|
Tunbridge Ware
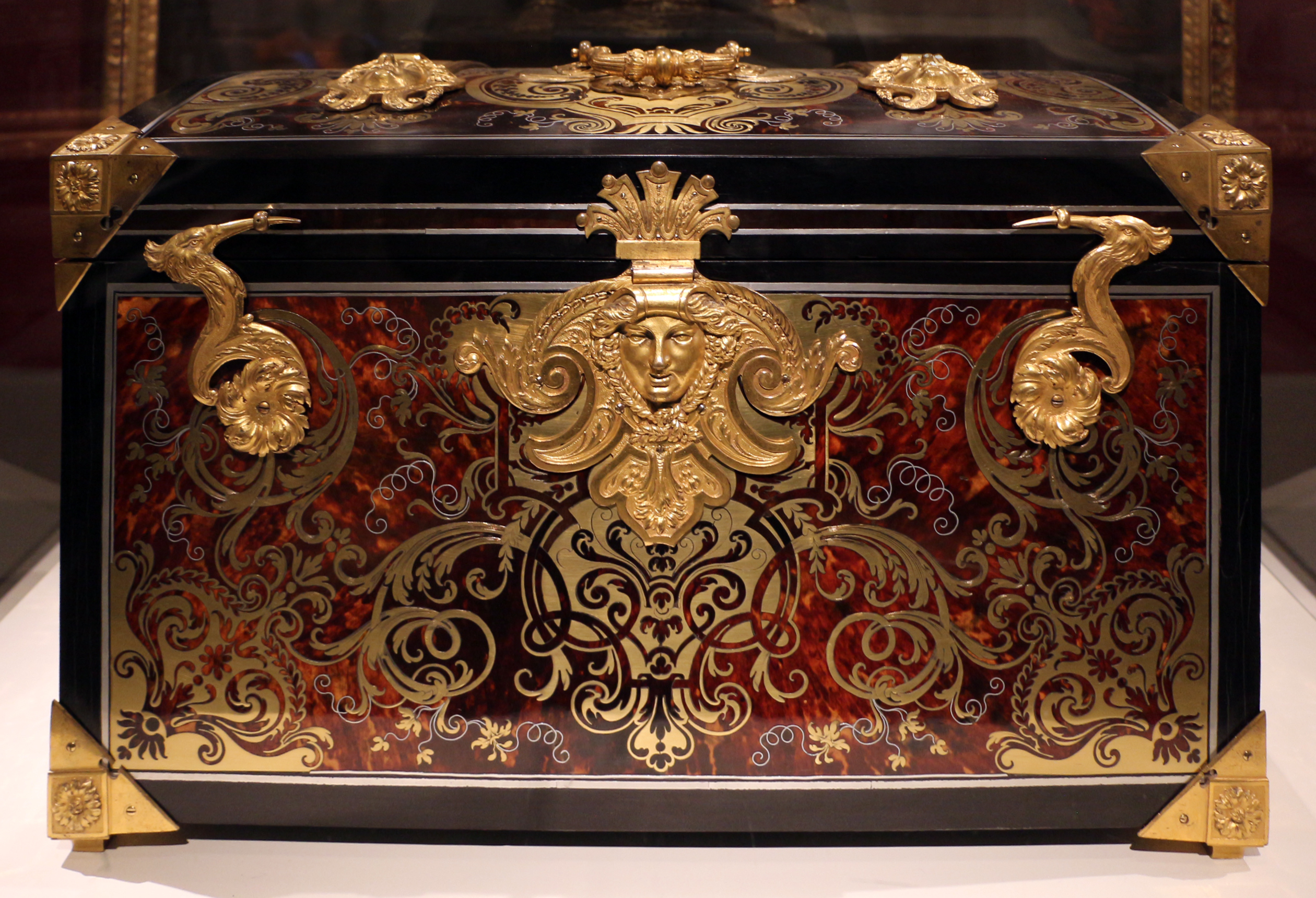
Tunbridge ware is a form of decoratively inlaid woodwork, typically in the form of boxes, that is characteristic of Tonbridge and the spa town of Royal Tunbridge Wells in Kent in the 18th and 19th centuries. The decoration typically consists of a mosaic of many very small pieces of different coloured woods that form a pictorial vignette. Shaped rods and slivers of wood were first carefully glued together, then cut into many thin slices of identical pictorial veneer with a fine saw. Elaborately striped and feathered bandings for framing were pre-formed in a similar fashion. There is a collection of Tunbridge ware in the Tunbridge Wells Museum and Art Gallery in Tunbridge Wells.Tunbridge ware Tunbridge Wells Museum and Art Gallery. Retrieved from archive at |
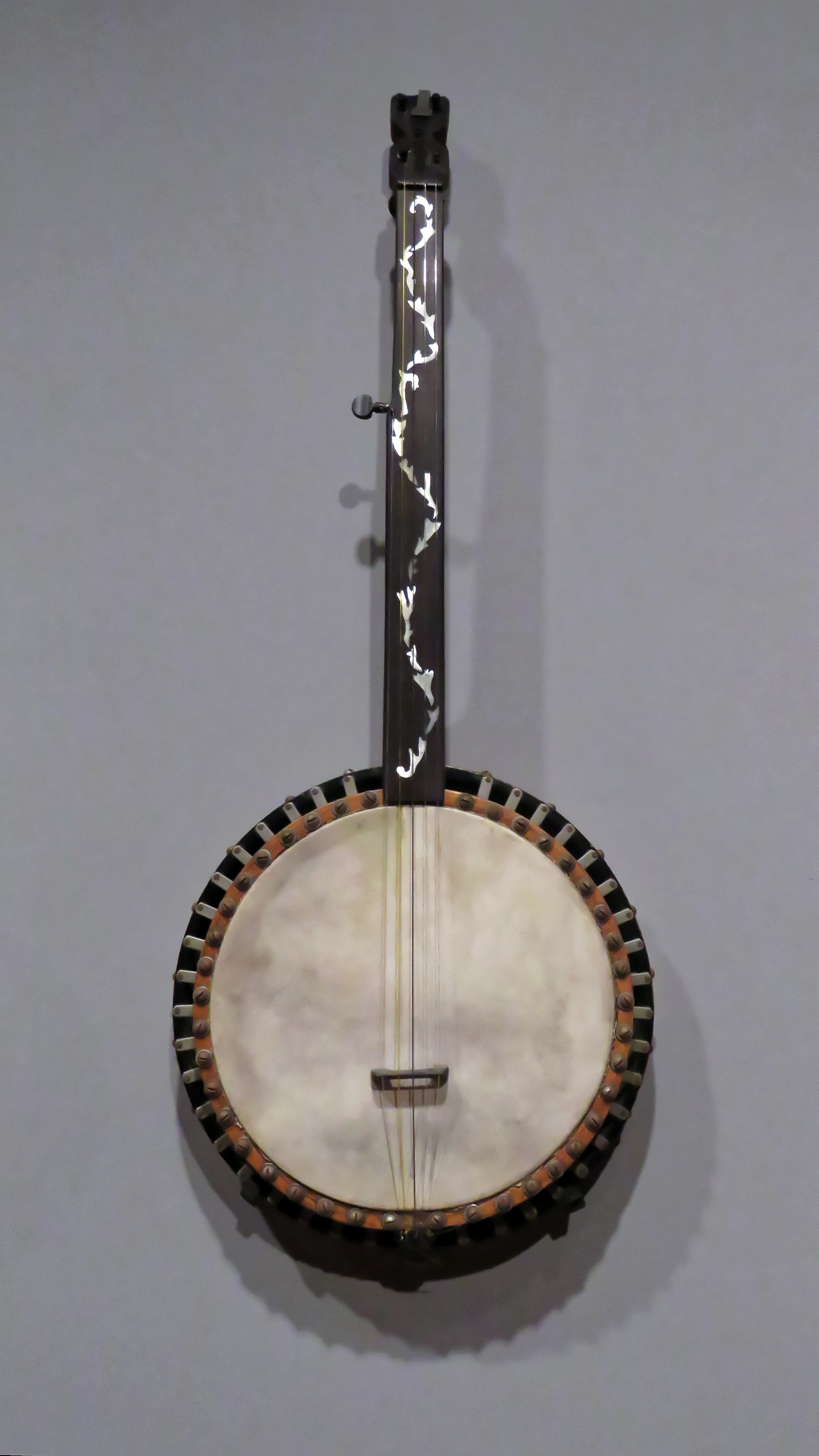
Tunbridge Ware Banjo 1870 At Two Temple Place, Astor House
{{geodis ...
Tunbridge may refer to the following places: * Tunbridge, Illinois, United States * Tunbridge, North Dakota, see Locations in the United States with an English name#North Dakota * Tunbridge, Tasmania, Australia * Tunbridge, Vermont, United States * The old spelling of Tonbridge, Kent, England ** Tunbridge (UK Parliament constituency) * Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent, England See also * Tonbridge (other) Tonbridge may refer to: Places * Tonbridge, a town in Kent, England, containing: ** Tonbridge Grammar School, state-funded ** Tonbridge School, independent ** Tonbridge (UK Parliament constituency), former constituency ** Tonbridge and Malling (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decorative Arts
] The decorative arts are arts or crafts whose object is the design and manufacture of objects that are both beautiful and functional. It includes most of the arts making objects for the interiors of buildings, and interior design, but not usually architecture. Ceramic art, metalwork, furniture, jewellery, fashion, various forms of the textile arts and glassware are major groupings. Applied arts largely overlaps with decorative arts, and the modern making of applied art is usually called design. The decorative arts are often categorized in distinction to the "fine arts", namely painting, drawing, photography, and large-scale sculpture, which generally produce objects solely for their aesthetic quality and capacity to stimulate the intellect. Distinction from the fine arts The distinction between the decorative and fine arts essentially arose from the post-Renaissance art of the West, where the distinction is for the most part meaningful. This distinction is much less me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietre Dure
''Pietra dura'' () or ''pietre dure'' () ( see below), called parchin kari or parchinkari ( fa, ) in the Indian Subcontinent, is a term for the inlay technique of using cut and fitted, highly polished colored stones to create images. It is considered a decorative art. The stonework, after the work is assembled loosely, is glued stone-by-stone to a substrate after having previously been "sliced and cut in different shape sections; and then assembled together so precisely that the contact between each section was practically invisible". Stability was achieved by grooving the undersides of the stones so that they interlocked, rather like a jigsaw puzzle, with everything held tautly in place by an encircling 'frame'. Many different colored stones, particularly marbles, were used, along with semiprecious, and even precious stones. It first appeared in Rome in the 16th century, reaching its full maturity in Florence. Pietra dura items are generally crafted on green, white or black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
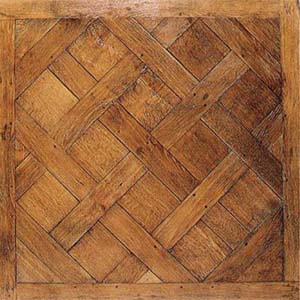
Parquetry
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Timber contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, lime, pine, maple etc. are sometimes employed, and in the more expensive kinds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Sectile
''Opus sectile'' is a form of pietra dura popularized in the ancient and medieval Roman world where materials were cut and inlaid into walls and floors to make a picture or pattern. Common materials were marble, mother of pearl, and glass. The materials were cut in thin pieces, polished, then trimmed further according to a chosen pattern. Unlike tessellated mosaic techniques, where the placement of very small uniformly sized pieces forms a picture, ''opus sectile'' pieces are much larger and can be shaped to define large parts of the design. Origin and evolution Early examples Early examples have been found from Egypt and Asia Minor. The Herodian Temple in Jerusalem was built during the second half of the 1st century BCE and the first half of the 1st century CE. Recent work by the Temple Mount Sifting Project has recovered enough pieces of polished stone triangles and squares from the Herodian Temple Mount to reconstruct geometric patterns of ''opus sectile'' flooring. Evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lath Art
Lath art is a form of woodworking folk art for making rustic pictures out of strips out of old "lath" from "plaster and lath" walls. Today it is commonly made from lattice, lumber stickers and weathered lobster traps. Beach scenes and rural scenes are the most popular themes. Techniques Lath art has a lot in common with marquetry and intarsia. They are all woodworking hobbies to make pictures out of sections of wood, but marquetry and intarsia use the wood grain as a design element, and lath art uses the direction of the lath stick and the colors of the stains as a design element. See also *Parquetry *Scroll saw A scroll saw is a small electric or pedal-operated saw used to cut intricate curves in wood, metal, or other materials. The fineness of its blade allows it to cut more delicately than a power jigsaw, and more easily than a hand coping saw or ... * Tunbridge ware Decorative arts Woodworking Visual arts genres Folk art {{art-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intarsia
Intarsia is a form of wood inlaying that is similar to marquetry. The start of the practice dates from before the seventh century AD. The technique of intarsia inlays sections of wood (at times with contrasting ivory or bone, or mother-of-pearl) within the solid wood matrix of floors and walls or of tabletops and other furniture; by contrast marquetry assembles a pattern out of veneers glued upon the carcass. The word ''intarsia'' may derive from the Latin word '' interserere'' (to insert). Certosina is a variant also using pieces of ivory, bone or mother of pearl. Intarsia is mostly used of Italian, or at least European work. Similar techniques are found over much of Asia and the Middle East. History When Egypt came under Arab rule in the seventh century, indigenous arts of intarsia and wood inlay, which lent themselves to non-representational decors and tiling patterns, spread throughout the Maghreb. The technique of intarsia was already perfected in Islamic Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Wool Work
Berlin wool work is a style of embroidery similar to today's needlepoint that was particularly popular in Europe and America from 1804 to 1875. It is typically executed with wool yarn on canvas, worked in a single stitch such as cross stitch or tent stitch, although ''Beeton's book of Needlework'' (1870) describes 15 different stitches for use in Berlin work. It was traditionally stitched in many colours and hues, producing intricate three-dimensional looks by careful shading. Silk or beads were frequently used as highlights. The design of such embroidery was made possible by the great progress made in dyeing, initially with new mordants and chemical dyes, followed in 1856, especially by the discovery of aniline dyes, which produced bright colors. Berlin work creates very durable and long-lived pieces of embroidery that can be used as furniture covers, cushions, bags, or even clothing. History Berlin wool work patterns were first published in Berlin, Germany, early in the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesselate
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane (mathematics), plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to high-dimensional spaces, higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include ''regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and ''semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An ''aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. A ''tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorociboria Aeruginascens Or Green Elfcup And Fruiting Bodies
''Chlorociboria'' is the type genus of in the fungal family Chlorociboriaceae within order Helotiales. The genus includes 23 species. Two common temperate zone species, ''Chlorociboria aeruginascens'' and ''Chlorociboria aeruginosa'', can only reliably be distinguished by microscopic examination. ''Chlorociboria aeruginosa'' has larger spores (9–15 µm × 1.5–2.5 µm) and the worm-like cells of the outer surface are rough, unlike the commoner ''C. aeruginascens'', of which the spores are 6–10 µm × 1.5–2 µm. The hyphae and fruit bodies of all species make xylindein, a secondary metabolite that stains the substrate wood blue-green, with "green oak" being a valued commodity in woodworking. The blue-green pigmented wood is featured in Tunbridge ware. Habit Blue-green stain is evident year-round, with ascocarp production occurring from summer to fall. Species *''Chlorociboria aeruginascens'' *'' Chlorociboria aeruginosa'' *''Chlorociboria albo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquetry
Marquetry (also spelled as marqueterie; from the French ''marqueter'', to variegate) is the art and craft of applying pieces of veneer to a structure to form decorative patterns, designs or pictures. The technique may be applied to case furniture or even seat furniture, to decorative small objects with smooth, veneerable surfaces or to freestanding pictorial panels appreciated in their own right. Marquetry differs from the more ancient craft of inlay, or intarsia, in which a solid body of one material is cut out to receive sections of another to form the surface pattern. The word derives from a Middle French word meaning "inlaid work". Materials The veneers used are primarily woods, but may include bone, ivory, turtle-shell (conventionally called " tortoiseshell"), mother-of-pearl, pewter, brass or fine metals. Marquetry using colored straw was a specialty of some European spa resorts from the end of the 18th century. Many exotic woods as well as common European variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)