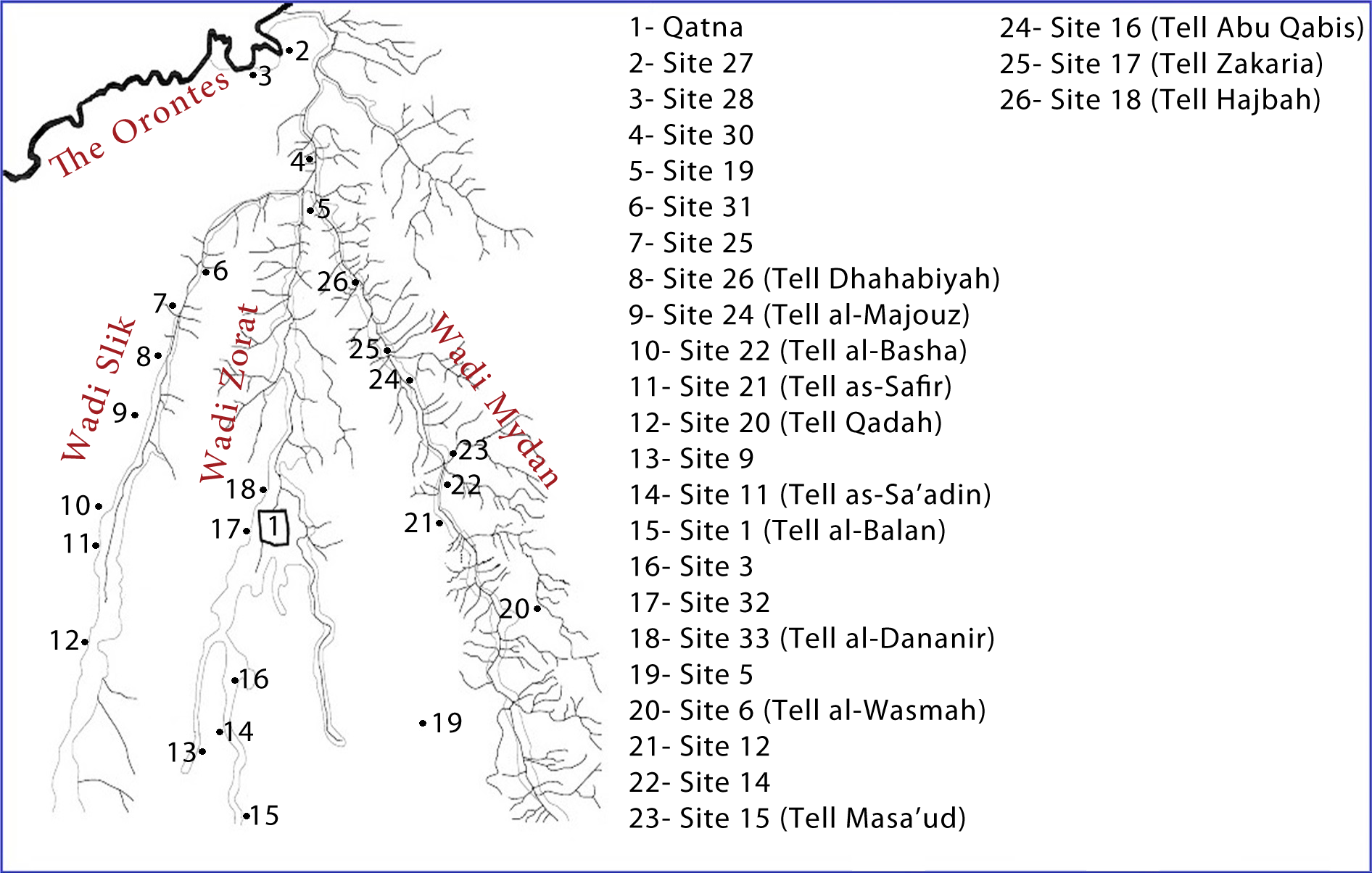
Qatna
Qatna (modern: ar, تل المشرفة, Tell al-Mishrifeh) (also Tell Misrife or Tell Mishrifeh) was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an important center through most of the second millennium BC and in the first half of the first millennium BC. It contained one of the largest royal palaces of Bronze Age Syria and an intact royal tomb that has provided a great amount of archaeological evidence on the funerary habits of that period. First inhabited for a short period in the second half of the fourth millennium BC, it was repopulated around 2800 BC and continued to grow. By 2000 BC, it became the capital of a regional kingdom that spread its authority over large swaths of the central and southern Levant. The kingdom enjoyed good relations with Mari, but was engaged in constant warfare against Yamhad. By the 15th century BC, Qatna lost its hegemony an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apina
The pasture day moth (''Apina callisto'') is a species in the moth family Noctuidae which is active during the day, as its common name implies, making it unlike most other noctuid species. It is found in most southern areas of Australia, ranging from lower Queensland to Tasmania. The species was first described by George French Angas in 1847. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Apina'', erected by Francis Walker in 1855. The pasture day moth lays its eggs in pastures, and they hatch after heavy rains in early spring. When the larvae are fully grown, measuring about , they burrow down before becoming pupae. They have striking coloration; two yellow stripes run down their mottled-black back, interspersed with blue spots. Their bodies are covered with white spines. They feed on various broad leaved plants (see list below). The adult moth's wings are black with cream and chestnut markings, with a wingspan of approximately . Its thorax is black and the abdomen is orange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niya (kingdom)
Niya, Niye, and also Niy of Thutmose I's Ancient Egypt, also Nii of the Amarna letters, and Nihe, etc. was a kingdom in Syria, or northern Syria. In the Amarna letters correspondence of 1350- 1335 BC, ''Nii'' is only referenced in two letters, but each is of some importance. The city of Tunip in the northern Levant had been trying to communicate to the Egyptian pharaoh for two decades, and finally resorted to another letter, EA 59: entitled: ''"From the citizens of Tunip"'', ( EA for 'el Amarna'). The city-state of Arqa also sent a letter to pharaoh, requesting aid (EA 100). The other letter referencing ''Nii'' concerns the individual Etakkama, his collusion with the Hittites, and the takeover of territory, 'city-states', and peoples in the northern and western Levant. Amarna letters ''"Nii"'', 2--letters EA 59, title: "From the citizens of Tunip" :"To the king of Egypt, our lord: Message of "the citizens of Tunip", your servant. For you may all go well. And we fall at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukish
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished, as an urban settlement, in the Middle and Late Bronze Age, c. 2000-1200 BC. The city contained palaces, temples, private houses and fortifications. The remains of Alalakh have formed an extensive mound covering around 22 hectares. In Late Bronze Age, Alalakh was the capital of the local kingdom of Mukiš. The first palace was built around 2000 BC, and likely destroyed in the 12th century BC. The site was thought to have never been reoccupied after that, but archaeologist Timothy Harrison showed, in a (2022) lecture's graphic, it was inhabited also in Amuq Phases N-O, Iron Age, c. 1200-600 BC.Harrison, Timothy, Lynn Welton, and Stanley Klassen, (13 July 2022)"Highway to Science: The Tayinat and CRANE Projects" ARWA Association, Lecture min. 6:58, n the graphic "Iron Age, Ca. 1200-600 BCE, Amuq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halab
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black". , motto = , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Asia#Syria Aleppo , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_relief = yes , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Aleppo in Syria , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_type3 = Subdistrict , subdivision_name1 = Aleppo Governorate , subdivision_name2 = Mount Simeon (Jabal Semaan) , subdivision_name3 = Mount Simeon ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washshukanni
Washukanni (also spelled Waššukanni) was the capital of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni, from around 1500 BC to the 13th century BC. Location The precise location of Waššukanni is unknown. A proposal by Dietrich Opitz located it under the largely unexcavated mound of Tell el Fakhariya, near Tell Halaf in Syria. This position was supported by M. Oppenheim and more recently by others. A neutron activation comparison with clay from relevant Amarna tablets appeared to rule out Tell Fakhariya. This idea was also rejected by Edward Lipinski. However, this identification received a new support by Stefano de Martino, Mirko Novák and Dominik Bonatz due to recent archaeological excavations by a German team. This is counterbalanced by the fact that despite many seasons of excavations over the years no documentation of the name of the Mittani capital has yet been found. History Waššukanni is known to have been sacked by the Hittites under Suppiluliuma I (reigned c. 1344–1322 BC) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isuwa
Isuwa (transcribed Išuwa and sometimes rendered Ishuwa) was the ancient Hittite name for one of its neighboring Anatolian kingdoms to the east, in an area which later became the Luwian Neo-Hittite state of Kammanu. The land The land of Isuwa was situated in the upper Euphrates river region. The river valley was here surrounded by the Anti-Taurus Mountains. To the northeast of the river lay a vast plain stretching up to the Black Sea mountain range. The plain had favourable climatic conditions due to the abundance of water from springs and rainfall. Irrigation of fields was possible without the need to build complex canals. The river valley was well suited for intensive agriculture, while livestock could be kept at the higher altitudes. The mountains possessed rich deposits of copper which were mined in antiquity. The people The Isuwans left no written record of their own, and it is not clear which of the Anatolian peoples inhabited the land of Isuwa prior to the Luwians. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |