|
Turlough MacShane O'Neill
Sir Turlough McHenry O'Neill (died 1608) is known for having been killed together with his father, Henry, fighting for the crown in O'Doherty's Rebellion and for being the father of Sir Phelim O'Neill, who started the Irish Rebellion of 1641. Birth and origins Turlough was a son of Henry Oge O'Neill and his wife Cortine (or Catherine) O'Neill. Turlogh's father was called "oge" (cf. Irish '' óg'', young) to distinguish him from Turlough's grandfather who was also named Henry O'Neill. His father was the head of the O'Neills of Kinard, who were a cadet branch that parted from the O'Neill More when Turlough's great grandfather Shane O'Neill (died 1517), a younger son of Conn More O'Neill, King of Tir Eoghan, received Kinard as appanage. His mother was a daughter of Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone. Both parents were thus part of the Gaelic O'Neill Dynasty of Ulster. Tyrone's Rebellion Turlough's branch of the family had served on the Crown's side ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War (Ireland)
The Nine Years' War, sometimes called Tyrone's Rebellion, took place in Ireland from 1593 to 1603. It was fought between an Irish alliance—led mainly by Hugh O'Neill of Tyrone and Hugh Roe O'Donnell of Tyrconnell—against English rule in Ireland, and was a response to the ongoing Tudor conquest of Ireland. The war was fought in all parts of the country, but mainly in the northern province of Ulster. The Irish alliance won some important early victories, such as the Battle of Clontibret (1595) and the Battle of the Yellow Ford (1598), but the English won a victory against the alliance and their Spanish allies in the siege of Kinsale (1601–02). The war ended with the Treaty of Mellifont (1603). Many of the defeated northern lords left Ireland to seek support for a new uprising in the Flight of the Earls (1607), never to return. This marked the end of Gaelic Ireland and led to the Plantation of Ulster. The war against O'Neill and his allies was the largest conflict fought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English dissenting churches, such as the Methodist church, though some were Roman Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior army and naval officers since Kingdom of England and Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland until 1800, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) for over a century. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterians in the province of Ulster, whose ancestry is mostly Lowland Scottish, rather than English or Irish, and who are sometimes id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Phelim O'Neill
Sir Phelim Roe O'Neill of Kinard (Irish: ''Sir Féilim Rua Ó Néill na Ceann Ard''; 1604–1653) was an Irish politician and soldier who started the Irish rebellion in Ulster on 23 October 1641. He joined the Irish Catholic Confederation in 1642 and fought in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms under his cousin, Owen Roe O'Neill, in the Confederate Ulster Army. After the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland O’Neill went into hiding but was captured, tried and executed in 1653. Birth and origins Phelim was born in 1604, the eldest son of Turlough O'Neill and his wife Catherine O'Neill. His father was a member of the Kinard branch of the O'Neills who were descendants of Shane O'Neill of Kinard, a half-brother of Conn Baccach O'Neill. His father and paternal grandfather were killed on 20 June 1608, while defending Kinard against the insurgents during the O'Doherty's Rebellion. This grandfather, Sir Henry Óg O'Neill, had fought for his second cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kilmacrennan
The Battle of Kilmacrennan was a skirmish fought near Kilmacrennan, County Donegal in 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion. Sir Cahir O'Doherty was a traditional supporter of the Crown whose treatment at the hands of local officials had led him to launch a rebellion in which he had seized the garrison town of Derry, killing his enemy George Paulet. O'Doherty raised local forces and possibly hoped to negotiate an agreement with the government as had been common with leaders of previous rebellions. However, the Viceroy in Dublin, Arthur Chichester, responded quickly and despatched reinforcements to the area under Richard Wingfield. They were a mixture of professional soldiers of the Royal Irish Army and Gaelic warriors allied to the government. They met the rebels at Kilmacrennan and O'Doherty was killed by a musket shot to the head. His troops' morale collapsed and they fled the field. A £500 bounty had been placed on O'Doherty and, while a number of outlandish legends exist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
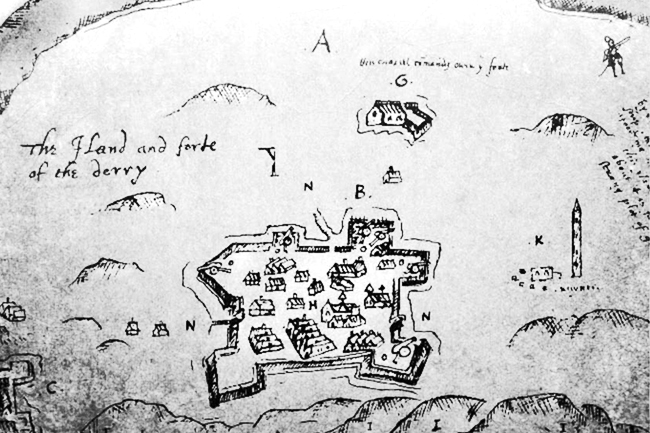
Burning Of Derry
The Burning of Derry took place on 19 April 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion when Sir Cahir O'Doherty led a force of rebels to storm Derry in Ulster. He launched his rebellion with an attack on the garrison town of Derry, which was taken thanks to the element of surprise. The town was then almost entirely destroyed by fire. Background O'Doherty was the Gaelic Lord of Inishowen. He had been allied with the government during the Nine Years' War (1594-1603), and has been described as "a youthful war hero on the side of the crown". During the conflict, he fought alongside Sir Henry Docwra's troops from the key base of Derry. O'Doherty, along with other pro-English Irish lords, was unhappy when the Treaty of Mellifont restored the leading rebels, Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone and Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, to land which had been promised to them. O'Doherty was further unsettled when his friend and ally Docwra was replaced as Governor of Derry by Sir George Paulet. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry (), is the second-largest city in Northern Ireland and the fifth-largest city on the island of Ireland. The name ''Derry'' is an anglicisation of the Old Irish name (modern Irish: ) meaning 'oak grove'. The old walled city lies on the west bank of the River Foyle, which is spanned by two road bridges and one footbridge. The city now covers both banks (Cityside on the west and Waterside on the east). The population of the city was 83,652 at the 2001 Census, while the Derry Urban Area had a population of 90,736. The district administered by Derry City and Strabane District Council contains both Londonderry Port and City of Derry Airport. Derry is close to the border with County Donegal, with which it has had a close link for many centuries. The person traditionally seen as the founder of the original Derry is Saint , a holy man from , the old name for almost all of modern County Donegal, of which the west bank of the Foyle was a part before 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Paulet (1553–1608)
Sir George Paulet (1553–1608), also known as Pawlett, Pawlet, or Powlet, was an English soldier and administrator. He served as governor of Derry in Ireland. His arrogant and insolent behaviour caused O'Doherty's Rebellion in 1608. Paulet was killed by the rebels during the Burning of Derry. Birth and origins George was born in 1553 in England, a son of Sir George Paulet and his third wife Elizabeth Windsor. His father was Sir George Paulet (died 1558) of Crondall, Hampshire. His father's eldest brother William was created Earl of Wiltshire in 1550 and Marquess of Winchester 1551. George's mother was a daughter of William Windsor, 2nd Baron Windsor. George was one of 10 siblings. Early life Paulet was educated at Eton, 1564–72, and at King's College, Cambridge, 1572-5. His contemporaries call Paulet a gentleman of Hampshire. Marriage and children Before 1586 Paulet married Joan Kyme, daughter of Richard Kyme of Lewes, Sussex, and his wife Margery Humphrey. George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahir O'Doherty
Sir Cahir O'Doherty ( ga, Cathaoir Ó Dochartaigh or ga, label=none, Caṫaoir Ó Doċartaiġ; 1587–5 July 1608) was the last Gaelic Chief of the Name of Clan O'Doherty and Lord of Inishowen, in what is now County Donegal. O'Doherty was a noted loyalist during Tyrone's Rebellion and became known as the Queen's O'Doherty for his service on the Crown's side during the fighting. After the war O'Doherty had ambitions to become a courtier and applied for a position in the household of Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, but he increasingly came into dispute with Irish-based officials such as the Viceroy Sir Arthur Chichester and the Governor of Derry Sir George Paulet. In 1608 he launched a rebellion, seizing Derry from Paulet and burning it to the ground. O'Doherty was subsequently killed in a battle at Kilmacrennan, and the rebellion swiftly collapsed. Early life Cahir was the son of Sir John O'Doherty, the head of the O'Dohertys and effective ruler of Inishowen. One of Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry MacShane O'Neill
Henry MacShane O'Neill or Anraí MacSéan Ó Néill ( – 1622) was an Irish ''flaith'', a son of Shane O'Neill. He was the leader of the MacShane in the late 16th century and early 17th century, and sought control of the O'Neill Clan, fighting with his brother against Hugh O'Neill. Early life Henry was born to the ruling family of Ulster at the time. His father is known to history as "Shane the Proud", though in his own lifetime he went by Sean Donnellach O'Neill, as he was fostered by the Donnelly clan. It is believed Henry's mother was Catherine MacDonnell, Shane's first wife, which makes him one of Shane's oldest and legitimate children. He had many half brothers, but his only full brother was Shane Og, Shane O'Neill's oldest son. He was fostered in the households of the O'Cahan's, the O'Cuinn's and possibly MacDonnell Gallowglass, due to the danger posed by other O'Neill family members. Henry led his half brothers Hugh Gavelagh and Con MacShane O'Neill. Collectivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Carey (c
George Leonard Carey, Baron Carey of Clifton (born 13 November 1935) is a retired Anglican bishop who was the Archbishop of Canterbury from 1991 to 2002, having previously been the Bishop of Bath and Wells. During his time as archbishop the Church of England ordained its first women priests and the debate over attitudes to homosexuality became more prominent, especially at the 1998 Lambeth Conference of Anglican bishops. In June 2017, Lord Carey of Clifton resigned from his last formal role in the church after Dame Moira Gibb's independent investigation found he covered up, by failing to pass to police, six out of seven serious sex abuse allegations relating to 17- to 25-year-olds against Bishop Peter Ball a year after Carey became archbishop. The next year the UK Child Sex Abuse Report confirmed Carey had committed serious breaches of duty in wrongly discrediting credible allegations of child sex abuse within the Church and failing to accompany disciplinary action with addin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)